Medical term:
Ambien
zolpidem tartrate
Pharmacologic class: Imidazopyridine
Therapeutic class: Sedative-hypnotic
Controlled substance schedule IV
Pregnancy risk category B
Action
Depresses CNS by binding to gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors
Availability
Oral spray: 5 mg/actuation
Tablets: 5 mg, 6.25 mg, 10 mg, 12.5 mg
Tablets (sublingual): 1.75 mg, 3.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg
Indications and dosages
➣ Insomnia
Adults: 10 mg P.O. (Ambien) or 12.5 mg P.O.(Ambien CR), or 10 mg (Edluar) sublingual, or 10 mg oral spray (two sprays) immediately before bedtime
➣ As-needed use for treatment of insomnia when middle-of-the-night awakening is followed by difficulty returning to sleep
Adults: 1.75 mg (Intermezzo) sublingually for women and 3.5 mg (Intermezzo) sublingually for men, taken only once per night if needed
Dosage adjustment
• Hepatic impairment
• Concurrent use of CNS depressants
• Elderly or debilitated patients
Off-label uses
• Long-term treatment of insomnia
• Insomnia related to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
• Postoperative sedation
Contraindications
• Hypersensitivity to drug
Precautions
Use cautiously in:
• pulmonary disease, hepatic or severe renal impairment
• history of psychiatric illness, suicide attempt, or substance abuse
• elderly or debilitated patients
• pregnant or breastfeeding patients
• children (safety not established).
Administration
• Don't give with or immediately after a meal.
Adverse reactions
CNS: amnesia, ataxia, confusion, euphoria, vertigo, daytime drowsiness, dizziness, drugged feeling
EENT: diplopia, abnormal vision
GI: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dry mouth
Other: hypersensitivity reaction, physical or psychological drug dependence, drug tolerance
Interactions
Drug-drug. Antihistamines, opioid analgesics, phenothiazines, sedative-hypnotics, tricyclic antidepressants: increased CNS depression
Ketoconazole, ritonavir: increased blood level and enhanced effects of zolpidem
Rifampin: decreased zolpidem efficacy
Drug-herbs. Chamomile, hops, kava, skullcap, valerian: increased CNS depression
Drug-behaviors. Alcohol use: increased CNS depression
Patient monitoring
• Monitor for physical and psychological drug dependence. Watch for drug hoarding.
• Assess for adverse reactions, including confusion, ataxia, and amnesia.
Patient teaching
• Tell patient to take immediately before bedtime (and not after a meal), because it works quickly.
• Instruct patient to place sublingual tablet under the tongue, where it will disintegrate; tell patient not to swallow tablet and not to take it with water.
• Instruct patient that oral spray pump needs to be primed initially and after not using spray for 14 days. Tell patient to fully press down on pump to make sure a full dose (5 mg) of oral spray is sprayed directly into the mouth over the tongue with each spray.
• Advise patient to take only when he is able to get a full night's sleep (7 to 8 hours) before he needs to be active again. Tell patient to use oral spray only if 4 hours of bedtime remain before planned time of waking.
• Stress that drug is meant only for short-term use (7 to 10 days).
• Tell patient rebound insomnia may occur for 1 to 2 nights after he discontinues drug.
• Inform patient that drug may cause amnesia, drowsiness, and a drugged feeling the next day.
• Caution patient to avoid driving and other hazardous activities while under drug's influence.
• As appropriate, review all other significant adverse reactions and interactions, especially those related to the drugs, herbs, and behaviors mentioned above.
zolpidem
(zole-pi-dem) ,Ambien
(trade name),Ambien CR
(trade name),Edluar
(trade name),Intermezzo
(trade name),Sublinox
(trade name),Zolpimist
(trade name)Classification
Therapeutic: sedative hypnoticsIndications
Action
Therapeutic effects
Pharmacokinetics
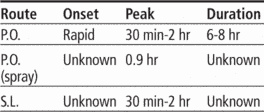
Time/action profile (sedation)
| ROUTE | ONSET | PEAK* | DURATION |
|---|---|---|---|
| PO | rapid | 30 min–2 hr | 6–8 hr |
| PO-ER | rapid | 2–4 hr | 6–8 hr |
| PO-Spray | rapid | unknown | unknown |
| SL | rapid | unknown | unknown |
Contraindications/Precautions
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Central nervous system
- daytime drowsiness (most frequent)
- dizziness (most frequent)
- abnormal thinking
- agitation
- amnesia
- behavior changes
- "drugged" feeling
- hallucinations
- sleep-driving
Gastrointestinal
- diarrhea
- nausea
- vomiting
Miscellaneous
- anaphylaxis (life-threatening)
- hypersensitivity reactions
- physical dependence
- psychological dependence
- tolerance
Interactions
Drug-Drug interaction
CNS depression may ↑ with sedatives/hypnotics, alcohol, phenothiazines, tricyclicantidepressants, opioid analgesics, or antihistamines.Concomitant use of kava-kava, valerian, or chamomile can ↑ CNS depression.Food ↓ and delays absorption.Route/Dosage
Availability (generic available)
Nursing implications
Nursing assessment
- Assess mental status, sleep patterns, and potential for abuse prior to administration. Prolonged use of >7–10 days may lead to physical and psychological dependence. Limit amount of drug available to the patient.
- Assess alertness at time of peak effect. Notify health care professional if desired sedation does not occur.
- Assess patient for pain. Medicate as needed. Untreated pain decreases sedative effects.
Potential Nursing Diagnoses
(Indications)Risk for injury (Side Effects)
Implementation
- Before administering, reduce external stimuli and provide comfort measures to increase effectiveness of medication.
- Protect patient from injury. Raise bed side rails. Assist with ambulation. Remove patient’s cigarettes.
- Use lowest effective dose.
- Oral: Tablets should be swallowed whole with full glass of water. For faster onset of sleep, do not administer with or immediately after a meal.
- Swallow extended-release tablets whole; do not crush, break, or chew.
- Sublingual: To open the blister pack, separate the individual blisters at the perforations. Peel off top layer of paper and push tablet through foil. Place the tablet under the tongue, allow to disintegrate; do not swallow or take with water.
- Intermezzo: Only take if at least 4 hr left prior to time to awakening.
- Oral Spray: Do not take with or immediately after a meal. Spray is a clear, colorless, and cherry-flavor solution.
Patient/Family Teaching
- Instruct patient to take zolpidem as directed. Advise patient not to take zolpidem unless able to stay in bed a full night (7–8 hours) before being active again. Do not take more than the amount prescribed because of the habit-forming potential. Not recommended for use longer than 7–10 days. If used for 2 wk or longer, abrupt withdrawal may result in fatigue, nausea, flushing, light-headedness, uncontrolled crying, vomiting, GI upset, panic attack, or nervousness. Instruct patient to read Patient Information for correct product before taking and with each Rx refill, changes may occur.
- Because of rapid onset, advise patient to go to bed immediately after taking zolpidem.
- May cause daytime drowsiness or dizziness. Advise patient to avoid driving or other activities requiring alertness until response to this medication is known.
- Caution patient that complex sleep-related behaviors (sleep-driving) may occur while asleep.
- Advise patient to notify health care professional immediately if signs of anaphylaxis (swelling of the tongue or throat, trouble breathing, and nausea and vomiting) occur.
- Caution patient to avoid concurrent use of alcohol or other CNS depressants.
- Oral Spray: To prime, patients should be told to point the black spray opening away from their face and other people and spray 5 times. For administration, hold container upright with the black spray opening pointed directly into the mouth. Press down fully on pump to make sure a full dose (5 mg) is sprayed directly into mouth over tongue. For 10-mg dose, a second spray should be administered. If not used for 14 days, re-prime with 1 spray.
Evaluation/Desired Outcomes
- Relief of insomnia.
- Re-evaluate insomnia after 7–10 days of Intermezzo.
Ambien
(ăm′bē-ən)Ambien®
Zolpidem tartrate Neurology A hypnotic used for short-term management of insomnia See Osteoprotegerin.Latest Searches:
zoopharmacy - zoopharmacology - zoophagous - zoopery - zooperal - zoopathology - zooparasitica - zooparasitic - zooparasite - zoonotic - zoonosology - Zoonosis - zoonoses - zoonomy - zoonite - zoonerythrin - zoomastigophorean - Zoomastigophorea - Zoomastigophora - zoomania -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp