Medical term:
Ultram
tramadol hydrochloride
Pharmacologic class: Opioid agonist
Therapeutic class: Analgesic
Pregnancy risk category C
Action
Inhibits reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine in CNS
Availability
Tablets: 50 mg
Tablets (extended-release): 100 mg, 200 mg, 300 mg
Tablets (orally disintegrating [ODT]): 50 mg
Indications and dosages
➣ Moderate to moderately severe pain in patients who require around-the-clock treatment of pain for an extended period
Adults: In rapid titration, 50 to 100 mg (immediate-release) P.O. q 4 to 6 hours p.r.n. (not to exceed 400 mg/day, or 300 mg/day in patients older than age 75). In gradual titration, initially 25 mg (immediate-release) P.O. daily; increase by 25 mg/day q 3 days to 100 mg/day, then increase by 50 mg/day q 3 days, up to 200 mg/day p.r.n. Alternately, 100 mg P.O (extended-release) up to a maximum of 300 mg daily. Titrate daily doses by 100-mg/day increments q 2 to 3 days (Ryzolt) or q 5 days (ConZip) to achieve a balance between adequate pain control and individual tolerability. Continue with lowest effective dose. Maximum dose is 300 mg/day. For patients on immediate-release product, calculate total 24-hour immediate-release dose and initiate at a dose rounded down to next lower 100-mg increment. Individualize dose according to patient need and tolerance, not to exceed 300 mg daily. Or, in patients not requiring rapid analgesic effect, tolerability can be improved by initiating therapy with a titration regimen. Total daily dose may be increased by 50 mg (ODT tablets) P.O. as tolerated q 3 days to reach 200 mg/day (50 mg q.i.d.). After titration, 50 to 100 mg (ODT tablets) P.O. can be administered as needed for pain relief q 4 to 6 hours, not to exceed 400 mg/day.
Dosage adjustment
• Renal or hepatic impairment
Contraindications
• Hypersensitivity to drug, its components, or opioids
• Acute intoxication with alcohol, sedative-hypnotics, centrally acting analgesics, opioid analgesics, or psychotropic agents
• Physical opioid dependence
• Significant respiratory depression, acute or severe bronchial asthma or hypercapnia in unmonitored settings or absence of resuscitative equipment
Precautions
Use cautiously in:
• seizure disorder or risk factors for seizures, increased intracranial pressure, head trauma, acute abdomen, patients at risk for respiratory depression, patients who use alcohol in excess, patients who suffer from emotional disturbance or depression, patients receiving CNS depressants, other opioids, anesthetics, tranquilizers, or sedative-hypnotics
• mild to severe hepatic impairment, and renal impairment with creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/minute
• history of sensitivity to phenylketones (avoid ODT use)
• history of opioid dependence or recent use of large opioid doses or patients who are suicidal or addiction-prone (use not recommended)
• concurrent use of monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors (use with great caution)
• elderly patients
• pregnant or breastfeeding patients
• children younger than age 16 or 18 (ConZip) (safety not established, use not recommended).
Administration
• Give as prescribed, preferably before pain becomes severe.
Be aware that serious and rarely fatal anaphylactoid reactions have occurred, often following first dose.
Adverse reactions
CNS: dizziness, vertigo, headache, drowsiness, anxiety, stimulation, confusion, incoordination, euphoria, nervousness, sleep disorder, asthenia, hypertonia, seizures, suicide
CV: vasodilation
EENT: visual disturbances
GI: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, flatulence, dry mouth, anorexia
GU: urinary retention and frequency, proteinuria, menopausal symptoms
Respiratory: respiratory depression (with large doses, concomitant anesthetic use, or alcohol ingestion), bronchospasm
Skin: pruritus, sweating, hives, angioedema, toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Other: physical or psychological drug dependence, drug tolerance, serotonin syndrome, serious and rarely fatal anaphylactoid reactions
Interactions
Drug-drug. Anesthetics, antihistamines, CNS depressants, other opioids, psychotropic agents, sedative-hypnotics: increased risk of CNS depression
Carbamazepine: increased tramadol metabolism and decreased efficacy
Serotonergic drugs (including MAO inhibitors, selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants, triptans), drugs that impair serotonin metabolism (including MAO inhibitors), drugs that impair tramadol metabolism (such as CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 inhibitors): increased risk of serotonin syndrome and seizures
Drug-diagnostic tests. Creatinine, hepatic enzymes: increased levels
Hemoglobin: decreased level
Drug-herbs. Chamomile, hops, kava, skullcap, valerian: increased CNS depression
Drug-behaviors. Alcohol use: increased CNS depression
Patient monitoring
• Assess patient's response to drug 30 minutes after administration.
• Monitor respiratory status. Withhold drug and contact prescriber if respirations become shallow or slower than 12 breaths/minute.
• Monitor for physical and psychological drug dependence. Report signs to prescriber.
Monitor patient for signs and symptoms of potentially life-threatening serotonin syndrome, which may range from shivering and diarrhea to muscle rigidity, fever, mental-status changes, and seizures.
Patient teaching
• Tell patient drug works best when taken before pain becomes severe.
• Tell patient to take extended-release tablets with or without food, to swallow them whole at same time each day with a sufficient quantity of liquid, and not to split, chew, dissolve, or crush them.
• Instruct patient to open ODT tablet blister pack and to peel back the foil on the blister; caution patient not to push tablet through foil. Instruct patient to remove a tablet and place it in the mouth, where it will dissolve in seconds and then be swallowed with saliva. Tell patient not to chew, break, or split tablet. Inform patient who has phenylketonuria that ODT tablet contains phenylalanine.
• Inform patient (and significant other as appropriate) that drug may cause respiratory depression if used with alcohol. Recommend abstinence.
Instruct patient to immediately report seizure, suicidal behavior, or suicidal ideation.
Instruct patient to watch for and immediately report signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome (shivering and diarrhea, muscle rigidity, fever, and seizures).
Tell patient to immediately report sign and symptoms of allergic reaction (such as itching, hives, difficulty breathing, or swelling of face, tongue, or throat).
• Tell patient drug interacts with many common over-the-counter drugs and herbal remedies. Instruct him to consult prescriber before taking these products.
• Inform patient that drug can cause physical and psychological dependence. Urge him to take it only as prescribed and needed.
• Caution patient to avoid driving and other hazardous activities until he knows how drug affects concentration and alertness.
• Caution patient to avoid alcohol use while taking this drug.
• As appropriate, review all other significant and life-threatening adverse reactions and interactions, especially those related to the drugs, tests, herbs, and behaviors mentioned above.
traMADol
(tra-ma-dol) ,Conzip
(trade name),Durela
(trade name),Ralivia
(trade name),Tridural
(trade name),Ultram
(trade name),Ultram ER
(trade name),Zytram XL
(trade name)Classification
Therapeutic: analgesicsIndications
Action
Therapeutic effects
Pharmacokinetics
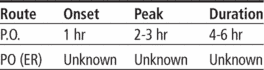
Time/action profile (analgesia)
| ROUTE | ONSET | PEAK | DURATION |
|---|---|---|---|
| PO | 1 hr | 2–3 hr | 4–6 hr |
| ER | unknown | 12 hr | 24 hr |
Contraindications/Precautions
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Central nervous system
- seizures (life-threatening)
- dizziness (most frequent)
- headache (most frequent)
- somnolence (most frequent)
- anxiety
- CNS stimulation
- confusion
- coordination disturbance
- euphoria
- malaise
- nervousness
- sleep disorder
- weakness
Ear, Eye, Nose, Throat
- visual disturbances
Cardiovascular
- vasodilation
Gastrointestinal
- constipation (most frequent)
- nausea (most frequent)
- abdominal pain
- anorexia
- diarrhea
- dry mouth
- dyspepsia
- flatulence
- vomiting
Genitourinary
- menopausal symptoms
- urinary retention/frequency
Dermatologic
- pruritus
- sweating
Neurologic
- hypertonia
Miscellaneous
- serotonin syndrome (life-threatening)
- physical dependence
- psychological dependence
- tolerance
Interactions
Drug-Drug interaction
↑ risk of CNS depression when used concurrently with other CNS depressants, including alcohol, antihistamines, sedative/hypnotics, opioid analgesics, anesthetics, or psychotropic agents.↑ risk of seizures with high doses of penicillins, cephalosporins, phenothiazines, opioid analgesics, or antidepressants.Carbamazepine ↑ metabolism and ↓ effectiveness of tramadol (increased doses may be required).Use cautiously in patients who are receiving MAO inhibitors (↑ risk of adverse reactions).Quinidine, fluoxetine, paroxetine, amitriptyline, ketoconazole, and erythromycin may ↑ levels.↑ risk of serotonin syndrome when used with SSRI and SNRI antidepressants, TCAs, MAO inhibitors, 5HT1 agonists, CYP2D6 inhibitors, and CYP3A4 inhibitors.Concomitant use of kava-kava, valerian, or chamomile can ↑ CNS depression.↑ risk of serotonin syndrome when used with St. Johns' wort.Route/Dosage
Immediate-releaseRenal Impairment
Oral (Adults) CCr <30 mL/min—↑ dosing interval to q 12 hr (not to exceed 200 mg/day).Hepatic Impairment
Oral (Adults) 50 mg q 12 hr.Availability (generic available)
Nursing implications
Nursing assessment
- Assess type, location, and intensity of pain before and 2–3 hr (peak) after administration.
- Assess BP and respiratory rate before and periodically during administration. Respiratory depression has not occurred with recommended doses.
- Assess bowel function routinely. Prevention of constipation should be instituted with increased intake of fluids and bulk and with laxatives to minimize constipating effects.
- Assess previous analgesic history. Tramadol is not recommended for patients dependent on opioids or who have previously received opioids for more than 1 wk; may cause opioid withdrawal symptoms.
- Prolonged use may lead to physical and psychological dependence and tolerance, although these may be milder than with opioids. This should not prevent patient from receiving adequate analgesia. Most patients who receive tramadol for pain do not develop psychological dependence. If tolerance develops, changing to an opioid agonist may be required to relieve pain.
- Monitor patient for seizures. May occur within recommended dose range. Risk is increased with higher doses and in patients taking antidepressants (SSRIs, SNRIs, tricyclics, or MAO inhibitors), opioid analgesics, or other drugs that decrease the seizure threshold. Also monitor for serotonin syndrome (mental-status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile BP, hyperthermia), neuromuscular aberrations (e.g., hyperreflexia, incoordination) and/or gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea) in patients taking these drugs concurrently.
- Lab Test Considerations: May cause ↑ serum creatinine, ↑ liver enzymes, ↓ hemoglobin, and proteinuria. Overdose may cause respiratory depression and seizures. Naloxone may reverse some, but not all, of the symptoms of overdose. Treatment should be symptomatic and supportive. Maintain adequate respiratory exchange. Hemodialysis is not helpful because it removes only a small portion of administered dose. Seizures may be managed with barbiturates or benzodiazepines; naloxone increases risk of seizures.
Potential Nursing Diagnoses
Acute pain (Indications)Risk for injury (Side Effects)
Implementation
- Do not confuse tramadol with trazodone.
- Tramadol is considered to provide more analgesia than codeine 60 mg but less than combined aspirin 650 mg/codeine 60 mg for acute postoperative pain.
- For chronic pain, daily doses of 250 mg of tramadol provide pain relief similar to that of 5 doses/day of acetaminophen 300 mg/codeine 30 mg, 5 doses/day of aspirin 325 mg/codeine 30 mg, or 2–3 doses/day of acetaminophen 500 mg/oxycodone 5 mg.
- Explain therapeutic value of medication before administration to enhance the analgesic effect.
- Regularly administered doses may be more effective than prn administration. Analgesic is more effective if given before pain becomes severe.
- Tramadol should be discontinued gradually after long-term use to prevent withdrawal symptoms.
- Oral: Tramadol may be administered without regard to meals. Swallow extended-release tablets and capsules whole; do not crush, break, dissolve, or chew .
Patient/Family Teaching
- Instruct patient on how and when to ask for pain medication.
- May cause dizziness and drowsiness. Caution patient to avoid driving or other activities requiring alertness until response to medication is known.
- Advise patient to change positions slowly to minimize orthostatic hypotension.
- Caution patient to avoid concurrent use of alcohol or other CNS depressants with this medication. Advise patient to notify health care professional before taking other RX, OTC, or herbal products concurrently.
- Advise patient to notify health care professional if seizures or if symptoms of serotonin syndrome occur.
- Encourage patient to turn, cough, and breathe deeply every 2 hr to prevent atelectasis.
- Advise female patients to notify health care professional if pregnancy is planned or suspected, or if breast feeding.
Evaluation/Desired Outcomes
- Decrease in severity of pain without a significant alteration in level of consciousness or respiratory status.
Ultram
(ŭl′trăm′)Latest Searches:
Voraxaze - Voranil - Voorhoeve - voodoo - VOO - Vontrol - von - vomitus - vomiturition - vomitory - vomitoria - vomito - vomitive - vomiting - vomit - vomica - vomerovaginalis - vomerovaginal - vomerorostralis - vomerorostral -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp