Medical term:
Embryon
embryo
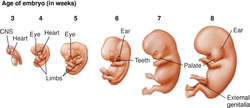
[em´bre-o]Immediately after fertilization takes place, cell division begins and progresses at a rapid rate. At approximately 4 weeks the cell mass becomes a recognizable embryo from 7 to 10 mm long with rudimentary organs. The beginnings of the eyes, ears, and extremities can be seen. By the end of the second month the embryo has grown to a length of 2 to 2.5 cm, and the head is the most prominent part because of the rapid development of the brain; the sex can be distinguished at this stage.
At the time of fertilization the ovum contains the potential beginnings of a human being. As cell division takes place the cells of the blastoderm (embryonic disk) gradually form three layers from which all the body structures develop. The ectoderm (outer layer) gives rise to the epidermis of the skin and its appendages, and to the nervous system. The mesoderm (middle layer) develops into muscle, connective tissue, the circulatory organs, circulating lymph and blood cells, endothelial tissues within the closed vessels and cavities, and the epithelium portion of the urogenital system. From the endoderm (internal layer) are derived those portions not arising from the ectoderm, the liver, the pancreas, and the lungs.

em·bry·o
(em'brē-ō),embryo
(ĕm′brē-ō′)embryo
An early stages of a developing organism, which follows fertilization of an egg including implantation and very early pregnancy–ie, from conception to the 8th wk of pregnancy. See Preembryo. Cf Fetus.em·bry·o
(em'brē-ō)embryo
(em′brē-ō″) [Gr. embryon, growing inside]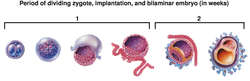
Development
First week after fertilization: The zygote begins a series of mitotic divisions called cleavage and forms a morula, a solid sphere of cells. The morula develops into a blastocyst, which has an outer trophoblast and an inner cell mass. The trophoblast gives rise to the chorion, and after implantation in the uterus, becomes the fetal placenta. Second week: The amniotic cavity and yolk sac form within the inner cell mass; they are separated by the embryonic disk, which at this time consists of ectoderm and endoderm. Third week: Mesoderm develops between ectoderm and endoderm; all three germ layers are established.
The epithelium of the alimentary canal, liver, pancreas, and lungs develops from endoderm. Muscle, all connective tissues, blood, lymphatic tissue, and the epithelium of blood vessels, body cavities, kidneys, gonads, and suprarenal cortex develop from mesoderm. The epidermis, nervous tissue, hypophysis, and the epithelium of the nasal cavity, mouth, salivary glands, bladder, and urethra develop from ectoderm.
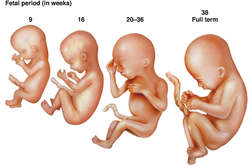
Embryo (Third through eighth weeks): The embryo increases in length from about 1.5 mm to 23 mm. The organ systems develop and the embryo begins to show human form. During this period of organogenesis, the embryo is particularly sensitive to the effects of viral infections of the mother, e.g., rubella, and toxic chemicals, including alcohol and tobacco smoke, and is sensitive to hypoxemia.
| Ectoderm | Mesoderm | Endoderm |
|---|---|---|
| Nervous tissue | Bone, cartilage, and other connective tissues | Epithelium of respiratory tract except nose; digestive tract except mouth and anal canal; bladder except trigone |
| Sense organs | Male and female reproductive tracts | Proximal portion of male urethra |
| Epidermis, nails, and hair follicles | Heart, blood vessels, and lymphatics | Female urethra |
| Epithelium of external and internal ear, nasal cavity and sinuses, mouth, anal canal | Kidneys, ureters, trigone of bladder | Liver |
| Distal portion of male urethra | Pleura, peritoneum, and pericardium | Pancreas |
| Skeletal muscle |
embryo
An organism in its earliest stages of development, especially before it has reached a stage at which it can be distinguished from other species. The human embryo is so called up to the eighth week after fertilization. After that it is called a fetus.embryo
- (in animals), the stage immediately after the beginning of CLEAVAGE up to the time when the developing animal hatches, or breaks out of egg membranes, or in higher animals, is born. In humans the developing embryo is called a FOETUS after eight weeks of gestation.
- (in plants), the partly developed SPOROPHYTE, which in ANGIOSPERMS is protected within a seed. At one end of the embryo axis is the RADICLE or ROOT, and at the other the apical MERISTEM, or PLUMULE in some forms, and one or two young leaves (COTYLEDONS).
Embryo
em·bry·o
(em'brē-ō)em·bry·o·nal
(em'brē-ō'năl),embryonal
adjective Referring to an embryo..Pronunciation
Medspeak-UK: pronounced, em BREE own ull
Medspeak-US: pronounced, em BRAI own ull
em·bry·o·nal
(em'brē-ōn'ăl)Latest Searches:
Voraxaze - Voranil - Voorhoeve - voodoo - VOO - Vontrol - von - vomitus - vomiturition - vomitory - vomitoria - vomito - vomitive - vomiting - vomit - vomica - vomerovaginalis - vomerovaginal - vomerorostralis - vomerorostral -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp