Medical term:
Primaxin
imipenem and cilastatin sodium
Pharmacologic class: Carbapenem
Therapeutic class: Anti-infective
Pregnancy risk category C
Action
Acts against many gram-positive and gram-negative organisms by binding to bacterial cell wall, causing cell death. Addition of cilastatin prevents renal inactivation of imipenem, resulting in increased urinary concentration. Imipenem resists actions of many enzymes that degrade most other penicillins and penicillin-like drugs.
Availability
Powder for I.M. injection: 500 mg
imipenem/500 mg cilastatin, 750 mg
imipenem/750 mg cilastatin
Powder for I.V. injection: 250 mg
imipenem/250 mg cilastatin, 500 mg
imipenem/500 mg cilastatin
Indications and dosages
➣ Lower respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, abdominal infections, gynecologic infections, skin infections, bone and joint infections, endocarditis, and polymicrobial infections
Adults: For mild infections, 250 to 500 mg I.V. q 6 hours; for moderate infections, 500 mg I.V. q 6 to 8 hours or 1 g I.V. q 8 hours; for serious infections, 500 mg I.V. q 6 hours to 1 g q 6 to 8 hours or 500 to 750 mg I.M. q 12 hours
Children: 15 to 25 mg/kg I.V. q 6 hours or 10 to 15 mg/kg I.M. q 6 hours
Infants ages 4 weeks to 3 months: 25 mg/kg I.V. q 6 hours
Infants ages 1 to 4 weeks: 25 mg/kg I.V. q 8 hours
Infants age 1 week and younger: 25 mg/kg I.V. q 12 hours
Dosage adjustment
• Renal impairment
Contraindications
• Hypersensitivity to drug, penicillins, or cephalosporins
Precautions
Use cautiously in:
• seizure disorders, renal impairment
• history of multiple hypersensitivity reactions
• elderly patients
• pregnant or breastfeeding patients.
Administration
• For I.V. use, reconstitute each 250- or 500-mg vial with 10 ml of diluent; shake well.
• For piggyback infusion, add 250- or 500-mg I.V. dose to 100 ml of diluent; shake solution until clear and drug has dissolved completely.
• Infuse doses of 500 mg or less over 20 to 30 minutes; infuse doses of 750 to 1,000 mg over 40 to 60 minutes.
• Slow infusion rate if patient experiences nausea, vomiting, dizziness or sweating.
• For I.M. use, inject into large muscle.
Adverse reactions
CNS: dizziness, drowsiness, seizures
CV: hypotension
GI: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, pseudomembranous colitis
Hematologic: eosinophilia
Skin: rash, pruritus, diaphoresis, urticaria
Other: phlebitis at I.V. site, fever, superinfection, allergic reactions including anaphylaxis
Interactions
Drug-drug. Cyclosporine, ganciclovir: increased risk of seizures
Probenecid: decreased renal excretion of imipenem
Drug-diagnostic tests. Alanine aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, aspartate aminotransferase, bilirubin, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, lactate dehydrogenase: increased values
Direct Coombs' test: positive result Hematocrit, hemoglobin: decreased
Patient monitoring
☞ Stay alert for seizures in patients with brain lesions, head trauma, or other CNS disorders and in those receiving more than 2 g daily.
☞ Monitor closely for severe diarrhea and hypersensitivity reaction.
• Assess tissue or fluid culture results obtained before and during therapy.
• Monitor for signs and symptoms of infection, such as fever and elevated white blood cell count. Also evaluate for bacterial and fungal superinfection.
• Monitor electrolyte levels, especially sodium.
Patient teaching
• Caution patient to report discomfort at I.V. site.
☞ Instruct patient to report rash, hives, difficulty breathing, and signs or symptoms of superinfection (such as diarrhea, mouth sores, and vaginal itching or discharge).
• As appropriate, review all other significant and life-threatening adverse reactions and interactions, especially those related to the drugs and tests mentioned above.
imipenem/cilastatin
(i-me-pen-em/sye-la-stat-in) ,Primaxin
(trade name)Classification
Therapeutic: anti infectivesPharmacologic: carbapenems
Indications
- Lower respiratory tract infections,
- Urinary tract infections,
- Abdominal infections,
- Gynecologic infections,
- Skin and skin structure infections,
- Bone and joint infections,
- Bacteremia,
- Endocarditis,
- Polymicrobic infections.
Action
Therapeutic effects
- Streptococcus pneumoniae,
- Group A beta-hemolytic streptococci,
- Enterococcus,
- Staphylococcus aureus.
- Escherichia coli,
- Klebsiella,
- Acinetobacter,
- Proteus,
- Serratia,
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
- Salmonella,
- Shigella,
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae,
- Numerous anaerobes.
Pharmacokinetics
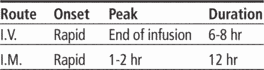
Time/action profile (blood levels)
| ROUTE | ONSET | PEAK | DURATION |
|---|---|---|---|
| IM | rapid | 1–2 hr | 12 hr |
| IV | rapid | end of infusion | 6–8 hr |
Contraindications/Precautions
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Central nervous system
- seizures (life-threatening)
- dizziness
- somnolence
Cardiovascular
- hypotension
Gastrointestinal
- pseudomembranous colitis (life-threatening)
- diarrhea (most frequent)
- nausea (most frequent)
- vomiting (most frequent)
Dermatologic
- rash (most frequent)
- pruritus
- sweating
- urticaria
Hematologic
- eosinophilia
Local
- phlebitis at IV site
Miscellaneous
- allergic reaction including anaphylaxis (life-threatening)
- fever
- superinfection
Interactions
Drug-Drug interaction
Do not admix with aminoglycosides (inactivation may occur).Probenecid ↓ renal excretion and ↑ blood levels.↑ risk of seizures with ganciclovir or cyclosporine (avoid concurrent use of ganciclovir).May ↓ serum valproate levels (↑ risk of seizures).Route/Dosage
Renal Impairment
Intravenous (Adults) If dose for normal renal function is 1 g/day: CCr 41–70 mL/min—125–250 mg q 6–8 hr, CCr 21–40 mL/min—125–250 mg q 8–12 hr, CCr 6–20 mL/min—125–250 mg q 12 hr; if dose for normal renal function is 1.5 g/day: CCr 41–70 mL/min—125–250 mg q 6–8 hr, CCr 21–40 mL/min—125–250 mg q 8–12 hr, CCr 6–20 mL/min—125–250 mg q 12 hr; if dose for normal renal function is 2 g/day: CCr 41–70 mL/min—125–500 mg q 6–8 hr, CCr 21–40 mL/min—125–250 mg q 8–12 hr, CCr 6–20 mL/min—125–250 mg q 12 hr; if dose for normal renal function is 3 g/day : CCr 41–70 mL/min—250–500 mg q 6–8 hr, CCr 21–40 mL/min—250–500 mg q 6–8 hr, CCr 6–20 mL/min—250–500 mg q 12 hr; if dose for normal renal function is 4 g/day: CCr 41–70 mL/min—250–750 mg q 6–8 hr, CCr 21–40 mL/min—250–500 mg q 6–8 hr, CCr 6–20 mL/min—250–250 mg q 12 hr.Availability (generic available)
Nursing implications
Nursing assessment
- Assess patient for infection (vital signs; appearance of wound, sputum, urine, and stool; WBC) at beginning of and throughout therapy.
- Obtain a history before initiating therapy to determine previous use of and reactions to penicillins. Persons with a negative history of penicillin sensitivity may still have an allergic response.
- Obtain specimens for culture and sensitivity before initiating therapy. First dose may be given before receiving results.
- Observe patient for signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis (rash, pruritus, laryngeal edema, wheezing). Discontinue the drug and notify the physician immediately if these occur. Have epinephrine, an antihistamine, and resuscitative equipment close by in the event of an anaphylactic reaction.
- Lab Test Considerations: BUN, AST, ALT, LDH, serum alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, and creatinine may be transiently ↑.
- Hemoglobin and hematocrit concentrations may be ↓.
- May cause positive direct Coombs’ test.
Potential Nursing Diagnoses
Risk for infection (Indications, Side Effects)Implementation
- Intramuscular: Only the IM formulation can be used for IM administration. Reconstitute 500-mg vial with 2 mL and 750-mg vial with 3 mL of lidocaine without epinephrine. Shake well to form a suspension. Withdraw and inject entire contents of vial IM.
Intravenous Administration
- pH: 6.5–8.5.
- Intermittent Infusion: Only the IV formulation can be used for IV administration.Diluent: Reconstitute each 250- or 500-mg vial with 10 mL of D5W or 0.9% NaCl and shake well. Further dilute in 100 mL of D5W or 0.9% NaCl. Solution may range from clear to yellow in color. Infusion is stable for 4 hr at room temperature and 24 hr if refrigerated.Concentration: 2.5 mg/mL (with 250–mg vial); 5 mg/mL (with 500-mg vial).
- Rate: Infuse doses ≤500 mg over 20–30 min. Infuse doses ≥750 mg over 40–60 min. Pediatric: Infuse doses ≤500 mg over 15–30 min. Infuse doses >500 m g over 40–60 min.
- Rapid infusion may cause nausea and vomiting. If these symptoms develop, slow infusion.
- Y-Site Compatibility: acyclovir, alfentanil, amifostine, amikacin, aminocaproic acid, anidulafungin, argatroban, ascorbic acid, atracurium, atropine, benztropine, bivalirudin, bleomycin, bumetanide, buprenorphine, butorphanol, carboplatin, carmustine, caspofungin, cefazolin, cefepime, cefotaxime, cefoxitin, ceftazidime, cefuroxime, chloramphenicol, cisatracurium, clindamycin, cyanocobalamin, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, cytarabine, dactinomycin, dexamethasone sodium phosphate, dexmedetomidine, dexrazoxane, digoxin, diltiazem, diphenhydramine, docetaxel, dolasetron, dopamine, doxacurium, doxorubicin, doxorubicin liposomal, doxycycline, enalaprilat, ephedrine, epinephrine, epirubicin, epoetin, eptifibatide, erythromycin, esmolol, etoposide, famotidine, fenoldopam, fentanyl, fludarabine, fluorouracil, folic acid, foscarnet, furosemide, gentamicin, glycopyrrolate, granisetron, heparin, hydrocortisone sodium succinate, hydromorphone, idarubicin, ifosfamide, indomethacin, insulin, irinotecan, isoproterenol, ketorolac, labetalol, leucovorin, levofloxacin, lidocaine, linezolid, magnesium sulfate, melphalan, methotrexate, methylprednisolone sodium succinate, metoclopramide, metoprolol, metronidazole, mitoxantrone, morphine, multivitamins, nafcillin, naloxone, nesiritide, nitroglycerin, norepinephrine, octreotide, ondansetron, oxacillin, oxaliplatin, oxytocin, paclitaxel, pamidronate, pancuronium, pantoprazole, pemetrexed, penicillin G, pentobarbital, phentolamine, phenylephrine, phytonadione, potassium acetate, potassium chloride, propranolol, propofol, propranoplol, protamine, ranitidine, remifentanil, rituximab, rocuronium, sodium acetate, streptokinase, succinylcholine, sufentanil, tacrolimus, teniposide, theophylline, thiotepa, ticarcillin/clavulanate, tigecycline, tirofiban, tobramycin, tolazoline, trastuzumab, vasopressin, verapamil, vinblastine, vincristine, vinorelbine, voriconazole, zidovudine
- Y-Site Incompatibility: alemtuzumab, alopurinol, amiodarone, amphotericin B cholesteryl sulfate, amphotericin B lipid complex, amphotericin B liposome, azathioprine, ceftriaxone, chlorpromazine, dantrolene, daptomycin, diazepam, diazoxide, etoposide phosphate, galliun nitrate, ganciclovir, gemcitabine, haloperidol, lorazepam, mannitol, mechlorethamine, metaraminol, methyldopate, milrinone, mycophenolate, nalbuphine, nicardipine, palonosetron, phenytoin, prochlorperazine, pyridoxime, quinupristin/dalfopristin, sargramostim, sodium bicarbonate, thiamine, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, vecuronium
- Additive Incompatibility: May be inactivated if administered concurrently with aminoglycosides. If administered concurrently, administer in separate sites, if possible, at least 1 hr apart. If second site is unavailable, flush lines between medications.
Patient/Family Teaching
- Advise patient to report the signs of superinfection (black, furry overgrowth on the tongue; vaginal itching or discharge; loose or foul-smelling stools) and allergy. Consult health care professional before treating with antidiarrheals.
- Caution patient to notify health care professional if fever and diarrhea occur, especially if stool contains blood, pus, or mucus. Advise patient not to treat diarrhea without consulting health care professional. May occur up to several weeks after discontinuation of medication.
Evaluation/Desired Outcomes
- Resolution of the signs and symptoms of infection. Length of time for complete resolution depends on the organism and site of infection.
Primaxin
A brand name for CILASTATIN.Latest Searches:
Voraxaze - Voranil - Voorhoeve - voodoo - VOO - Vontrol - von - vomitus - vomiturition - vomitory - vomitoria - vomito - vomitive - vomiting - vomit - vomica - vomerovaginalis - vomerovaginal - vomerorostralis - vomerorostral -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp