bandage
[ban´dij] 1. a strip or roll of gauze or other material for wrapping or binding any part of the body.
2. to cover by wrapping with such material. Bandages may be used to stop the flow of blood, absorb drainage, cushion the injured area, provide a safeguard against contamination, hold a medicated dressing in place, hold a splint in position, or otherwise immobilize an injured part of the body to prevent further injury and to facilitate healing.
Application of Bandages. In applying a bandage: (1) If the skin is broken a sterile pad or several thicknesses of sterile gauze should be placed over the wound before tape or bandaging material is applied over the pad to hold it in place. Adhesive tape is never applied directly on a wound. (2) The bandage should not be made so tight that it interferes with circulation. A pressure bandage should be applied only for the purpose of arresting hemorrhage. (3) A bandage does not have to look good to be effective; in an emergency, that the bandage serves its purpose is more important than its appearance.
Ace bandage trademark for a bandage of woven elastic material.
adhesive bandage a sterile compress of layers of gauze or other material, affixed to a fabric or film coated with a pressure-sensitive adhesive.
cravat bandage one made by bringing the point of a triangular bandage to the middle of the base and then folding lengthwise to the desired width.
demigauntlet bandage one that covers the hand, but leaves the fingers uncovered.
Esmarch's bandage a rubber bandage applied upward around a part (from the distal to the proximal part) to expel blood from it; the part is often elevated as the elastic pressure is applied. This is often used in conjunction with a pneumatic tourniquet. Called also Martin bandage.
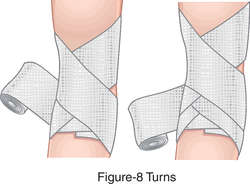
figure-of-eight bandage one in which the turns cross each other like the figure 8.
gauntlet bandage one that covers the hands and fingers like a glove.
Martin bandage Esmarch's bandage.
plaster bandage a bandage stiffened with a paste of plaster of Paris.
pressure bandage one for applying pressure, for the purpose of arresting hemorrhage; pressure is applied directly over the wound.
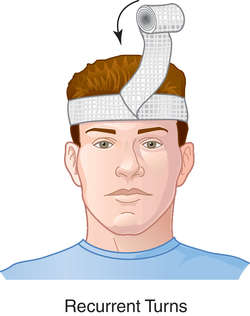
recurrent bandage one used on a distal stump, such as that of a finger, toe, or limb, turned lengthwise to cover the end of the stump and secured in place by circular turns.
roller bandage a tightly rolled, circular bandage of varying widths and materials, often prepared commercially. In an emergency, strips may be torn from a sheet or piece of yard goods and rolled. When more than a few inches of length is needed, rolling is essential for quick and clean bandaging.
Scultetus bandage a large rectangular cloth bandage whose ends are split into many tails; the tails overlap each other and are tied or pinned across a compress covering the bandaged area, usually the abdomen.
spiral bandage a roller bandage applied spirally around a limb.
tailed bandage a square piece of cloth cut or torn into strips from the ends toward the center, with as large a center left as necessary. The bandage is centered over a compress on the wound and the ends are then tied separately. A four-tailed bandage is useful for wounds of the nose and chin.
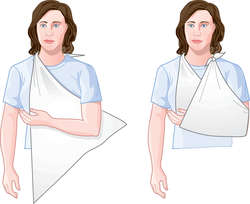
triangular bandage one made by folding or cutting a large square of cloth diagonally. It may form a sling for an injured arm, or can be folded several times into a cravat of any desired width.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
bandage
(ban'daj) 1. A piece of soft, usually absorbent gauze or other material applied to a limb or other part of the body as a dressing.

APPLYING BANDAGES

APPLYING BANDAGES

APPLYING BANDAGES

APPLYING BANDAGES

APPLYING BANDAGES
2. To cover by wrapping with a piece of gauze or other material.
Bandages are used to hold dressings in place, apply pressure to a part, immobilize a part, obliterate cavities, support an injured area, and check hemorrhages. Types of bandages include roller, triangular, four-tailed, many-tailed (Scultetus), quadrangular, elastic (elastic knit, rubber, synthetic, or combinations of these), adhesive, elastic adhesive, newer cohesive bandages under various proprietary names, impregnated bandages (plaster of Paris, waterglass [silica], starch), and stockinet. Use of a self-adhering, form-fitting roller bandage facilitates bandaging by eliminating the special techniques needed when ordinary gauze roller bandages are used. See: illustration; sling
CAUTION!
Skin-to-skin contact will, if continuous, cause ulceration or infection.
abdomenal bandage
A single wide cravat or several narrow ones used to hold a dressing in place or to exert moderate pressure.
adhesive bandage
A bandage made of adhesive tape.
amputation-stump bandage
An elastic bandage applied to an amputation stump to control postoperative edema and to shape the stump. The elastic bandage is applied in a recurrent or figure-of-eight fashion with more pressure applied to the distal, rather than the proximal, portion of the limb.
ankle bandage
A bandage in which one loop is brought around the sole of foot and the other around the ankle and is secured in front or on the side.
axilla bandage
A bandage with a spica-type turn starting under the affected axilla, crossing over the shoulder of the affected side, and making the long loop under the opposite armpit.
back bandage
An open bandage to the back, applied like a chest bandage, the point placed above the scapula of the injured side.
Barton bandage
See: Barton bandagebreast bandage
A suspensory bandage and compress for the breasts.
butterfly bandage
An adhesive bandage used in place of sutures to hold wound edges together. Filmy sterile adhesive strips have replaced the butterfly bandage.
buttocks bandage
T bandage.capeline bandage
A bandage applied to the head or shoulder or to a stump like a cap or hood.
chest bandage
A bandage applied to the chest, e.g., figure of eight (spica).
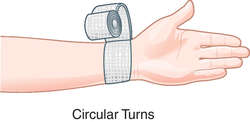
circular bandage
A bandage applied in circular turns about a part.
See: Bandaging with Circular and Spiral Turnscohesive bandage
A bandage made of material that sticks to itself but not to other substances, used to bandage fingers and extremities or to build up pads.
cravat bandage
A triangular bandage folded to form a band around an injured part.
cravat bandage for clenched fist
A hand bandage to arrest bleeding or to produce pressure. The wrist is placed on the center of the cravat; one end is brought around over the fist and back to the starting point, and the same procedure is then repeated with the other end. The two ends are pulled tight, twisted, and carried around the fist again so that pressure is placed on the flexed fingers.
cravat elbow bandage
A bandage in which the elbow is bent about 45° and the center of the bandage is placed over the point of the elbow. One end is brought around the forearm and the other end around the upper arm; the bandage is pulled tight and tied. See: sling
cravat bandage for fracture of clavicle
A bandage in which one first puts a soft pad 2 × 4 in (5.1 × 10.2 cm) in the forepart of the axilla. A sling is made by placing the point of the open bandage on the affected shoulder; the hand and wrist are laid on it and directed toward the opposite shoulder, and the point is brought over and tucked underneath the wrist and hand. The ends are then lifted; the bandage is laid flat on the chest; the covered hand is carried up on the shoulder; the ends are brought together in the back and tied, the tightness being decided by how high the shoulder should be carried. A cravat bandage is then applied horizontally above the broad part of the elbow and tied over a pad on the opposite side of the chest. Tightening this cravat retracts the shoulders and scapulae.
crucial bandage
See: T bandagedemigauntlet bandage
A bandage that covers the hand but leaves the fingers uncovered.
ear bandage
A T bandage for the ear. A piece is sewn across the right angle of the T bandage.
elastic bandage
A bandage that can be stretched to exert continuous pressure. It usually is made of special weaves or of material containing rubber and is used on swollen extremities or joints, on the chest in empyema, on fractured ribs, or on the legs to support varicose veins.
Esmarch bandage
See: Esmarch bandageeye bandage
A bandage for retaining dressings. The simple roller bandage for one eye or the monocle or crossed bandage. The binocular or crossed bandage for both eyes is 2 in × 6 yd (5.1 cm × 5.49 m).
figure-of-eight bandage
A bandage in which the turns cross each other like the figure eight, used to retain dressings, to exert pressure for joints (or to leave the joint uncovered), to fix splints for the foot or hand, for the great toe, and for sprains or hemorrhage.
See: Apply Bandages: Figure 8finger bandage
A roller bandage with oblique fixation at the wrist.
foot bandage
A triangular bandage in which the foot is placed on the triangle with the base of the bandage backward and behind the ankle, and the apex carried upward over the top of the foot. The ends are brought forward, folded once or twice, crossed and carried around the foot, and tied on top.
forearm bandage
A triangular open sling bandage for support of the forearm.
four-tailed bandage
A strip of cloth with each end split into two. The tails are used to cover prominences such as elbow, chin, nose, or knee.
Fricke bandage
See: Fricke bandagegroin bandage
A bandage that is most easily applied with the patient standing or lying on a pelvic rest. A spica bandage encircles the trunk and the crossing is placed either anteriorly or laterally. To bandage both groins, the double spica is used. Such a double bandage is used principally in applying a plaster cast.
hand bandage
A demigauntlet bandage that secures a dressing on the back of the hand. For thumb and hand, the ascending spica of the thumb, with spiral of the hand, is used. A triangular bandage is used for an open bandage of the hand. A descending spica is used for the thumb and figure-of-eight bandage for an amputation stump or clenched fist.
head bandage
Any bandage applied to the head, usually by wrap-around technique, that uses bony prominences as anchors or stays, and that carefully and completely covers the site of injury or the suture line.
heel bandage
A triangular bandage used for the heel.
hip bandage
A triangular open bandage of the hip. A cravat bandage or other band is tied around the waist; the point of another bandage is slipped under and rolled or pinned directly above the position of the wound. The base is rolled up and the ends are carried around the thigh, crossed, and tied.
immobilization bandage
, immovable bandageA bandage for immobilizing a part.
impregnated bandage
A wide-meshed bandage used to make molds or immobilize parts of the body. The material is impregnated with a substance such as plaster of Paris, which is applied wet and hardens after drying.
knee bandage
A knee cravat in which triangular and the figure-of-eight bandages are used.
leg bandage
A bandage applied by fixing the initial end by a circular or oblique fixation at the ankle or with a figure-of-eight of the foot and ankle.
many-tailed bandage
A bandage with split ends used for the trunk and limbs; a piece of roller to which slips are stitched in an imbricated fashion.
See: four-tailed bandage; Scultetus, JohannesMartin bandage
See: Martis bandageneck bandage
Neck spica: Bandage 2 1 2 in × 8 yd (6.4 cm × 7.3 m). Bandage following thyroid gland surgery: Roller bandage 2 1 2 in × 9 yd (6.4 cm × 8.2 m). Adhesive plaster bandage for thyroidectomy: Used to hold dressing on wound in place. A small dressing is applied to center of strip and then applied to back of neck. Special bandage: A double-loop bandage of the head and neck made by using a figure-of-eight turn.
oblique bandage
A bandage applied obliquely to a limb, without reverses.
plaster bandage
A bandage stiffened with a paste of plaster of Paris, which sets and becomes very hard.
See: cast (4)pressure bandage
A bandage for applying pressure, usually used to stop hemorrhage or prevent edema.
protective bandage
A bandage that covers a part or keeps dressings in place.
quadrangular bandage
A towel or large handkerchief, folded variously and applied as a bandage of head, chest, breast, or abdomen.
recurrent bandage
A bandage over the end of a stump.
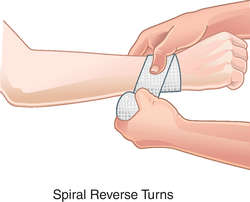
reversed bandage
A bandage applied to a limb in such a way that the roller is inverted or half twisted at each turn so as to make it fit smoothly and resist slipping off the limb. See: spiral reverse bandage
roller bandage
A long strip of soft material, usually from 1 2 to 6 in (1.3 to 15.2 cm) wide and 2 to 5 yd (1.83 to 4.57 m) long, rolled on its short axis. When rolled from both ends to meet at the center, it is called a double-headed roller.
rubber bandage
A rubber roller bandage used to apply pressure to prevent swelling or hemorrhage of a limb. See: Esmarch bandage
Scultetus bandage
See: Scultetus, Johannesshoulder bandage
An open bandage of the shoulder (spica bandage); a shawl bandage of both shoulders and neck.
smart bandage
A removable wireless monitor that attaches to a patient and monitors blood pressure, cardiac rhythm, pulse, respiratory rate, and volume status.
spica bandage
A bandage in which a number of figure-of-eight turns are applied, each a little higher or lower, overlapping a portion of each preceding turn so as to give an imbricated appearance. This type of bandage is used to support, to exert pressure, or to retain dressings on the breast, shoulder, limbs, thumb, great toe, and hernia at the groin.
See: basic thumb spicaspiral bandage
A roller bandage to be applied spirally.
spiral reverse bandage
A technique of twisting, in its long axis, a roller bandage on itself at intervals during application to make it fit more uniformly. These reverse folds may be necessary every turn or less often, depending on the contour of the part being bandaged.
stellate bandage
A bandage that is wrapped crosswise on the back.
suspensory bandage
A bandage for supporting any part but esp. the breast or scrotum.
T bandage
A bandage shaped like the letter T and used for the female perineum and, in certain cases, the head.
Synonym: buttocks bandage; T bindertailed bandage
A bandage split at the end.
triangular bandage
A square bandage folded diagonally. When folded, the several thicknesses can be applied to afford support.
Velpeau bandage
See: Velpeau, Alfred See: closed basket weaveMedical Dictionary, © 2009 Farlex and Partners




