device
(di-vis') [Fr. devis, contrivance] An apparatus, tool, or machine made for a specific function.
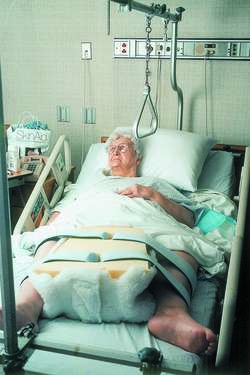

ABDUCTION DEVICE
abduction device
A trapezoidal pillow, wedge, or splint placed between the arm and torso to prevent adduction. It is commonly used postoperatively for patients having total joint replacement or open reduction or internal fixation of the hip or shoulder.
See: illustrationadaptive device
Assistive technology.adaptive seating device
Abbreviation: ASD
A device that provides a proper sitting position for those with limited motor control. Such devices include seating inserts, wheelchairs, and postural support systems designed to prevent deformities and enhance function.
Synonym: seating systemassistive technology device
Assistive technology.augmentative device
A device that helps people with limited or no speech to communicate. Examples include communication boards, pictographs, or ideographs (symbols representing ideas, not sounds).
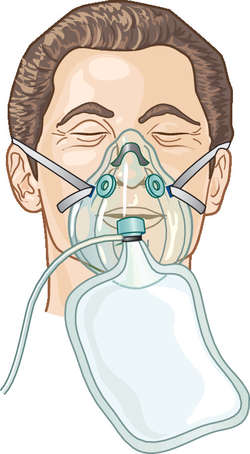

BAG MASK DEVICE
bag mask device
A manually operated resuscitator used to ventilate a nonbreathing patient or assist the ventilation of a patient who is not breathing at an effective rate or tidal volume. The device consists of a bag, an oxygen reservoir system, a one-way flow valve, and a clear face mask. It is designed to be attached to an oxygen source by tubing to deliver concentrations approaching 100%.
See: illustrationbelay device
A device using friction to brake or slow the movement of a rope, or to protect a patient, basket, climber, or other rescuer.
biventricular assist device
Abbreviation: BiVAD
A device that helps both ventricles of the heart contract more effectively. It is used to treat heart failure by propelling blood out of the chambers of the heart.
cardiac rhythm management device
Abbreviation: CRMD
An umbrella term for pacemakers and implantable cardioverter/defibrillators.
cervical immobilization device
Abbreviation: CID
A stiff neck brace or collar to prevent movement of the cervical spine in order to maintain spinal alignment and prevent injury or paralysis.
charge-coupled device
Abbreviation: CCD
A device used in video and digital imaging (such as in CT scanning) that creates electronic images from light.
clitoral vacuum device
A mechanical device used to engorge and stimulate the clitoris. It is used as a U.S. FDA–approved treatment for female sexual dysfunction.
electronic infusion device
Abbreviation: EID
A device for monitoring intravenous infusions. The device may have an alarm in case the flow is restricted because of an occlusion of the line. In that case, the alarm will sound when a preset pressure limit is sensed. The device can also signal that an infusion is close to completion. The pressure is regulated by the height at which the container is positioned above the level of the heart when the patient is lying flat. A height of 36 in (91 cm) provides a pressure of 1.3 lb/sq in (70 mm Hg). Most EIDs are equipped to stop the flow of the infused liquid if accidental free flow occurs.
See: infusion pumpesophageal intubation detector device
A syringe attached to the endotracheal tube immediately after an intubation attempt.
Patient care
If aspiration is difficult or stomach contents are withdrawn, or both, the endotracheal (ET) tube may have been placed in the esophagus and needs to be removed and reinserted. If aspiration is easy and free of stomach contents, it is probable that the ET tube is located in the trachea; the rescuer should then confirm tube placement by other techniques, e.g., a combination of auscultation, x-ray, and pulse oximetry.
femoral compression device
A device used to apply pressure to the large artery or vein in the thigh after it has been cannulated in order to reduce bleeding from the punctured vessel. Femoral compression devices are used, e.g., after angiography.
flow-restricted oxygen-powered ventilation device
Abbreviation: FROPVD
A ventilation device that provides a peak flow rate of 100% oxygen at up to 40 L/min. See: oxygen-powered ventilation device
Flutter device
See: Flutter devicehead immobilization device
A device that attaches to a long back board and holds the patient's head in neutral alignment.
See: long back boardhumanitarian use device
Humanitarian device exemption.improvised explosive device
Abbreviation: IED
Military jargon for a homemade bomb or land mine used in unconventional warfare.
input device
In assistive technology, the device that activates an electronic device. This can be a manual switch, a remote control, or a joystick.
See: switchinspiratory impedance threshold device
Inspiratory impedance threshold valve.intrauterine contraceptive device
Abbreviation: IUCD, IUD
See: intrauterine contraceptive device.Kendrick extrication device
See: Kendrick extrication deviceleft ventricular assist device
Abbreviation: LVAD
A pump surgically implanted in patients with severe heart failure to move blood from the left ventricle to the ascending aorta. The LVAD usually augments the heart's function until it heals (following a severe myocardial infarction) or until a heart transplant becomes available, e.g., for patients with heart failure with a markedly diminished ejection fraction. The LVAD also may be used permanently for a patient who does not meet criteria for transplantation.
listening device
A speech amplifier that aids the hearing-impaired in direct person-to-person communication or telephone conversation. Such devices differ from conventional hearing aids in that they reduce interference from background noises.
medical device
Any health care product that is intended for the diagnosis, prevention, or treatment of disease and does not primarily work by effecting a chemical change in the body
mobility device
Any assistive technology that aids the movement of people with physical impairments. Examples include lift chairs, scooters, or wheelchairs.
needleless device
A device that has no exposed sharp surface, used to inject drugs and fluids. It is designed to decrease the risk of needle-stick injuries by health care professionals.
oxygen-conserving device
Abbreviation: OCR
Any device that reduces the loss of administered oxygen into the environment, e.g., one that releases oxygen to a patient only when the patient inhales.
oxygen-powered ventilation device
A multifunction ventilation devicehat uses high-flow oxygen. This device can often be triggered by negative pressure caused by an inhaling patient; it can also be operated by a button while the operator watches the patient's chest rise.
CAUTION!
During resuscitation, it is necessary to use the positive-pressure aspect of this device and manually trigger or compress the button because the patient cannot open the valve by inhaling. These devices should be fitted with an overinflation high-pressure alarm to avoid gastric distention and/or barotrauma. personal flotation device
Abbreviation: PFD
A life vest to prevent drowning and near drowning. People engaged in water sports, such as boating or water skiing, or rescuers working on or near the water should wear PFDs at all times. The U.S. Coast Guard sets standards and establishes specifications for the manufacture and use of PFDs. Personal flotation devices may be used to provide added buoyancy for the patient during aquatic therapy.
personal assistive mobility device
Personal mobility device.personal mobility device
Any assistive device that facilitates individual human transportation. Examples include powered wheelchairs, scooters, bicycles and unicycles. Although many such devices are used by people with activity or mobility restrictions, mobility aids can be employed generally, e.g., for urban transportation in place of automobiles.
Synonym: personal assistive mobility devicepointing device
A type of input device for sending commands to a computer. Moving the device results in movement of a cursor on the monitor or computer screen. Pointing devices range from the conventional desktop mouse, trackball, and touch-sensitive screens to infrared and ultrasound pointers mounted on the head.
See: light pointer; switchposition-indicating device
Abbreviation: PID
A device to guide the direction of the x-ray beam during the exposure of dental radiographs. This devices improves and standardizes dental radiographic imaging and reduces the patient's risk of radiation exposure.
positive beam limiting device
A collimator that automatically adjusts the size of the radiation field to match the size of the imaging device. Synonym: automatic collimator
powered mobility device
Abbreviation: PMD
Any assistive device (such as a powered wheelchair, a lift chair, or a scooter) that improves the movement of the functionally impaired.
pressure relief device
An appliance filled with air, water, gel, or foam, to reduce pressure points caused by the patient’s body weight when seated or bedridden. Examples include wheelchair cushions and air or water flotation mattresses.
prosthetic terminal device
A component of an upper extremity prosthesis that substitutes for the functions of the hand. There are many types of terminal devices, some of which are designed for use with specific tools and implements. These devices have two primary actions: voluntary opening and voluntary closing.
Synonym: hookprotective device
An external support applied to vulnerable joints or other body parts to guard against injury. Protective devices include helmets, braces, tape or wrapping, and padding.
pubovaginal device
A device fitted for use in the vagina to help prevent urinary incontinence.
See: pessarysequential compression device
Abbreviation: SCD.
A device to reduce edema or prevent the formation of blod clots in an extremity. A chambered nylon sleeve is progressively inflated from its distal segment to the proximal segment, forcing venous and lymphatic return. Sequential compression devices are inflated with air (pneumatic compression) or, less commonly, chilled water (cryocompression). SCDs are used frequently in the perioperative period. See: intermittent compression
single-use device
A medical device used once for the care of a single patient and then immediately discarded.
spine arthroplasty device
A prosthesis to replace a damaged intervertebral disk.
superconductive quantum interference device
Abbreviation: SQUID
A biomagnetometer used to measure magnetic fields in the body or the presence of magnetically active elements or minerals, such as body stores of iron.
telecommunication device for the deaf
Abbreviation: TDD
A device that allows the hearing-impaired to use the telephone even if they cannot comprehend speech. A keyboard and display screen are used.
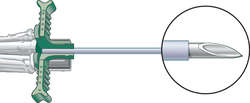

VENOUS ACCESS DEVICES: A. An over-the-needle catheter; B. An inside-the-needle catheter.
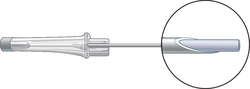

VENOUS ACCESS DEVICES: A. An over-the-needle catheter; B. An inside-the-needle catheter.
venous access device
A specially designed catheter for gaining and maintaining access to the venous system. This device provides access for patients who require intravenous fluids or medications for several days or more, e.g., those having a bone marrow transplant or who are receiving long-term total parenteral nutrition. See: venous port
See: illustrationventricular assist device
Abbreviation: VAD
A pump to treat heart failure. It helps the ventricles to contract and move blood to the lungs and/or the aorta.
See: left ventricular assist device
position-indicating device
Abbreviation: PID
A device to guide the direction of the x-ray beam during the exposure of dental radiographs. This devices improves and standardizes dental radiographic imaging and reduces the patient's risk of radiation exposure.
See also: device
pelvic inflammatory disease
, PID
Infection of the uterus, fallopian tubes, and adjacent pelvic structures that is not associated with surgery or pregnancy. PID usually is caused by an ascending infection in which disease-producing germs spread from the vagina and cervix to the upper portions of the female reproductive tract. chlamydia; gonorrhea;
Etiology
Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae are the most frequent causes of PID, although anaerobic microorganisms, Escherichia coli, and other microorganisms also are often involved.
Symptoms
The most common symptom is lower abdominal or pelvic pain, typically beginning after the start of a menstrual period. Exquisite tenderness during physical examination of the cervix, fallopian tubes, or ovaries is a common sign. Clear, white, or purulent vaginal discharge is sometimes present. Fevers, chills, nausea, vomiting, vaginal bleeding, dysuria, dyspareunia, or anorectal pain are seen in smaller numbers of patients.
Diagnosis
Distinguishing PID from other causes of lower abdominal or pelvic pain can be difficult. The disease may be confused with appendicitis, diverticulitis, tubo-ovarian abscess, endometritis, ectopic pregnancy, and other serious illnesses. PID is most likely to be found in young, sexually active patients with multiple sexual partners, esp. if there is a history of previous sexually transmitted illnesses or of substance abuse. Leukocytosis and an elevated sedimentation rate are commonly found, and a mucopurulent discharge is often present on pelvic examination. Cultures from the vagina or cervix may be helpful in identifying the causative organism. In patients for whom the diagnosis is unclear, laparoscopy, ultrasonography, or computed tomography may be needed.
Complications
PID may result in adhesions or scarring of the fallopian tubes and pelvis, and is a common cause of pelvic pain and ectopic pregnancy. About a third of all women who are infertile have lost the ability to conceive because of PID. Occasionally, PID causes intraperitoneal abscesses.
Treatment
Antibiotics effective against gonococci, chlamydiae, anaerobes, and gram-negative rods usually are used to treat PID. Typical therapy includes a tetracycline derivative, like doxycycline, and a cephalosporin. Early therapy prevents infertility caused by fallopian tube adhesions or scarring. In patients with tubal or pelvic abscesses, drainage is required. Sexual partners should be examined for evidence of sexually transmitted diseases and treated if culture results are positive. See: safe sex
Medical Dictionary, © 2009 Farlex and Partners



