disk
[disk] a circular or rounded flat plate; often spelled disc in names of anatomic structures.
articular disk a pad of fibrocartilage or dense fibrous tissue present in some synovial joints.
Bowman's disk one of the flat plates making up a striated muscle fiber.
choked disk papilledema.
ciliary disk pars plana.
embryonic disk (germ disk) (germinal disk) a flattened round bilaminar plate of cells in the blastocyst of a mammal, where the first traces of the embryo are seen; called also embryonic or germinal area.
herniated disk see herniated disk.
intervertebral disk the layer of fibrocartilage between the bodies of adjoining vertebrae; see also herniated disk.
intra-articular d's articular disk.
Merkel's d's small cup-shaped tactile receptors in the skin that are particularly sensitive to continuous pressure.
optic disk the intraocular part of the optic nerve formed by fibers converging from the retina and appearing as a pink to white disk in the retina; there are no sensory receptors in the region and hence no response to stimuli. Called also blind spot.
ruptured disk herniated disk.
slipped disk popular term for herniated disk.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
disc
(disk), [TA] 1. A round, flat plate; any approximately flat circular structure.
2. Synonym(s): lamella (2)
3. In dentistry, a circular piece of thin paper or other material, coated with an abrasive substance, used for cutting and polishing teeth and fillings.
Synonym(s): disk [TA]
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
disk
also disc
(dĭsk)n.1. A round, flattened structure in a plant or animal, such as an intervertebral disk.
2. Botany The central area bearing numerous disk flowers in the flower head of a composite plant such as a daisy.
The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
disc
(disk) 1. A round, flat plate; any approximately flat circular structure.
2. dentistry A circular piece of thin paper or other material, coated with an abrasive substance, used for cutting and polishing teeth and fillings.
3. microbiology A plate coated with an antibiotic to measure susceptibility and resistance.
4. The optic nerve head as viewed during ophthalmoscopy.
[L. discus; G. diskos, a quoit, disc]
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
disk
(disk) [Gr. diskos, a dish, quoit] A flat, round, platelike structure. Synonym: disc
anisotropic disk
A band.articular disk
The biconcave oval disk of fibrous connective tissue that separates the two joint cavities of the temporomandibular joint on each side.
choked disk
Papilledema.dental disk
A thin circular paper (or other substance) used to abrade, cut, or polish teeth or dental appliances.
embryonic disk
An oval disk of cells in the blastocyst of a mammal from which the embryo proper develops. Its lower layer, the endoderm, forms the roof of the yolk sac. Its upper layer, the ectoderm, forms the floor of the amniotic cavity. The primitive streak develops on the upper surface of the disk. See: embryo for illus.
Engelmann disk
[Theodor W. Engelmann, Ger. physiologist, 1843–1909]
H band.epiphyseal disk
A disk of cartilage at the junction of the diaphysis and epiphyses of growing long bones. Cartilage synthesis provides for growth in length; eventually the cartilage is replaced by bone.
germinal disk
A disk of cells on the surface of the yolk of a teloblastic egg from which the embryo develops. Synonym: proligerous disk; blastoderm
Hensen disk
See: Hensen, Christian Andreas Victor.herniated disk
Rupture of the soft tissue that separates two vertebral bones into the spinal canal or adjacent spinal nerve roots. Herniation of intervertebral disks can cause back pain and, occasionally, loss of neurological function in the distribution of affected nerves. Synonym: herniated intervertebral disk; lumbar disk prolapse; slipped disk See: herniation of nucleus pulposus for illus
herniated intervertebral disk
herniated disk.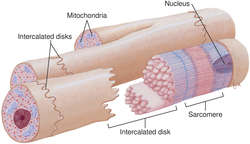

INTERCALATED DISK: Intercalated disk at the ends of adjacent cardiac muscle cells
intercalated disk
A modification of the cell membrane of adjacent cardiac muscle cells; it consists of extensive folds and intercellular junctions for electrical and mechanical linkage of contiguous cells.
See: illustrationintervertebral disk
The fibrocartilaginous tissue between the vertebral bodies. The outer portion is the anulus fibrosus; the inner portion is the nucleus pulposus. The disk is a shock absorber, or cushion, and permits movement.
M disk
M line.Merkel disk
See: Merkel diskoptic disk
The area of the retina where the optic nerve enters.
Synonym: blind spot (1)Placido disk
See: Placido diskproligerous disk
Germinal disk.slipped disk
Colloquial term for herniated disk.
tactile disk
Merkel disk.Z disk
A thin, dark disk that transversely bisects the I band (isotropic band) of a striated muscle fiber. The thin filaments, made primarily of actin, are attached to the Z disk; the area between the two Z disks is a sarcomere, the unit of contraction.
Medical Dictionary, © 2009 Farlex and Partners
disc
or disk
that part of the receptacle surrounding the plant ovary which is fleshy and sometimes nectar-secreting.Collins Dictionary of Biology, 3rd ed. © W. G. Hale, V. A. Saunders, J. P. Margham 2005
Disk
A ringlike structure that fits between the vertebrae in the spine to protect the bones, nerves, and blood vessels. The outer layer is a tough, fibrous tissue, and the inner core is composed of more elastic tissue.
Mentioned in: Cervical Spondylosis, Sciatica
Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights reserved.
disc
, disk (disk) dentistry a circular piece of thin paper or other material, coated with an abrasive substance, used for cutting and polishing teeth and fillings.
[L. discus; G. diskos, a quoit, disc]
Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions © Farlex 2012
Patient discussion about disk
Q. Is degenerative disc disease and arthritis the same thing? My husband was recently in a auto accident at work. They did a CT Scan of his head and neck. The doctor said that the CT Scan found that he has arthritis in his neck. After receiving the report ourselves to take to another doctor it reads: "There is minimal early degenerative disc disease with osteophyte formation predominately at C5-6. " My husband never had a problem with his neck before the accident
A. I was suffering from pain for 2 years and undergoing numerous test for causes when a trip to a neurologist for migraines gave me an answer. FINALLY! This was in July of this year so I am still learning and finding out about fibromyalgia but I do know in the last couple of years there has been a greater acceptance BUT there are still a lot of doctors not being supportive (from experience and talking with others) and the public in general can be unaccepting b/c you look healthy, seem to be healthy and they can not understand why you are in pain that "can't be explained!" I encourage suffers of fibro to find support within their peers! it really helps to talk to people that understand! That's what brought me to this site to start with and I am so glad I found it!
Q. What alternatives are there for DDD.De generative Disc Disease? I can't sit upright for long periods of time, at times the symptoms are worse and then days and weeks where I feel fine. When I lean into my right legit alleviates it a little but it is excruciating when I shift weight. I also have to sleep with a pillow between my legs and have to shift frequently.I have a lot of strength in my legs and back. But if I stuck in my stomach more and curve my like doing a crunch. the pain is fine.
A. Degenerative disc disease can often be successfully treated without surgery. One or a combination of treatments such as Physical therapy, chiropractic manipulative therapy (CMT), osteopathic manipulation, anti-inflammatory medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, chiropractic treatments, Traction (orthopedics), or spinal injections often provide adequate relief of these troubling symptoms.
The option of surgery may be recommended if the conservative treatment options do not provide relief within 2 to 3 months. If leg or back pain limits normal activity, if there is weakness or numbness in the legs, if it is difficult to walk or stand, or if medication or physical therapy are ineffective, surgery may be necessary. You should dicucss this with an orthopedic surgeon.
Q. what does c4-5 mild central disk bulging impinging upon cervical cord without spinal stenosis or distortion of the cord . mild righ neural foraminal narrowing from uncovertebral joint hypertropy mean
A. Well this basically means there is a very small narrowing of the cervical (your neck area) spinal canal (where the spinal cord is), however the narrowing does not cause any damage to the spinal cord, therefore probably does not cause any major symptoms involving the nerves. The c4-5 bulging part refers to the part in between the two cervical vertebras c4 and c5, in which the disc (a part in the spinal cord) is sliding a bit side-ways, but again, it does not seem to be causing any trouble.
More discussions about diskThis content is provided by iMedix and is subject to iMedix Terms. The Questions and Answers are not endorsed or recommended and are made available by patients, not doctors.
