Medical term:
eared
ear
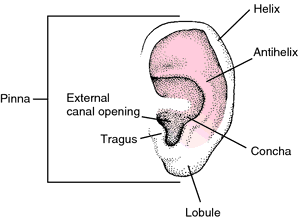
[ēr]The outer ear consists of the auricle or pinna and the external acoustic meatus. The auricle collects sound waves and directs them to the external acoustic meatus; from there the waves travel through the external auditory canal to the eardrum (tympanic membrane).
The middle ear is separated from the outer ear by the eardrum. It contains the three ossicles, the malleus (hammer), incus (anvil), and stapes (stirrup), so called because of their resemblance to these objects. These three small bones form a chain across the middle ear from the eardrum to the oval window. The stapes causes a membrane in the oval window to vibrate, and the vibrations are transmitted to the inner ear. The middle ear is connected to the nasopharynx by the eustachian tube, through which the air pressure in the middle ear is equalized with the air pressure in the nose and throat. The middle ear is also connected with the cells in the mastoid bone just behind the outer ear. Two muscles attached to the ossicles contract when loud noises strike the tympanic membrane, limiting its vibration and thus protecting it and the inner ear from damage.
The inner ear (or labyrinth) contains the cochlea, as well as the nerves that transmit sound to the brain. It also contains the semicircular canals, which are essential to the sense of equilibrium.
When a sound strikes the ear it causes the tympanic membrane to vibrate. The ossicles function as levers, amplifying the motion of the tympanic membrane, and passing the vibrations on to the cochlea. From there the vestibulocochlear (eighth cranial) nerve transmits the vibrations, translated into nerve impulses, to the auditory center in the brain.
The patient should be instructed to avoid nose blowing, especially after surgery, when there is a possibility that such an action can alter pressure within the ear. Observation of the patient after surgery of the ear includes assessing function of the facial nerve; evidence of dysfunction could include inability to wrinkle the forehead, close the eyes, pucker the lips, or bare the teeth. Any sign of facial nerve damage should be reported to the surgeon. vertigo is another common occurrence after surgery of the ear; it is usually only temporary and will subside as the operative site heals. The patient with vertigo requires special protective measures such as side rails and support when out of bed, so as to avoid falls or other accidental injuries.
Most surgeons prefer that the dressings around the ear not be changed during the immediate postoperative period. Should excessive drainage require more dressings, these can be applied over the basic dressing. Any drainage should be noted and recorded, with excessive drainage reported immediately to the surgeon. (See also care of the patient with hearing loss.)

ear
(ēr), [TA]See also: auricle.
ear
(îr)ear
Physical exam The auditory apparatus, which is divided into the external ear–a conical tube that collects sound that vibrates the tympanic membrane–the outer barrier of the middle ear, which contains the ossicles–malleus, incus, and stapes, that mechanically amplify the sound transmitted at the oval window to the cochlea; the cochlea's neuroepithelial hair cells convert the mechanical signal into an electrical/neural signal that is identified by the brain as sounds, speech, music, etc. See Blue ear, Cauliflower ear, Inner ear, Lop ear, Malrotated ear, Middle ear, Mozart ear, Outer ear, Outstanding ear, Satyr ear, Swimmer's ear, Third ear.EAR
ear
(ēr) [TA]See also: auricle
Synonym(s): auris [TA] .
ear
(er)
The pathway of hearing is as follows: the auricle funnels sound waves from the environment through the external auditory canal to the tympanic membrane, which makes this thin epithelial structure vibrate. The vibrations are transmitted to the auditory ossicles and then to the perilymph and endolymph. The receptors are part of the organ of Corti and generate impulses transmitted by the cochlear branch of the eighth cranial nerve to the spiral ganglion and auditory tracts of the brain. The auditory areas are in the temporal lobes.
The healthy human ear responds to a variety of sounds, with frequencies ranging from about 20 to 20,000 Hz. It is most sensitive, however, to sounds whose frequencies fall in the 1500- to 3000-Hz range, the frequency range of most human speech. See: hearing
The receptors for equilibrium are in the utricle, saccule, and semicircular ducts, which are innervated by the vestibular branch of the eighth cranial nerve. Impulses from the utricle and saccule provide information about the position of the head, those from the semicircular ducts about the speed and direction of three-dimensional movement.
Blainvilleear
See: Blainville earCagot ear
cauliflower ear
darwinian ear
See: darwinian earexternal ear
foreign bodies in ear
Symptoms
Foreign objects cause pain, ringing, or buzzing in the ear. A live insect usually causes a noise.
Treatment
Water must not introduced if any vegetable matter is in the ear because the water may push the foreign body further into the ear or cause the matter to swell and become firmly embedded.
To remove insects from the ear, a few drops of lidocaine should be instilled. Inorganic foreign bodies can be removed with small forceps by a health care provider.
glue ear

inner ear
internal ear
Inner ear.lop ear
middle ear
Mozart ear
See: Mozart earnerve supply of ear
outer ear
External ear.pierced ear
surfer's ear
swimmer's ear

ear
the sense organ of vertebrates concerned with reception of sound (hearing), BALANCE (detecting position with respect to gravity) and acceleration. The external ear is absent in amphibia and some reptiles, where the eardrum (tympanum) is at the skin surface; in other forms the external ear consists of an AUDITORY CANAL and the pinna, a projection of skin and cartilage. The middle ear or tympanic cavity (not present in some amphibians and some reptiles) lies between the ear drum and the auditory capsule. The EUSTACHIAN TUBE connects the middle ear to the pharynx; it contains the ear ossicles and lies within the bulla which is a projection of the skull. The inner ear or membranous labyrinth is contained in the auditory capsule; the utricle gives rise to the semicircular canals (for balance), and from the saccule the hearing organ arises in the form of the COCHLEA in some tetrapods.Hearing results from sound waves striking the tympanic membrane and causing it to vibrate. The vibrations are transmitted to the oval window by means of a lever system operating between the three ear ossicles which magnify them. This disturbs the fluid in the vestibular canal of the cochlea and causes movement in REISSNER'S MEMBRANE, which then results in the fluid of the middle canal being displaced. This moves the basilar membrane and then disturbs the fluid in the tympanic canal which stretches the membrane covering the round window. Movement of the basilar membrane stimulates the organ of Corti (see COCHLEA and impulses are fired in the auditory nerve. Loud sounds cause greater movement of the basilar membrane and a higher frequency of impulses from the organ of Corti. Pitch of a sound determines the frequency of movement of the basilar membrane.
EAR
ear
(ēr) [TA]Synonym(s): auris.
Patient discussion about ear
Q. Tinnitus (Ringing and Other Ear Noise) Anybody have this problem? Urrrrrrrrrrr, I think I want to shoot myself,you know what I mean. It is worst than the chinese torture. Someone, please send me a good tip how to stop it. I have this for 4 yrs and it is driving me crazy. You cannot enjoy total complete silence. They say silence is golden but not when you have this ringgi in your ears. It gets worst when there is no noise. The only remedy I have is eating hot spicy curry, it helps for 2-3 wks and then it comes back again and then eating spicy food again. Listening to classical music helps to. Oh well.....just have to suck it up.
Q. What causes high pitch ringing in one ear?
Q. my ears do not hear well especially when it's cold. i hear my breath and heart beat. what's my prolem? Denis when i breathe it feels like the breath goes through the ear when the weather is cold or when i do some excercise like jogging
Latest Searches:
antimitotic - antimetabolites - antilogous - antileishmanial - antihelmintic - antifibrotic - antiendotoxin - anticoagulative - anticoagulant - anticholelithogenic - antiasthmatics - antianxiety - antiantibody - anthropical - anthraquinone - anteorbital - Anorgasmy - anociassociation - ankerite - anitrogenous -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp