tomography
[to-mog´rah-fe] any method that produces images of single tissue planes. In conventional radiology, tomographic images (body section radiographs) are produced by motion of the x-ray tube and film or by motion of the patient that blurs the image except in a single plane. In reconstruction tomography (CT and PET) the image is produced by a computer program.
computed tomography (CT) (
computerized axial tomography (CAT)) a radiologic imaging modality that uses computer processing to generate an image (CAT
scan) of the tissue density in a “slice” as thin as 1 to 10 mm in thickness through the patient's body. These images are spaced at intervals of 0.5 to 1 cm. Cross-sectional anatomy can be reconstructed in several planes without exposing the patient to additional radiation.
Since its introduction in 1972, the use of this modality has grown rapidly. Because it is noninvasive and has high contrast resolution, it has replaced some radiographic procedures using contrast media. It also has a better spatial resolution than scintillation imaging (about 1 mm for CAT compared to 15 mm for a scintillation camera).
A CAT scan is divided into a square matrix of
pixels (picture elements). The newer CAT scanners use a high resolution matrix with 256 × 256 or 512 × 512 pixels. The region of the tissue slice corresponding to a pixel has a cross-sectional area of 1 × 1 mm to 2 × 2 mm; because of the thickness of the slice, it has a finite height and is therefore referred to as a
voxel (volume element).
The actual measurements made by the scanner are the x-ray attenuations along thousands of rays traversing the slice at all angles. The attenuation value for a ray is the sum of the values for all of the voxels it passes through. A computer program called a
reconstruction algorithm can solve the problem of assigning attenuation values for all the pixels that add up to the measured values along each ray.
The attenuation values are converted to CAT numbers by subtracting the attenuation value of water and multiplying by an arbitrary coefficient to produce values ranging from −1000 for air to +1000 for compact bone with water as 0. CT numbers are sometimes expressed in
Hounsfield units, named after Godfrey Hounsfield, the inventor of the CT scanner; Hounsfield and Allan Cormack were co-winners of the Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine in 1979 for the development of computerized axial tomography.
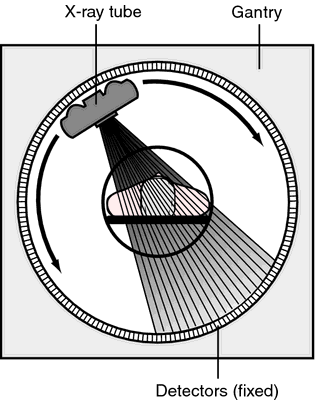
Computed tomography. Relative position of the x-ray tube, patient, and detectors in a fourth generation CT unit.
electron beam computed tomography (EBCT) ultrafast computed tomography done with a scanner in which the patient is surrounded by a large circular anode that emits x-rays as the electron beam is guided around it.
extended narrow tomography tomography involving an increase in amplitude and increase in exposure angle resulting in greater thinness of the cut for examination.
linear tomography tomography in which the tube and film move in the same direction.
narrow angle tomography a type of tomography that results in thicker sections for examination.
pluridirectional tomography tomography in which there is a great deal of movement in a variety of directions.
positron emission tomography (PET) a combination of computed tomography and scintillation scanning. Natural biochemical substances or drugs tagged with a positron-emitting radioisotope are administered to the subject by injection; the tagged substance (tracer) then becomes localized in specific tissues like its natural analogue. When the isotope decays, it emits a positron, which then annihilates with an electron of a nearby atom, producing two 511 keV gamma rays traveling in opposite directions 180 degrees apart. When the gamma rays trigger a ring of detectors around the subject, the line between the detectors on which the decay occurred is stored in the computer. A computer program (reconstruction algorithm), like those used in computed tomography, produces an image of the distribution of the tracer in the plane of the detector ring.
Most of the isotopes used in PET scanning have a half-life of only 2 to 10 minutes. Therefore, they must be produced by an on-site cyclotron and attached chemically to the tracer and used within minutes. Because of the expense of the scanner and cyclotron, PET is used only in research centers. However, PET is important because it provides information that cannot be obtained by other means. By labeling the blood with 11C-carbon monoxide, which binds to hemoglobin, images can be obtained showing the regional perfusion of an organ in multiple planes. By using labeled metabolites, images can be obtained showing metabolic activity of an organ. 15O-oxygen and 11C-glucose have been used for brain imaging and 11C-palmitate for heart imaging. 81Rb, which is distributed like potassium, is also used for heart imaging. By using labeled neurotransmitters, hormones, and drugs the distribution of receptors for these substances in the brain and other organs can be mapped.
single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) a type of tomography in which gamma photon–emitting radionuclides are administered to patients and then detected by one or more gamma cameras rotated around the patient. From the series of two-dimensional images produced, a three-dimensional image can be created by computer reconstruction. The technique improves resolution of, and decreases interference by, overlapping organs. It is used particularly for assessment of cardiac disease, stroke, and liver disease; for staging of cancer; and to diagnose physical abnormalities through evaluation of function.
ultrasonic tomography the ultrasonographic visualization of a cross-section of a predetermined plane of the body; see B-mode ultrasonography.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
PET
Abbreviation for positron emission tomography.
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
PET
Abbreviation for:
pancreatic endocrine tumour
paraffin-embedded tissue
partial-exchange transfusion
peak ejection time
peritoneal equilibration test
photosynthetic electron transport
positron emission tomography
post-exposure treatment
pre-eclamptic toxaemia
Project Executive Team
psychiatric emergency teamSegen's Medical Dictionary. © 2012 Farlex, Inc. All rights reserved.
PET
1. Pancreatic endocrine tumor, see there Nephrology 1. Peritoneal equilibration test, which is used to assess peritoneal transport characteristics in CAPD Pts.
2. Photoemission tube, see there.
PET
PET scan, positron emission transaxial tomography Imaging A non-invasive imaging modality in which emission computed axial tomography is used to detect positron-emitting isotopes–radionuclides that reflect biochemical and pathologic defects in tissues and evaluate blood flow and metabolism in the cerebral cortex, heart, whole body scanning; PET scans may be used to evaluate AIDS-related neuropathology–response to AZT by local ↑ of glucose metabolism, gliosis, differentiating among Alzheimer's, multi-infarct, and other forms of dementia, Huntington's disease, tardive dyskinesia, epilepsy for localization of seizure focus, making surgical therapy viable, malignancy–gliomas, residual tumor, pituitary adenomas, Parkinson's disease–↓ dopamine, psychiatric disease–depression, schizophrenia, and analysis of radiopharmaceuticals; PET scanning may be used in cardiology to evaluate coronary arteriosclerosis, differentiate between benign and malignant tumors, stage CA, detect CA recurrence and metastases, monitor response to therapy and target biopsy sites, assess myoardial viability, regional myocardial blood flow, and ischemia, using 15CO2; after an AMI, there is an severely attenuated vasodilator response in the resistance vessels in both the infarcted myocardium and in the myocardium perfused by normal vesselsMcGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine. © 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
PET
Abbreviation for positron emission tomography.
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
tomography
(to-mog'ra-fe) [ tomo- + -graphy] A radiographic technique that selects a level in the body and blurs out structures above and below that plane, leaving a clear image of the selected anatomy. This is accomplished by moving the x-ray tube in the opposite direction from the imaging device around a stationary fulcrum defining the plane of interest. Tube movements can be linear, curvilinear, circular, elliptical, figure eight, hypocycloidal, or trispiral. With the exception of renal tomography most tomographic procedures have been replaced by computed tomography (CT). Synonym: body section radiography; body section roentgenography
computed axial tomography
Abbreviation: CAT
See: computed tomographycomputed tomography
Abbreviation: CT
A computerized x-ray scanning system that produces a sectional anatomic image. It is achieved by digital processing of x-ray attenuation coefficients from a 360° wedge scan of ionizing radiation. There is considerable use of data from the attenuation coefficients in diagnosis. Computed tomography is colloquially called a cat scan.
CAUTION!
CT scans expose patients to radiation on the order of 10 mSv per scan. Educational materials about the potential risks and benefits of scanning should be provided to patients to ensure that scans are performed safely and carefully.computerized axial tomography
Abbreviation: CAT
See: computed tomographyelectrical impedance tomography
Cross-sectional body imaging that reconstructs pictures of internal organs based on measurements of their electrical activity as detected by electrodes placed on the surface of the body.
electron-beam tomography
Ultrafast computed tomographyfull body computed tomography
Abbreviation: FBCT
An examination from head to toe of the body with computed tomographic imaging, promoted as a screening test for cancer and other illnesses.
CAUTION!
The test exposes patients to high levels of radiation, reveals more false positive findings than true positives, and is expensive.Heidelberg retinal tomography
Abbreviation: HRT
A confocal laser scanning system that produces three-dimensional images of the posterior segment of the eye. It is used to diagnose and treat glaucoma.
helical computed tomography
Computed tomographic (CT) images that are obtained as the CT table moves continuously during a single, held breath. Detailed evaluation of dynamic internal features is feasible with this technique.
Synonym: spiral computed tomographyoptical coherence tomography
Abbreviation: OCT
A radiographical method used to obtain high-resolution cross-sectional images of tissues and their defects, e.g., of the structures of the eye.
panoramic tomography
Zonography.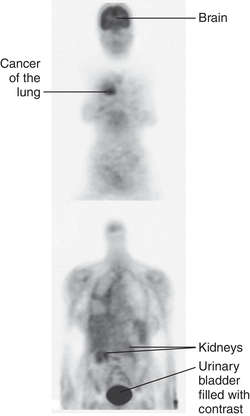

POSITRON EMISSION TOMOGRAPHY: PET SCAN revealing lung cancer

PET SCAN OF BRAIN
positron emission tomography
Abbreviation: PET
Reconstruction of brain sections by using positron-emitting radionuclides. By using several different radionuclides, researchers can measure regional cerebral blood flow, blood volume, oxygen uptake, and glucose transport and metabolism, and can locate neurotransmitter receptors. PET has been used with fludeoxyglucose F 18 to identify and localize regional lymph node metastases and to help assess response to therapy.
The images produced by PET are in colors that indicate the degree of metabolism or blood flow. The highest rates appear red, those lower appear yellow, then green, and the lowest rates appear blue. The images in various disease states may then be compared to those of normal subjects. Three- and four-dimensional reconstructions are often achieved through the use of computed tomography (CT) with the same machine. See: illustration
quantitative computed tomography
Abbreviation: QCT
A method for determining the bone mineral density of a three-dimensional bony specimen, e.g., in the vertebral bodies or the forearms. It is used in the diagnosis of osteopenia and osteoporosis.
single photon emission computed tomography
Abbreviation: SPET, SPECT
A medical imaging method for reconstructing sectional images of radiotracer distributions.
See: nuclear medicine scanning test; positron emission tomographyspiral computed tomography
Helical computed tomography.ultrafast computed tomography
Computed tomographic scanning that produces images by rotating the x-ray beam at targets placed around a patient, instead of moving a patient on a gantry through the scanner. The technique minimizes patient movement artifacts and decreases scanning times to about 50 to 100 msec. It is capable of providing good resolution of vascular structures, such as the aorta and the coronary arteries. Synonym: electron-beam tomography
xenon-enhanced computed tomography
Computed tomographic scanning that uses the inert gas xenon to improve the visual distinction between healthy and abnormal tissues, esp. to visualize blood flow to different regions of the brain in stroke.


POSITRON EMISSION TOMOGRAPHY: PET SCAN revealing lung cancer


PET SCAN OF BRAIN
positron emission tomography
Abbreviation: PET
Reconstruction of brain sections by using positron-emitting radionuclides. By using several different radionuclides, researchers can measure regional cerebral blood flow, blood volume, oxygen uptake, and glucose transport and metabolism, and can locate neurotransmitter receptors. PET has been used with fludeoxyglucose F 18 to identify and localize regional lymph node metastases and to help assess response to therapy.
The images produced by PET are in colors that indicate the degree of metabolism or blood flow. The highest rates appear red, those lower appear yellow, then green, and the lowest rates appear blue. The images in various disease states may then be compared to those of normal subjects. Three- and four-dimensional reconstructions are often achieved through the use of computed tomography (CT) with the same machine. See: illustration
See also: tomography
Medical Dictionary, © 2009 Farlex and Partners
Positron emission tomography (PET)
A diagnostic technique in which computer-assisted x rays are used to track a radioactive substance inside a patient's body. PET can be used to study the biochemical activity of the brain.
Mentioned in: Movement Disorders
Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights reserved.
PET
Abbreviation for positron emission tomography.
Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions © Farlex 2012
Patient discussion about PET
Q. Can a pet allergy cause your nose to plug, give you a sore throat and a bad cough? I recently adopted a puppy. I felt fine for about a week an a half, but 2 days ago I began to sneeze a lot. My nose plugged and I had to blow almost constantly. I also came down with a sore throat and a bad cough. Is this a result of a pet allergy or did I just come down with a cold? I've been around dogs all my life and I don't ever recall reacting like this before.
A. It can happen. Go to the doctor, if you want to know for sure. See a veterinarian for tips on making your dog more hypoallergenic. There are ways to take care of a dog and not have so many allergy issues. :D Good luck.
Q. What kind of dogs are considered "low allergy" breeds? My son really wants a dog and I am allergic. Not severely but... Promised to look into getting a low allergy one. Appreciate any info including how to source free/low cost as money is tight.
A. Take in mind that there are also other criteria for choosing a dog. Some of them need special grooming and some aren't really great with kids, but you can check out these breeds and more at www. dogbreedfacts.com. As for myself, I have had several Bichon Frises, and they can be great with kids and other pets, and they are hardy and very, very intelligent!! They arent too big either! Good luck on your hunt!
More discussions about PETThis content is provided by iMedix and is subject to iMedix Terms. The Questions and Answers are not endorsed or recommended and are made available by patients, not doctors.




