Medical term:
DRE
DRE
examination
(eg-zam?i-na'shon) [L. examinatio, equipoise, balance, examination]examination under anesthesia
Abbreviation: EUAbimanual examination
See: pelvic examinationdental examination
digital rectal examination
Abbreviation: DREPatient care
The patient should be positioned for comfort, e.g., in Sims position (lying on the left side with knees and hips comfortably flexed). A chaperone and/or a drape should be provided for patient safety, comfort, and dignity. After an explanation of the procedure to the patient, several mL of surgical lubricant are placed on the examiner's glove, usually on the index finger. The examiner visually inspects the anus and perineum, then places the gloved finger on the anal opening while asking the patient to bear down gently. After the finger enters the anus, it is used to sweep circumferentially around the interior of the distal intestine. It is then directed anteriorly (when examining a male patient) to evaluate the consistency, size, and nodularity of the prostate gland. Samples of stool obtained during the exam may be sent to the lab to test them for the presence of occult blood.
double-contrast examination
endoscopic examination
Folstein Mini Mental Status Examination
See: Folstein Mini Mental Status Examlaboratory examination
Mini-Mental State Examination
Abbreviation: MMSEmultilingual aphasia examination
Abbreviation: MAE
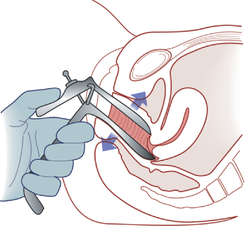

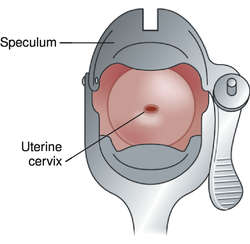
pelvic examination
periodic health examination
periodic medical examination
Periodic health examination.physical examination
Abbreviation: PExradiological examination
rapid trauma exam
Rapid trauma assessment.rectoabdominal examination
digital rectal examination
Abbreviation: DREPatient care
The patient should be positioned for comfort, e.g., in Sims position (lying on the left side with knees and hips comfortably flexed). A chaperone and/or a drape should be provided for patient safety, comfort, and dignity. After an explanation of the procedure to the patient, several mL of surgical lubricant are placed on the examiner's glove, usually on the index finger. The examiner visually inspects the anus and perineum, then places the gloved finger on the anal opening while asking the patient to bear down gently. After the finger enters the anus, it is used to sweep circumferentially around the interior of the distal intestine. It is then directed anteriorly (when examining a male patient) to evaluate the consistency, size, and nodularity of the prostate gland. Samples of stool obtained during the exam may be sent to the lab to test them for the presence of occult blood.
DRE
dream
[drēm]The interpretation of dream material is an important part of psychoanalysis. According to psychoanalytic theory, dreams have both manifest content and latent content (see under content). The patient's free associations are used to discover the latent content and to discover how that affects waking life.
dream
(drēm),dream
(drēm)Conclusion Among persons with impaired fasting glucose levels or impaired glucose tolerance, the use of ramipril for 3 years does not significantly reduce the incidence of diabetes or death but does significantly increase regression to normoglycemia; 10.6% of people receiving rosiglitazone progressed to type 2 diabetes vs. 25% of people treated with placebo
dream
Neurology A series of images and thought processes that occur during sleep which, in the framework of psychoanalysis, are believed to have latent and manifest content; eyelid movement and REM sleep coincide during dreams; dreaming is more common during REM sleep. See Wet dream.dream
(drēm)Patient discussion about dream
Q. Hi! I am Kennedy.From my childhood I have always been dreaming of slim body. Hi! I am Kennedy. From my childhood I have always been dreaming of slim body and in fact I was slim before my wedding. But after my pregnancy and delivery, I lost my shape and I am desperate to regain my shape. I tried with post-pregnancy exercises, but they didn’t help me. I am open to any kind of treatment to get shape. I hate to hang out with my hubby as I feel inferior with my shape. I feel my muscles are not tight for my age. I just want to feel good for which I need to get shape. So what kind of fitness classes shall I join? I am not comfortable with body pumping…….Please let me know?
Q. I also fear that if my case is diagnosed as Breast Cancer how can I achieve my dreams? I am a Mechanical Student currently in my second year. It is very rare to find a girl pursuing this course. In fact, all my friends and well wishers too have advised me that it may be tough for a girl pursuing this course of study. I am a very stubborn girl very much firm in my opinion. For the recent past months, I fear that I may be having a breast cancer. I have lethal classes which I always found to be difficult. Of late, I could see a lump in the under arm area which is painful when touched. I fear that this may be due to the heavy workout which I had to do as per my curriculum. I have got so many dreams to be achieved in the near future and this worry is causing me greater concern that I am not able to concentrate in my studies and my performance in the college has also declined to the significant level. I feel that this needs to be diagnosed without any further delay. I also fear that if my case is diagnosed as Breast Cancer how can I achieve my dreams and lead a full-fledged life? Please advise me suitably….
Latest Searches:
wisdom - WISC - wiry - Wirtz - wiring - wireworm - wire - Wintrobe - Wintrich - Winton - winthemi - Wintersteiner - Winternitz - wintergreen - Winterbottom - winter - Winstrol - winslowii - Winscan - WinRho -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp