catheter
[kath´ĕ-ter] a tubular, flexible instrument, passed through body channels for withdrawal of fluids from (or introduction of fluids into) a body cavity.
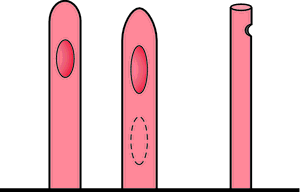
Straight catheters. May have one or two eyes, a round tip, or a “whistle” tip. These catheters are not self-retaining.
acorn-tipped catheter one used in ureteropyelography to occlude the ureteral orifice and prevent backflow from the ureter during and following the injection of an opaque medium.
Amplatz coronary catheter a J-shaped angiographic catheter used as an alternative to a Judkins coronary catheter in coronary arteriography.
angiographic catheter one through which a contrast medium is injected for visualization of the vascular system of an organ. Such catheters may have preformed ends to facilitate selective locating (as in a renal or coronary vessel) from a remote entry site. They may be named according to the site of entry and destination, such as femoral-renal and brachial-coronary.
arterial catheter one inserted into an artery, used as part of a catheter-transducer-monitor system to continuously observe the blood pressure of critically ill patients. An arterial catheter also may be inserted for x-ray studies of the arterial system and for delivery of chemotherapeutic agents directly into the arterial supply of malignant tumors.
atherectomy catheter a catheter containing a rotating cutter and a collecting chamber for debris, used for atherectomy and endarterectomy; it is inserted percutaneously under radiographic guidance.
balloon catheter (balloon-tip catheter) a catheter with a balloon at the tip that may be inflated or deflated while the catheter is in place to create, enlarge, or occlude a passageway; see also balloon angioplasty. The pressure-sensitive balloon may be used to facilitate hemodynamic monitoring.
Braasch bulb catheter a bulb-tipped ureteral catheter used for dilation and determination of the inner diameter of the ureter.
Brockenbrough transseptal catheter a specialized cardiac catheter with a curved steel inner needle that can puncture the interatrial septum; used to catheterize the left ventricle when the aortic valve cannot be crossed in a retrograde approach.
Broviac catheter a central venous catheter similar to the Hickman catheter but with a smaller lumen.
cardiac catheter a long, fine catheter especially designed for passage into the chambers of the heart, usually through a peripheral blood vessel under fluoroscopic control. See also cardiac catheterization.
Castillo catheter a cardiac catheter similar to an Amplatz coronary catheter in shape and use, but shorter and introduced via the brachial artery.
central venous catheter a long, fine catheter inserted via a large vein into the superior vena cava or right atrium to administer parenteral fluids (as in parenteral nutrition), antibiotics, or other therapeutic agents; it can also be used for measurement of central venous pressure and for temporary hemodialysis. See also central venous catheterization.
condom catheter an external urinary collection device that fits over the penis like a condom; used in the management of urinary incontinence.
conical catheter a ureteral catheter that has a cone-shaped tip designed to dilate the lumen.
Cournand catheter a cardiac catheter with a single end hole; used for pressure measurement, usually in the right heart.
DeLee catheter a catheter used to suction meconium and amniotic debris from the nasopharynx and oropharynx of neonates.
de Pezzer catheter a self-retaining urethral catheter with a bulbous end.
directional atherectomy catheter a type of atherectomy catheter whose direction can be shifted to shave off additional plaque.
double-channel catheter (double-lumen catheter) (dual-lumen catheter) a catheter with two channels, one for injection and the other for removal of fluids; called also two-way catheter.
elbowed catheter a catheter bent at an angle near the beak, used in cases of enlarged prostate. Called also prostatic catheter.
electrode catheter a cardiac catheter containing one or more electrodes; it may be used to pace the heart or to deliver high-energy shocks.
end-hole catheter a cardiac catheter with a hole in the tip, through which a guidewire may be passed or pressure monitored.
eustachian catheter one for inflating the eustachian tube.
female catheter a short urethral catheter for passage through the female urethra.
femoral catheter a central venous catheter inserted through the femoral vein.
fluid-filled catheter an intravascular catheter connected by a saline-filled tube to an external pressure transducer; used to measure intravascular pressure.
Fogarty catheter a type of balloon-tip catheter used to remove thrombi and emboli from blood vessels.
Foley catheter an indwelling catheter retained in the bladder by a balloon inflated with air or liquid; see illustration.
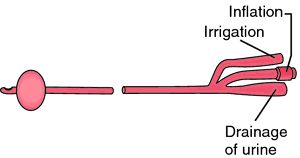
Three-way Foley catheter. Three separate lumens are incorporated within the round shaft of the catheter for drainage of urine, inflation, and introduction of irrigating solutions into the bladder.
Gensini coronary catheter a catheter used for coronary arteriography, having an end-hole to accommodate a guidewire or monitor pressure as well as side holes for rapid injection of large volumes of contrast material.
Groshong catheter a single or double lumen cardiac catheter inserted into the right atrium with an external port. Unlike the Hickman and Broviac catheters, this type has a valve at the distal end, eliminating the need for clamping and preventing blood from entering it when not in use.
Gruentzig balloon catheter a flexible balloon catheter with a short guidewire fixed to the tip, used for dilation of arterial stenoses; the balloon is made of low-compliance plastic to reduce the risk of arterial rupture.
hemodialysis catheter a catheter used on a temporary basis for vascular access for hemodialysis; usually some type of central venous catheter.
Hickman catheter a type of central venous catheter used for long term administration of substances via the venous system, such as antibiotics, total parenteral nutrition, or chemotherapeutic agents; it can be used for continuous or intermittent administration and may have either a single or a double lumen.
indwelling catheter a urethral catheter designed to be held in place to drain urine from the bladder.
internal jugular catheter a central venous catheter inserted through the internal jugular vein.
Judkins coronary catheter a preformed J-shaped angiographic catheter used in coronary arteriography to cannulate and deliver contrast material to one of the coronary arteries via a percutaneous femoral route.
left coronary catheter one designed for coronary arteriography of the left coronary artery.
Malecot catheter 1. a two- or four-winged female catheter.
2. a tube with an expanded tip that is used for gastrostomy feedings.
manometer-tipped catheter one with a small pressure transducer on its tip; used in measuring intravascular or intracardiac pressure.
multipurpose catheter 1. a catheter with several functions or applications.
2. a catheter for coronary angiography that is shaped so that it can be used in either coronary artery.
nasal catheter one made of flexible rubber or plastic with several holes near the end; used for the administration of oxygen. Called also oropharyngeal catheter.
NIH catheter one used for coronary arteriography; it has a closed end and several side holes for rapid injection of large volumes of contrast material.
olive-tip catheter a ureteral catheter with an olive-shaped end, used to dilate a constricted ureteral orifice; larger sizes are also used for dilating or calibrating the diameter of urethral strictures.
oropharyngeal catheter nasal catheter.
pacing catheter a cardiac catheter containing one or more electrodes on pacing wires; used as a temporary cardiac pacing lead.
Pezzer's catheter de Pezzer catheter.
pigtail catheter an angiographic catheter ending in a tightly curled tip that resembles the tail of a pig.
preformed catheter a preshaped catheter designed to require less operator manipulation but usually restricted to a single function.
prostatic catheter elbowed catheter.
right coronary catheter one designed for coronary arteriography of the right coronary artery.
Robinson catheter a straight urethral catheter with two to six openings to allow drainage, especially useful in the presence of blood clots which may occlude one or more openings.
self-retaining catheter a urethral catheter constructed to be retained in the bladder and urethra; see Foley catheter and indwelling catheter.
snare catheter one designed to remove intracardiac catheter fragments or pacing leads introduced iatrogenically.
Sones coronary catheter a woven Dacron or polyurethane catheter used in coronary arteriography to cannulate and deliver contrast material to the coronary arteries via the brachial artery.
subclavian catheter a central venous catheter inserted through the subclavian vein.
Swan-Ganz catheter see swan-ganz catheter.
Tenckhoff catheter a cuffed silicone catheter that is permanently inserted into the abdominal cavity for infusion of dialyzing solution in patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis.
Texas catheter trademark for a commercially made condom catheter.
thermodilution catheter a catheter used in thermodilution for introduction of the cold liquid indicator into the cardiovascular system.
toposcopic catheter a miniature catheter that can pass through narrow, tortuous vessels to convey chemotherapy directly to brain tumors.
tracheal catheter one with small holes at the end, especially designed for removal of secretions during tracheal suctioning.
transhepatic biliary catheter biliary c.
transluminal endarterectomy catheter a type of atherectomy catheter with a conical cutting window, inserted through the lumen of the vessel; debris is collected in a special vacuum bottle.
transtracheal catheter a catheter inserted into the trachea through a tracheostomy for patients who cannot tolerate an oral or nasal cannula.
two-way catheter double-lumen catheter.
ureteral catheter a long, small gauge catheter designed for insertion directly into a ureter, either through the urethra and bladder or posteriorly via the kidney.
urethral catheter any of various types of catheters designed for insertion via the urethra into the urinary bladder. See also catheterization.
whistle-tip catheter a urethral catheter with a terminal opening as well as a lateral one.
winged catheter a urethral catheter that has winglike projections on the end to retain it in the bladder.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
catheter
(kath'et-er) [Gr. katheter, a tube for insertion] 

TYPES OF CATHETERS: Single-lumen catheter


TYPES OF CATHETERS: Double-lumen catheter
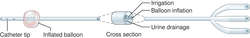

TYPES OF CATHETERS: Triple-lumen catheter
A tube passed into the body for evacuating or injecting fluids. It may be made of elastic, elastic web, rubber, glass, metal, or plastic. See: illustration
antimicrobial-impregnated central catheter
An intravenous catheter saturated with antibiotics, designed to decrease the likelihood of colonization or infection of indwelling infusion lines.
arterial catheter
A catheter inserted into an artery to measure pressure, remove blood, inject medication or radiographic contrast media, or perform an interventional radiological procedure.
balloon catheter
A multi-lumened catheter surrounded by a balloon. The balloon may be expanded by injecting air, saline, or contrast medium.
Bozeman-Fritsch catheter
See: Bozeman-Fritsch catheterBroviac catheter
Broviac catheter.cardiac catheter
A long, fine catheter specially designed for passage through the lumen of a blood vessel into the arteries or chambers of the heart.
See: cardiac catheterizationcaudal catheter
Caudal anesthesia.central catheter
A catheter inserted into a central vein or artery for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes.
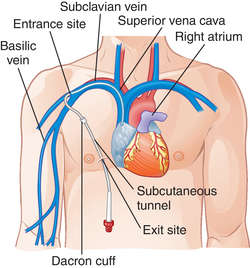

CENTRAL VENOUS CATHETER: A tunneled central venous catheter is inserted through subcutaneous tissue in the chest wall into the jugular or subclavian vein
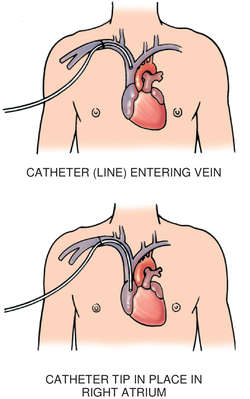

CENTRAL VENOUS CATHETER (SUBCLAVIAN)
central venous catheter
A catheter inserted into the superior vena cava to permit intermittent or continuous monitoring of central venous pressure, to administer fluids, medications or nutrition, or to facilitate obtaining blood samples for chemical analysis. See:
illustrationPatient care
Health care professionals must use caution to prevent life-threatening complications when inserting and maintaining a central line. The subclavian approach to the placement of a central line is preferred, because femoral placements may be complicated by deep venous thrombosis, and internal jugular sites carry an increased risk of infection. Sterile technique is a requirement during insertion. The skin should be prepared with chlorhexidine-gluconate (2%) or povidone-iodine. Ultrasound guidance improves the likelihood of entering the desired vein without injury to neighboring structures. With or without radiological guidance, the best results are obtained by practitioners who perform the procedure frequently. After the catheter is inserted, it should be firmly sewn to the skin to keep it from migrating in and out of the insertion site. An antibiotic impregnated patch covered by a sterile dressing should be placed at the insertion site. The catheter should be manipulated as infrequently as possible during its use. Dressing changes are carried out using sterile technique. IV tubing and solutions and injection caps also should be changed as required by the agency’s protocol. Health care professionals are responsible for preventing, assessing for, and managing central venous therapy complications (e.g., air embolism; cardiac tamponade; chylothorax, hemothorax, hydrothorax, or pneumothorax; local and systemic infections; and thrombosis). Documentation should include preprocedure and postprocedure physical assessment of the patient, catheter type and size, insertion site location, x-ray confirmation of the placement, catheter insertion distance (in centimeters), and the patient’s tolerance of the procedure. Maintenance care procedures also should be fully documented. The site should be carefully inspected for inflammation, and any drainage should be cultured. When catheter-related infections are suspected, the catheter tip provides valuable information about infection sources in cases of sepsis. The tip should be cut off with sterile scissors and dropped directly into a sterile specimen container.
condom catheter
A specially designed condom that includes a collection tube attached to the distal end. The tubing carries urine to a collecting bag. Its use prevents men with urinary incontinence from soiling clothes or bed linens.
CAUTION!
Continual use of this device may excoriate the skin of the penis. See: Catheter: External Condomdouble-channel catheter
A catheter providing for inflow and outflow.
elbowed catheter
Prostatic catheter.eustachian catheter
A catheter passed into the eustachian tube through the nasal passages to ventilate the middle ear.
female catheter
A catheter about 5 in (12.7 cm) long, used to pass into a woman's bladder.
Foley catheter
See: Foley catheterglide catheter
A catheter inserted into the ureter to remove impacted kidney stones. A lubricated wire is advanced past the obstructing stone. The glide catheter is mounted on the wire, moved toward the kidney beyond the stone, and used to snare and retrieve the stone.
guide catheter
A catheter that makes it easier to enter that vessel with other devices or instruments. Guide catheters are used to facilitate the placement of lasers, stents, and balloons for angioplasty.
heparin-bonded catheter
A pulmonary artery catheter with a heparin coating to reduce the risk of thrombus formation.
Hickman catheter
See: Hickman catheterimpregnated catheter
A catheter coated with a medication to prevent complications of prolonged insertion in the body. Commonly used coatings include antibiotics and antiseptics.
indwelling catheter
Any catheter that is allowed to remain in place in a vein, artery, or body cavity.
indwelling pleural catheter
Pleural catheter.intra-aortic catheter
See: intra-aortic balloon counterpulsationintrauterine pressure catheter
Abbreviation: IUPC
A catheter inserted into the uterus of a woman during labor, when labor is protracted, arrested, or when the force of uterine contractions are difficult to monitor indirectly.
intravenous catheter
A catheter inserted into a vein to administer fluids or medications or to measure pressure.
Karman catheter
See: Karman cathetermale catheter
A catheter 12 to 13 in (30.5 to 33 cm) long, used to pass into a man's bladder.
pacing catheter
A catheter inserted most commonly into the right side of the heart via the brachial, femoral, internal jugular, or subclavian vein for temporary pacing of the heart. The pacing wires or leads provide the electrical stimulus from an external source (a pulse generator).
peripherally inserted central venous catheter
Abbreviation: PICC, PICC line
A soft, flexible central venous catheter, inserted in a vein in the arm and advanced until the tip is positioned in the axillary, subclavian, or brachiocephalic vein. It may also be advanced into the superior vena cava. A PICC is commonly used for prolonged antibiotic therapy, total parenteral nutrition, continuous opioid infusion, or intermittent chemotherapy.
pharyngeal suction catheter
A rigid catheter used to suction the pharynx during direct visualization. Synonym: Yankauer suction catheter
pleural catheter
A small chest catheter inserted between the parietal and visceral pleura and used to drain recurrent pleural effusions, e.g., in patients with cancer.
Synonym: indwelling pleural catheterpresternal catheter
A catheter used for peritoneal dialysis that exits the chest instead of the lower abdomen. It is made of two silicone rubber tubes joined at the implantation site by a titanium connector that links its abdominal and presternal parts.
prostatic catheter
A catheter, 15 to 16 in (38 to 40.6 cm) long, with a short elbowed tip designed to pass prostatic obstruction. Synonym: elbowed catheter
pulmonary artery catheter
A catheter inserted into the pulmonary artery to measure pulmonary artery pressures, pulmonary capillary wedge pressure, and, indirectly, left atrial pressure and cardiac output.
self-retaining catheter
A bladder catheter designed to remain in place (e.g., a Foley catheter).
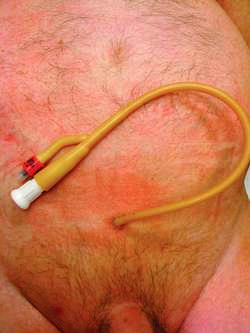

SUPRAPUBIC CATHETER: used to drain urine
suprapubic catheter
A catheter that permits direct urinary drainage from the bladder through the lower abdominal wall from a surgically fashioned opening located just above the pubic symphysis. Suprapubic urinary diversion is typically but not exclusively used as a temporary means of decompressing the bladder when the urethra is obstructed, e.g., in children with congenital deformities of the penis or urethra, or in adults with bladder outlet obstruction. When it is used for this purpose, it is considered a bridge before definitive surgery. See: suprapubic aspiration of urine;
illustrationPatient care
The nurse observes for hemorrhage or prolonged hematuria and signs of local or systemic infection. Aseptic technique is used during dressing or equipment changes. Bladder irrigation is performed as prescribed. Medications, e.g., analgesics, antispasmodics, and bowel stimulants, are administered as prescribed. The patient's ability to micturate is evaluated. Intake and output are monitored and recorded. Fluids are forced unless otherwise restricted to ensure passage of dilute urine.
Swan-Ganz catheter
See: Swan-Ganz catheterTenckhoff peritoneal catheter
See: Tenckhoff peritoneal cathetertriple-lumen catheter
Abbreviation: TLC
A central catheter containing three separate channels or passageways.
tunneled central venous catheter
An intravenous catheter inserted into the subclavian or internal jugular vein and then advanced into the right atrium or superior vena cava. The proximal end is tunneled subcutaneously from the insertion site and brought out through the skin at an exit site below the nipple line. Commonly used tunneled catheters include the Hickman and Broviac catheters.
umbilical vein catheter
A catheter placed in the umbilical vein of an infant to facilitate administration of medicines parenterally or to do an exchange transfusion.
vertebrated catheter
A catheter in sections to be fitted together so that it is flexible.
winged catheter
A catheter with little flaps at each side of the beak to help retain it in the bladder.
Word catheter
A rubber catheter with an inflatable balloon at its end, used to treat cysts or abscesses, e.g., Bartholin gland cysts in the vulva.
Yankauer suction catheter
See: Yankauer suction catheterMedical Dictionary, © 2009 Farlex and Partners




