Medical term:
Zipsor
diclofenac epolamine
diclofenac potassium
diclofenac sodium
Pharmacologic class: Cyclooxygenase inhibitor, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)
Therapeutic class: Nonopioid analgesic, antiarthritic
Pregnancy risk category C
FDA Box Warning
• Drug may increase risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, myocardial infarction, and stroke. Risk may increase with duration of use. Patients with cardiovascular disease or risk factors for it may be at greater risk.
• Drug increases risk of serious GI adverse events, including bleeding, ulcers, and stomach or intestinal perforation. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning. Elderly patients are at greater risk.
• Drug is contraindicated for treatment of perioperative pain in setting of coronary artery bypass graft surgery.
Action
Unclear. Thought to block activity of cyclooxygenase, thereby inhibiting inflammatory responses of vasodilation and swelling and blocking transmission of painful stimuli.
Availability
diclofenac epolamine
Flector patch: 1.3%
diclofenac potassium
Capsules, liquid-filled: 25 mg
Powder for oral solution: 50 mg
Tablets: 50 mg
diclofenac sodium
Tablets (delayed-release): 25 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg
Tablets (extended-release): 100 mg
Topical gel: 1%
Topical solution: 1.5%
Indications and dosages
➣ Acute migraine attacks
Adults: 50 mg P.O. (oral powder)
➣ Osteoarthritis pain of joints amenable to topical treatment
Adults: 2 g for each elbow, wrist, or hand; 4 g for each knee, ankle, or foot q.i.d. Maximum, 16 g daily to any single joint of lower extremities; maximum, 8 g daily to any single joint of upper extremities. Don't exceed 32 g/day over all affected joints.
➣ Osteoarthritis of knee
Adults: 40 drops on each painful knee q.i.d.
➣ Acute pain due to minor strains, sprains, and contusions (topical treatment)
Adults: One patch to most painful area b.i.d. Use lowest effective dosage for shortest duration consistent with individual patient's treatment goals.
➣ Analgesia; dysmenorrhea
Adults: Initially, 100 mg P.O., then 50 mg t.i.d. as needed
➣ Rheumatoid arthritis
Adults: Initially, 50 mg P.O. three to four times daily. After initial response, reduce to lowest dosage that controls symptoms. Usual maintenance dosage is 25 mg t.i.d.
➣ Osteoarthritis
Adults: Initially, 50 mg P.O. two to three times daily. After initial response, reduce to lowest dosage that controls symptoms.
➣ Ankylosing spondylitis
Adults: 25 mg P.O. four to five times daily. After initial response, reduce to lowest dosage that controls symptoms.
Dosage adjustment
• Renal impairment
• Elderly patients
Off-label uses
• Post-radial keratotomy symptoms
• Dental pain
Contraindications
• Hypersensitivity to drug or its components, other NSAIDs, or aspirin
• Active GI bleeding or ulcer disease
• Aspirin-sensitive asthma, urticaria
• Use as perioperative analgesia in coronary artery bypass graft surgery
• Use on nonintact or damaged skin (patch)
Precautions
Use cautiously in:
• severe cardiovascular (including patients taking diuretics or ACE inhibitors, patients with fluid retention, hypertension, or congestive heart failure), renal, or hepatic disease; bleeding tendency; dehydration
• advanced renal disease (not recommended)
• history of porphyria or preexisting asthma
• concurrent methotrexate or anticoagulant use; concurrent use of drugs known to be potentially hepatotoxic (such as acetaminophen, anti-infectives, or antiepileptics)
• concurrent use of aspirin (not recommended)
• concurrent use with oral NSAIDs (avoid use)
• elderly patients
• pregnant or breastfeeding patients
• children (safety and efficacy not established).
Administration
• Give on empty stomach 1 hour before or after a meal.
• If drug causes GI upset, give with milk or meals. Mix and give oral powder with 30 to 60 ml of water only.
• Make sure patient swallows extended-release and delayed-release forms whole without chewing or crushing.
• Know that oral powder isn't indicated for prophylactic migraine therapy or cluster headaches.
• Know that oral powder formulation isn't interchangeable with other oral forms.
• Don't apply patch to damaged or nonintact skin.
☞ Avoid contact of patch with eyes and mucosa. If eye contact occurs, immediately wash eyes with water or saline solution
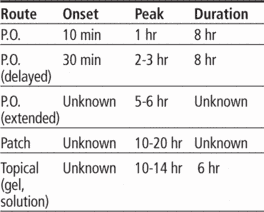
Adverse reactions
CNS: dizziness, drowsiness, headache, paresthesia
CV: hypertension, thrombosis
EENT: tinnitus
GI: dyspepsia, diarrhea, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, heartburn, peptic ulcer, GI bleeding, GI perforation
GU: dysuria, frequent urination, hematuria, proteinuria, nephritis, acute renal failure
Hepatic: liver failure
Hematologic: prolonged bleeding time
Hepatic: hepatotoxicity
Skin: eczema, photosensitivity, rash, contact dermatitis, dry skin, exfoliation; application-site reactions, including pruritus, dermatitis, burning (with patch); exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis
Other: dysgeusia, pain and redness allergic reactions (including edema), anaphylaxis
Interactions
Drug-drug. Anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, cephalosporins, plicamycin, thrombolytics: increased risk of bleeding
Antihypertensives, diuretics: decreased efficacy of these drugs
Antineoplastics: increased risk of hematologic adverse reactions
Aspirin: increased adverse reactions
Colchicine, corticosteroids, other NSAIDs: additive adverse GI effects
Cyclosporine, probenecid: increased risk of diclofenac toxicity
Digoxin, lithium, methotrexate, phenytoin, theophylline: increased levels of these drugs, greater risk of toxicity
Diuretics (furosemide, thiazides): reduced natriuretic effect of these drugs
Potassium-sparing diuretics: increased risk of hyperkalemia
Voriconazole: increased diclofenac Cmax and area under the curve
Drug-diagnostic tests. Alanine aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, aspartate aminotransferase, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, electrolytes, lactate dehydrogenase, urine uric acid: increased values
Bleeding time: prolonged
Hematocrit, hemoglobin, platelets, serum uric acid, urine electrolytes, white blood cells: decreased values
Drug-herbs. Anise, arnica, chamomile, clove, dong quai, fenugreek, feverfew, garlic, ginger, ginkgo, ginseng, and others: increased risk of bleeding
Drug-behaviors. Alcohol use: increased risk of adverse GI effects
Patient monitoring
• Monitor hepatic and renal function.
• Observe for and report signs and symptoms of bleeding.
• Assess for hypertension.
• Monitor sodium and potassium levels in patients receiving potassium-sparing diuretics.
☞ Discontinue drug if rash or other signs of local skin reaction occur.
☞ Discontinue drug immediately if abnormal liver test values persist or worsen.
• Weigh patient to detect fluid retention. Report gain of more than 2 lb in 24 hours.
Patient teaching
• Instruct patient to take drug on empty stomach 1 hour before or after a meal.
• Advise patient not to lie down for 15 to 30 minutes after taking oral drug, to minimize esophageal irritation.
• Instruct patient to mix oral powder in 1 to 2 ounces of water only before taking.
• Tell patient to measure proper amount of gel using measuring dosing card supplied and to gently massage gel into skin of entire affected foot, knee, or ankle.
• Instruct patient to apply 10 drops of topical solution to clean, dry skin and to spread evenly around front, back, and sides of knee; then repeat this procedure until 40 drops have been applied and knee is completely covered with solution.
• Instruct patient not to apply gel, patch, or topical solution to open wounds and to avoid contact with eyes and mucous membranes.
• Advise patient to avoid exposing treated sites to bath water and sunlight, external heat, occlusive dressings or clothing, sunscreens, cosmetics, lotions, moisturizers, insect repellants, or other topical drugs.
• Instruct patient to wash hands thoroughly after applying topical solution, patch, or gel except when gel is applied to the hand. If gel is applied to a hand, advise patient to avoid washing treated hands for at least 1 hour after application.
• Tell patient to discard used patches out of the reach of children and pets.
☞ Instruct patient to stop drug and immediately report wheezing and signs or symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions (rash, swelling of face or throat, shortness of breath) or liver impairment (unusual tiredness, weakness, nausea, yellowing of skin or eyes, tenderness on right upper side of abdomen, flulike symptoms).
☞ Instruct patient to stop taking drug and contact prescriber promptly if he experiences ringing or buzzing in ears, dizziness, GI discomfort, or bleeding.
☞ Inform patient that drug may cause serious CV side effects and to immediately report such signs and symptoms as unexplained weight gain, chest pain, shortness of breath, weakness, or slurred speech.
• Caution patient not to take over-the-counter analgesics during diclofenac therapy.
• Advise female patient to avoid pregnancy while taking this drug.
• Advise breastfeeding patient that she should decide whether to discontinue breastfeeding or discontinue drug, taking into account importance of drug for her treatment.
• As appropriate, review all other significant and life-threatening adverse reactions and interactions, especially those related to the drugs, tests, herbs, and behaviors mentioned above.
Latest Searches:
Voraxaze - Voranil - Voorhoeve - voodoo - VOO - Vontrol - von - vomitus - vomiturition - vomitory - vomitoria - vomito - vomitive - vomiting - vomit - vomica - vomerovaginalis - vomerovaginal - vomerorostralis - vomerorostral -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp