Medical term:
Albuterol
albuterol
[al-bu´ter-ol]albuterol (salbutamol)
albuterol sulfate (salbutamol sulfate)
Pharmacologic class: Sympathomimetic (beta2-adrenergic agonist)
Therapeutic class: Bronchodilator, antiasthmatic
Pregnancy risk category C
Action
Relaxes smooth muscles by stimulating beta2-receptors, thereby causing bronchodilation and vasodilation
Availability
Aerosol: 90 mcg/actuation, 108 mcg/inhalation
Oral solution: 2 mg/5 ml
Solution for inhalation: 0.083% (3 ml), 0.5% (0.5 and 20 ml), 0.63 mg/3 ml, 1.25 mg/3 ml
Syrup: 2 mg/5 ml
Tablets: 2 mg, 4 mg
Tablets (extended-release): 4 mg, 8 mg
Indications and dosages
➣ To prevent and relieve bronchospasm in patients with reversible obstructive airway disease
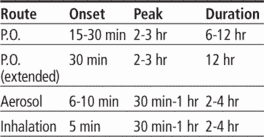
Adults and children ages 12 and older: Tablets-2 to 4 mg P.O. three or four times daily, not to exceed 32 mg daily. Extended-release tablets-4 to 8 mg P.O. q 12 hours, not to exceed 32 mg daily in divided doses. Syrup-2 to 4 mg (1 to 2 tsp or 5 to 10 ml) three or four times daily, not to exceed 8 mg q.i.d.
Aerosol-one to two inhalations q 4 to 6 hours to relieve bronchospasm; two inhalations q.i.d. to prevent bronchospasm. Solution for inhalation-2.5 mg three to four times daily by nebulization, delivered over 5 to 15 minutes.
Children ages 6 to 12: Tablets-2 mg P.O. three or four times daily; maximum daily dosage is 24 mg, given in divided doses. Extended-release tablets-4 mg q 12 hours; maximum daily dosage is 24 mg/kg given in divided doses. Syrup-2 mg (1 tsp or 5 ml) three or four times daily, not to exceed 24 mg.
Adults and children age 4 and older (with ProAir HFA): Two inhalations q 4 to 6 hours to treat acute bronchospasm
Children ages 2 to 12 weighing more than 15 kg (33 lb): Solution for inhalation-2.5 mg three to four times/day by nebulization
Children ages 2 to 6: Syrup-Initially, 0.1 mg/kg P.O. t.i.d., not to exceed 2 mg (1 tsp) t.i.d. Maximum dosage is 4 mg (2 tsp) t.i.d.
➣ To prevent exercise-induced bronchospasm
Adults and children older than age 4 (older than age 12 with Proventil): Two inhalations 15 minutes before exercise
Adults and children age 4 and older (with ProAir HFA): Two inhalations q 15 to 30 minutes before exercise
Dosage adjustment
• Sensitivity to beta-adrenergic stimulants
• Elderly patients
Off-label uses
• Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
• Hyperkalemia with renal failure
• Preterm labor management
Contraindications
• Hypersensitivity to drug
Precautions
Use cautiously in:
• cardiac disease, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, glaucoma, seizure disorder, hyperthyroidism, exercise-induced bronchospasm, prostatic hypertrophy
• elderly patients
• pregnant or breastfeeding patients
• children.
Administration
• Give extended-release tablets whole; don't crush or mix with food.
• Administer solution for inhalation by nebulization over 5 to 15 minutes, after diluting 0.5 ml of 0.5% solution with 2.5 ml of sterile normal saline solution.
• Know that children weighing less than 15 kg (33 lb) who require less than 2.5 mg/dose should receive 0.5% inhalation solution.
Adverse reactions
CNS: dizziness, excitement, headache, hyperactivity, insomnia
CV: hypertension, palpitations, tachycardia, chest pain
EENT: conjunctivitis, dry and irritated throat, pharyngitis
GI: nausea, vomiting, anorexia, heartburn, GI distress, dry mouth
Metabolic: hypokalemia
Musculoskeletal: muscle cramps
Respiratory: cough, dyspnea, wheezing, paradoxical bronchospasm
Skin: pallor, urticaria, rash, angioedema, flushing, sweating
Other: tooth discoloration, increased appetite, hypersensitivity reaction
Interactions
Drug-drug. Beta-adrenergic blockers: inhibited albuterol action, possibly causing severe bronchospasm in asthmatic patients
Digoxin: decreased digoxin blood level
MAO inhibitors: increased cardiovascular adverse effects
Oxytoxics: severe hypotension
Potassium-wasting diuretics: ECG changes, hypokalemia
Theophylline: increased risk of theophylline toxicity
Drug-food. Caffeine-containing foods and beverages (such as coffee, tea, chocolate): increased stimulant effect
Drug-herbs. Cola nut, ephedra (ma huang), guarana, yerba maté: increased stimulant effect
Patient monitoring
☞ Stay alert for hypersensitivity reactions and paradoxical bronchospasm. Stop drug immediately if these occur.
• Monitor serum electrolyte levels.
Patient teaching
• Tell patient to swallow extended-release tablets whole and not to mix them with food.
• Follow manufacturer's directions supplied with inhalation drugs.
☞ Teach patient signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity reaction and paradoxical bronchospasm. Tell him to stop taking drug immediately and contact prescriber if these occur.
☞ Instruct patient to notify prescriber immediately if prescribed dosage fails to provide usual relief, because this may indicate seriously worsening asthma.
• Advise patient to limit intake of caffeine-containing foods and beverages and to avoid herbs unless prescriber approves.
• Caution patient to avoid driving and other hazardous activities until he knows how drug affects concentration and alertness.
• Advise patient to establish effective bedtime routine and to take drug well before bedtime to minimize insomnia.
• As appropriate, review all other significant and life-threatening adverse reactions and interactions, especially those related to the drugs, foods, and herbs mentioned above.
al·bu·ter·ol
(al-bū'ter-ol),albuterol
(ăl-byo͞o′tə-rôl′)al·bu·ter·ol
(al-bū'ter-ol)Latest Searches:
zoopharmacy - zoopharmacology - zoophagous - zoopery - zooperal - zoopathology - zooparasitica - zooparasitic - zooparasite - zoonotic - zoonosology - Zoonosis - zoonoses - zoonomy - zoonite - zoonerythrin - zoomastigophorean - Zoomastigophorea - Zoomastigophora - zoomania -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp