Medical term:
bowlegs
genu
[je´nu] (pl. ge´nua) (L.)knee.
genu extror´sum genu varum.
genu intror´sum genu valgum.
genu recurva´tum hyperextensibility of the knee joint.
genu val´gum a childhood deformity, developing gradually, in which the knees rub together or “knock” in walking and the ankles are far apart; the most common causes are irregularity in growth of the long bones of the lower limb (sometimes from injury to the bone ends at the knee) and weak ligaments. The weight of the body, which is not supported properly, turns the knees in and the weak lower legs buckle until the ankles are spread far apart. See illustration. Called also knock-knee.
Genu valgum in young children varies in seriousness. Milder cases may disappear after early childhood as bones, ligaments, and muscles strengthen and coordination improves. More serious cases can often be corrected by strengthening exercises and by proper manipulation of the joints. Sometimes braces are used to ensure the proper alignment of growing legs. In a very young child, genu valgum involves only the soft bone ends where the bone grows. If allowed to continue for a number of years, the condition can lead to abnormal developments in body structure. The sooner corrective measures are taken, the more effective the treatment is likely to be.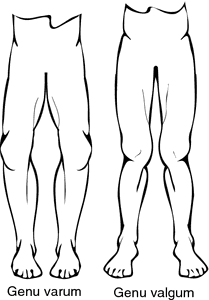
Genu valgum in young children varies in seriousness. Milder cases may disappear after early childhood as bones, ligaments, and muscles strengthen and coordination improves. More serious cases can often be corrected by strengthening exercises and by proper manipulation of the joints. Sometimes braces are used to ensure the proper alignment of growing legs. In a very young child, genu valgum involves only the soft bone ends where the bone grows. If allowed to continue for a number of years, the condition can lead to abnormal developments in body structure. The sooner corrective measures are taken, the more effective the treatment is likely to be.

Genu varum and genu valgum. From Copstead and Banasik, 2000.
genu va´rum an outward curvature of one or both lower limbs near the knee; see illustration. Called also bowleg.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
ge·nu va·'rum
a deformity marked by medial angulation of the leg in relation to the thigh; an outward bowing of the legs.
Synonym(s): bandy-leg, bowleg, bow-leg, tibia vara
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
bowleg
External deviation of the knee(s). A certain degree is normally present in infants, and corrects itself with bipedal ambulation; when excessive, rickets should be excluded, as vitamin D-induced osteomalacia may lead to bending of the femoral shaft bearing the mechanical brunt of ambulatory kinetics. When combined with anterior curvature of the tibia and fibula, affected children have a “saddle-sore” stance. Anterior or antero-lateral bowing of the tibia may occur in neurofibromatosis with fractures, and may be complicated by pseudoarthrosis .Segen's Medical Dictionary. © 2012 Farlex, Inc. All rights reserved.
bowleg
Genu varum Orthopedics External deviation of the knee(s); a certain degree is normally present in infants, and corrects itself with bipedal ambulation; when excessive, rickets is considered–vitamin D-induced osteomalacia allows bending of the femoral shaft bearing the mechanical brunt of ambulatory kinetics; when combined with anterior curvature of the tibia and fibula, the children have a 'saddle-sore' stance; anterior or antero-lateral bowing of the tibia may occur in neurofibromatosis with fractures, which may be complicated by pseudoarthrosisMcGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine. © 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
ge·nu va·rum
(jē'nyū vā'rŭm)A deformity marked by medial angulation of the leg in relation to the thigh; an outward bowing of the lower limbs.
Synonym(s): bowleg, bow-leg, tibia vara.
Synonym(s): bowleg, bow-leg, tibia vara.
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
Latest Searches:
Voraxaze - Voranil - Voorhoeve - voodoo - VOO - Vontrol - von - vomitus - vomiturition - vomitory - vomitoria - vomito - vomitive - vomiting - vomit - vomica - vomerovaginalis - vomerovaginal - vomerorostralis - vomerorostral -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp