Medical term:
Noritate
metronidazole
metronidazole hydrochloride
Pharmacologic class: Nitroimidazole derivative
Therapeutic class: Anti-infective, antiprotozoal
Pregnancy risk category B
FDA Box Warning
• Drug is carcinogenic in mice and rats. Avoid unnecessary use; reserve drug for indicated conditions.
Action
Disturbs DNA synthesis in susceptible bacterial organisms
Availability
Capsules: 375 mg
Powder for injection: 5 mg/ml, 500-mg vials
Premixed injection: 500 mg/100 ml
Tablets: 250 mg, 500 mg
Tablets (extended-release): 750 mg
Topical cream, topical gel: 0.75% in 28.4-g tubes
Topical lotion: 0.75% in 59-ml bottle
Vaginal gel: 0.75% (37.5 mg/5-g applicator) in 70-g tubes
Indications and dosages
➣ Trichomoniasis
Adults: 2 g P.O. as a single dose or in two 1-g doses given on same day. Alternatively, 500 mg P.O. b.i.d. for 7 days.
➣ Bacterial infections
Adults: Initially, 15 mg/kg I.V., followed by 7.5 mg/kg I.V. q 6 hours, not to exceed 4 g/day for 7 to 10 days
➣ Amebiasis
Adults: 750 mg P.O. q 8 hours for 5 to 10 days
➣ Amebic liver abscess
Adults: 500 to 750 mg P.O. t.i.d. for 5 to 10 days. If drug can't be given orally, administer 500 mg I.V. q 6 hours for 10 days.
Children: 35 to 50 mg/kg/day P.O. in three divided doses for 10 days, to a maximum of 750 mg/dose
➣ Bacterial vaginosis
Adults: In nonpregnant patients, 750 mg/day P.O. (extended-release) for 7 days or 5 g of 0.75% vaginal gel b.i.d. for 5 days. In pregnant patients, 250 mg P.O. t.i.d. for 7 days.
➣ Perioperative prophylaxis in colorectal surgery
Adults: Initially, 15 mg/kg I.V. infusion over 30 to 60 minutes, completed 1 hour before surgery; if necessary, 7.5 mg/kg I.V. infusion over 30 to 60 minutes at 6 and 12 hours after initial dose
➣ Rosacea
Adults: Rub a thin layer of topical lotion, gel, or cream onto entire affected area morning and evening. Improvement should occur within 3 weeks.
Contraindications
• Hypersensitivity to drug, other nitroimidazole derivatives, or parabens (topical form only)
• First-trimester pregnancy in patients with trichomoniasis
Precautions
Use cautiously in:
• severe hepatic impairment
• history of blood dyscrasias, seizures, or other neurologic problems
• breastfeeding patients
• children.
Administration
• Reconstitute powder for injection by adding 4.4 ml of sterile or bacteriostatic water for injection, 0.9% sodium chloride injection, or bacteriostatic sodium chloride injection to 500-mg vial. Further dilute resulting
concentration (100 mg/ml) in 0.9% sodium chloride injection, 5% dextrose injection, or lactated Ringer's injection solution to a concentration of 8 mg/ml or less. Infuse each I.V. dose over 1 hour.
• Be aware that for I.V. injection, drug need not be diluted or neutralized.
• Don't use equipment containing aluminum to reconstitute or transfer reconstituted solution to diluent; solution may turn reddish-brown.
• Don't interchange vaginal gel with topical gel, cream, or lotion.
Adverse reactions
CNS: dizziness, headache, ataxia, vertigo, incoordination, insomnia, fatigue
EENT: rhinitis, sinusitis, pharyngitis
GI: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, furry tongue, glossitis, dry mouth, anorexia
GU: dysuria, dark urine, incontinence
Hematologic: leukopenia
Skin: rash, urticaria, burning, mild skin dryness, skin irritation, transient redness (with topical forms)
Other: unpleasant or metallic taste, superinfection, phlebitis at I.V. site
Interactions
Drug-drug. Azathioprine, fluorouracil: increased risk of leukopenia
Cimetidine: decreased metronidazole metabolism, increased risk of toxicity
Disulfiram: acute psychosis and confusion
Lithium: increased lithium blood level
Phenobarbital: increased metronidazole metabolism, decreased efficacy
Warfarin: increased warfarin effects
Drug-diagnostic tests. Alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, lactate dehydrogenase: altered levels
Drug-behaviors. Alcohol use: disulfiram-like reaction
Patient monitoring
• Monitor I.V. site. Avoid prolonged use of indwelling catheter.
• Evaluate hematologic studies, especially in patients with history of blood dyscrasias.
Patient teaching
• Advise patient to take drug with food if it causes GI upset. However, instruct him to take extended-release tablets 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals.
• Tell patient with trichomoniasis to refrain from sexual intercourse or to have male partner wear a condom to prevent reinfection. Explain that asymptomatic sex partners should be treated simultaneously.
• Advise patient to report fever, sore throat, bleeding, or bruising.
• Inform patient that drug may cause metallic taste and may discolor urine deep brownish-red.
• Tell patient using topical form to clean area thoroughly with mild cleanser before use and then wait 15 to 20 minutes before applying drug. Tell her she may apply cosmetics to skin after applying drug; with topical lotion, instruct her to let skin dry at least 5 minutes before applying cosmetics.
• Tell female patient to consult prescriber if she is pregnant or plans to become pregnant.
• As appropriate, review all other significant and life-threatening adverse reactions and interactions, especially those related to the drugs, tests, and behaviors mentioned above.
metroNIDAZOLE
(me-troe-ni-da-zole) ,Flagyl
(trade name),Flagyl ER
(trade name),MetroCream
(trade name),MetroGel
(trade name),MetroGel-Vaginal
(trade name),MetroLotion
(trade name),Metro IV
(trade name),Nidagel
(trade name),Noritate
(trade name),Novonidazol
(trade name),Trikacide
(trade name),Vandazole
(trade name)Classification
Therapeutic: anti infectivesIndications
- Intra-abdominal infections (may be used with a cephalosporin),
- Gynecologic infections,
- Skin and skin structure infections,
- Lower respiratory tract infections,
- Bone and joint infections,
- CNS infections,
- Septicemia,
- Endocarditis.
- Treatment of peptic ulcer disease caused by Helicobacter pylori.
Action
Therapeutic effects
- Bacteroides,
- Clostridium.
- Trichomonas vaginalis,
- Entamoeba histolytica,
- Giardia lamblia,
- H. pylori,
- Clostridium difficile.
Pharmacokinetics
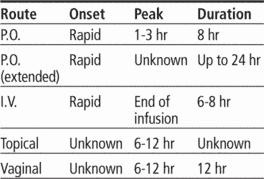
Time/action profile (PO, IV = blood levels; topical = improvement in rosacea)
| ROUTE | ONSET | PEAK | DURATION |
|---|---|---|---|
| PO | rapid | 1–3 hr | 8 hr |
| PO-ER | rapid | unknown | up to 24 hr |
| IV | rapid | end of infusion | 6–8 hr |
| Topical | 3 wk | 9 wk | 12 hr |
| Vaginal | unknown | 6–12 hr | 12 hr |
Contraindications/Precautions
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Central nervous system
- seizures (life-threatening)
- dizziness (most frequent)
- headache (most frequent)
- aseptic meningitis (IV) (most frequent)
- encephalopathy (IV) (most frequent)
Ear, Eye, Nose, Throat
- optic neuropathy
- tearing (topical only)
Gastrointestinal
- abdominal pain (most frequent)
- anorexia (most frequent)
- nausea (most frequent)
- diarrhea
- dry mouth
- furry tongue
- glossitis
- unpleasant taste
- vomiting
Dermatologic
- stevens-johnson syndrome (life-threatening)
- rash
- urticaria topical only:
- burning
- mild dryness
- skin irritation
- transient redness
Hematologic
- leukopenia
Local
- phlebitis at IV site
Neurologic
- peripheral neuropathy
Miscellaneous
- superinfection
Interactions
Drug-Drug interaction
Cimetidine may ↓ metabolism.Phenobarbital and rifampin ↑ metabolism and may ↓ effectiveness.Metronidazole ↑ the effects of phenytoin, lithium, and warfarin.Disulfiram-like reaction may occur with alcohol ingestion.May cause acute psychosis and confusion with disulfiram.↑ risk of leukopenia with fluorouracil or azathioprine.Route/Dosage
Availability (generic available)
Nursing implications
Nursing assessment
- Assess for infection (vital signs; appearance of wound, sputum, urine, and stool; WBC) at beginning of and throughout therapy.
- Obtain specimens for culture and sensitivity before initiating therapy. First dose may be given before receiving results.
- Monitor neurologic status during and after IV infusions. Inform health care professional if numbness, paresthesia, weakness, ataxia, or seizures occur.
- Monitor intake and output and daily weight, especially for patients on sodium restriction. Each 500 mg of premixed injectionfor dilution contains 14 mEq of sodium.
- Assess for rash periodically during therapy. May cause Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Discontinue therapy if severe or if accompanied with fever, general malaise, fatigue, muscle or joint aches, blisters, oral lesions, conjunctivitis, hepatitis and/or eosinophilia.
- Giardiasis: Monitor three stool samples taken several days apart, beginning 3–4 wk after treatment.
- Lab Test Considerations: May alter results of serum AST, ALT, and LDH tests.
Potential Nursing Diagnoses
Risk for infection (Indications)Diarrhea (Indications)
Implementation
- Do not confuse metronidzole with metformin.
- Oral: Administer on an empty stomach, or may administer with food or milk to minimize GI irritation. Tablets may be crushed for patients with difficulty swallowing. Swallow extended-release tablets whole; do not break, crush, or chew.
Intravenous Administration
- pH: 4.5–7.0.
- Intermittent Infusion: Diluent: Administer premixed injection (500 mg/100 mL) undiluted. Do not refrigerate. Once taken out of overwrap, premixed infusion stable for 30 days at room temperature.Concentration: 5 mg/mL.
- Rate: Infuse over 30–60 min.
- Y-Site Compatibility: acyclovir, alemtuzumab, alfentanil, allopurinol, amifostine, amikacin, aminocaproic acid, aminophylline, amiodarone, ampicillin, ampicillin/sulbactam, anidulafungin, argatroban, atracurium, bivalirudin, bleomycin, bumetanide, buprenorphine, busulfan, butorphanol, calcium acetate, calcium chloride, calcium gluconate, carboplatin, carmustine, cefazolin, cefepime, cefoperazone, cefotaxime, cefotetan, cefoxitin, ceftaroline, ceftazidime, ceftriaxone, cefuroxime, chloramphenicol, chlorpromazine, ciprofloxacin, cisatracurium, cisplatin, clindamycin, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, cytarabine, dactinomycin, dexamethasone, dexmedetomidine, dexrazoxane, digoxin, diltiazem, dimenhydrinate, diphenhydramine, dobutamine, docetaxel, dopamine, doripenem, doxacurium, doxapram, doxorubicin, doxorubicin liposome, doxycycline, droperidol, enalaprilat, ephedrine, epinephrine, epirubicin, eptifibatide, ertapenam, erythromycin, esmolol, etoposide, etoposide phosphate, famotidine, fenoldopam, fentanyl, fluconazole, fludarabine, fluorouracil, foscarnet, fosphenytoin, furosemide, gemcitabine, gentamicin, glycopyrrolate, granisetron, haloperidol, heparin, hetastarch, hydralazine, hydrocortisone, hydromorphone, idarubicin, ifosfamide, imipenem/cilastatin, insulin, irinotecan, isoproterenol, ketamine, ketorolac, labetalol, leucovorin, levofloxacin, lidocaine, linezolid, lorazepam, magnesium sulfate, mannitol, mechlorethamine, melphalan, meperidine, meropenem, mesna, metaraminol, methotrexate, methyldopate, methylprednisolone, metoclopramide, metoprolol, midazolam, milrinone, mitoxantrone, morphine, mycophenolate, nafcillin, nalbuphine, naloxone, nesiritide, nicardipine, nitroglycerin, nitroprusside, norepinephrine, octreotide, ondansetron, oxaliplatin, oxytocin, paclitaxel, palonosetron, pamidronate, pancuronium, pentamidine, pentazocine, pentobarbital, perphenazine, phentobarbital, phentolamine, phenylephrine, piperacillin/tazobactam, potassium acetate, potassium chloride, potassium phosphates, prochlorperazine, promethazine, propranolol, ranitidine, remifentanil, rituximab, rocuronium, sargramostim, sodium acetate, sodium bicarbonate, sodium phosphates, streptozocin, succinylcholine, sufentanil, tacrolimus, teniposide, theophylline, thiopental, thiotepa, ticarcillin/clavulanate, tigecycline, tirofiban, tobramycin, trastuzumab, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, vancomycin, vasopressin, vecuronium, verapamil, vincristine, vinorelbine, voriconazole, zidovudine, zoledronic acid
- Y-Site Incompatibility: amphotericin B cholesteryl, amphotericin B colloidal, amphotericin B lipid complex, amphotericin B liposome, aztreonam, dantrolene, daptomycin, diazepam, filgrastim, ganciclovir, pantoprazole, pemetrexed, phenytoin, procainamide, quinupristin/dalfopristin
- Topical: Cleanse affected area before application. Apply and rub in a thin film twice daily, morning and evening. Avoid contact with eyes.
Patient/Family Teaching
- Instruct patient to take medication as directed with evenly spaced times between doses, even if feeling better. Do not skip doses or double up on missed doses. Take missed doses as soon as remembered if not almost time for next dose.
- Advise patients treated for trichomoniasis that sexual partners may be asymptomatic sources of reinfection and should be treated concurrently. Patient should also refrain from intercourse or use a condom to prevent reinfection.
- Caution patient to avoid intake of alcoholic beverages or preparations containing alcohol during and for at least 3 days after treatment with metronidazole, including vaginal gel. May cause a disulfiram-like reaction (flushing, nausea, vomiting, headache, abdominal cramps).
- May cause dizziness or light-headedness. Caution patient to avoid driving or other activities requiring alertness until response to medication is known.
- Instruct patient to notify health care professional promptly if rash occurs.
- Inform patient that medication may cause an unpleasant metallic taste.
- Advise patient to notify health care professional of all Rx or OTC medications, vitamins, or herbal products being taken and to consult with health care professional before taking other medications.
- Advise patient that frequent mouth rinses, good oral hygiene, and sugarless gum or candy may minimize dry mouth. Notify health care professional if dry mouth persists for more than 2 wk.
- Inform patient that medication may cause urine to turn dark.
- Advise patient to consult health care professional if no improvement in a few days or if signs and symptoms of superinfection (black, furry overgrowth on tongue; vaginal itching or discharge; loose or foul-smelling stools) develop.
- Advise patient to inform health care professional if pregnancy is suspected before taking this medication or if breast feeding.
- Vaginal: Instruct patient in correct technique for intravaginal instillation. Advise patient to avoid intercourse during treatment with vaginal gel.
- Topical: Instruct patient on correct technique for application of topical gel. Cosmetics may be used after application of gel.
Evaluation/Desired Outcomes
- Resolution of the signs and symptoms of infection. Length of time for complete resolution depends on organism and site of infection.
- Significant results should be seen within 3 wk of application of topical gel. Application may be continued for 9 wk.
Noritate®
Metronidazole, see there.Latest Searches:
Voraxaze - Voranil - Voorhoeve - voodoo - VOO - Vontrol - von - vomitus - vomiturition - vomitory - vomitoria - vomito - vomitive - vomiting - vomit - vomica - vomerovaginalis - vomerovaginal - vomerorostralis - vomerorostral -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp