hair
[hār] 1. any thin, threadlike structure.
2. especially, the specialized epidermal structure produced only by mammals, developing from a papilla sunk in the
corium. The life cycle of a hair (hair
cycle) consists of three phases, called
anagen,
catagen, and
telogen. Called also pilus.
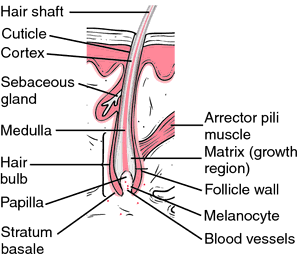
Structure of hair and hair follicles. From Applegate, 2000.
3. the aggregate of such structures.
bamboo hair trichorrhexis nodosa.
beaded hair hair marked with alternate swellings and constrictions; seen in monilethrix.
burrowing hair one that grows horizontally in the skin, causing a papule that may become infected; see also pili cuniculati, under pilus.
club hair a hair whose root is surrounded by a bulbous enlargement composed of keratinized cells, preliminary to normal loss of the hair from the follicle.
Frey's h's stiff hairs mounted in a handle; used for testing the sensitiveness of pressure points of the skin.
ingrown hair one that has curved and reentered the skin, causing a papule that may become infected. See also pili incarnati, under pilus.
lanugo hair the fine hair on the body of the fetus.
moniliform hair beaded hair.
pubic hair the hair on the external genitalia; called also pubes.
sensory h's hairlike projections on the surface of sensory epithelial cells.
tactile h's hairs sensitive to touch.
taste h's short hairlike processes projecting freely into the lumen of the pit of a taste bud from the peripheral ends of the taste cells.
terminal hair the coarse hair on various areas of the body during adult years.
twisted hair a hair that is twisted through an axis of 180 degrees at spaced intervals, being abnormally flattened at the site of twisting. See also pili torti, under pilus.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
hair
(hār), [TA] 1. One of the fine, keratinized filamentous epidermal growths arising from the skin of the body of mammals except the palms, soles, and flexor surfaces of the joints; the full length and texture of hair varies markedly in different body sites. Synonym(s): pilus (1) [TA]
2. One of the fine, hairlike processes of the auditory cells of the labyrinth, and of other sensory cells, called auditory hair, sensory hair, etc.
Synonym(s): thrix [TA]
[A.S. haer]
hair
trichophobia, trichopathophobia.
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
hair
(hâr)n.1. a. Any of the cylindrical, keratinized, often pigmented filaments characteristically growing from the epidermis of a mammal.
b. A growth of such filaments, as that forming the coat of an animal or covering the scalp of a human.
2. A filamentous projection or bristle similar to a hair, such as a seta of an arthropod or an epidermal process of a plant.
The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
A threadlike epidermal appendage consisting of keratinized dead cells that extrudes from a dividing basal layerSegen's Medical Dictionary. © 2012 Farlex, Inc. All rights reserved.
hair
Dermatology A threadlike epidermal appendage consisting of keratinized dead cells that extrudes from a dividing basal layer. Related terms are Anagen hair, Bamboo hair, Bayonet hair, Bundled hair, Catagen hair, Corkscrew hair, Green hair, Paintbrush hair, Pubic hair, Ringed hair, See-through hair, Telogen hair, Terminal hair, Vellus hair, Whisker hair.McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine. © 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
hair
(hār) [TA] 1. One of the fine, keratinized filamentous epidermal growths arising from the skin of the body of mammals except the palms, soles, and flexor surfaces of the joints; the full length and texture of hair varies markedly in different body sites.
2. One of the fine, hairlike processes of the auditory cells of the labyrinth, and of other sensory cells, called auditory hair, sensory hair, and other types.
Synonym(s): thrix.
[A.S. haer]
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
hair
(har) 1. A keratinized, threadlike outgrowth from the skin of mammals.
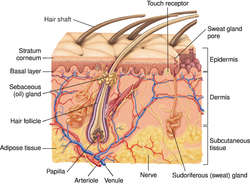

HAIR AND ADJACENT STRUCTURES OF CROSS-SECTION OF SKIN
2. Collectively, the threadlike outgrowths that form the fur of animals or that grow on the human body.
A hair is a thin, flexible shaft of cornified cells that develops from a cylindrical invagination of the epidermis, the hair follicle. Each consists of a free portion or shaft (scapus pili) and a root (radix pili) embedded within the follicle. The shaft consists of three layers of cells: the cuticle or outermost layer; the cortex, forming the main horny portion of the hair; and the medulla, the central axis. Hair color is due to pigment in the cortex. See: illustration
Hair in each part of the body has a definite period of growth, after which it is shed. In the adult human there is a constant gradual loss and replacement of hair. Hair of the eyebrows lasts only 3 to 5 months; that of the scalp 2 to 5 years. Baldness or alopecia results when replacement fails to keep up with hair loss. It may be hereditary or due to pathologic conditions such as infections or irradiation injury. Cytotoxic agents used in cancer chemotherapy may cause temporary loss of hair. See: alopecia
auditory hair
The stereocilia of a specialized epithelial cell. These are present in the ear in the spiral organ of Corti, concerned with hearing; and in the crista ampullaris, macula utriculi, and macula sacculi, concerned with equilibrium.
bamboo hair
Sparse, brittle hair with bamboo-like nodes. The nodes are partial fractures of the hair shaft, caused by atrophy of the hair.
Synonym: clastothrix; trichorrhexis nodosabeaded hair
Swellings and constrictions in the hair shaft caused by monilethrix.
burrowing hair
A hair that grows horizontally under the skin, causing a foreign body reaction.
gustatory hair
Any of several fine hairlike processes extending from the ends of gustatory cells in a taste bud. They project through the inner pore of a taste bud. Synonym: taste hair
ingrown hair
A hair that reenters the skin, causing a foreign body reaction.
kinky hair
Short, sparse, tightly twisted hair that may be poorly pigmented.
lanugo hair
See: lanugomoniliform hair
Monilethrix.moth-eaten hair
Patchy areas of baldness, with poorly defined borders. This type of alopecia is one of the cutaneous hallmarks of syphilis.
pubic hair
Hair over the pubes, which appears at onset of sexual maturity. The distribution is somewhat different in men than in women.
See: mons veneris; mons pubissensory hair
Specialized epithelial cells with hairlike processes.
tactile hair
Hair that is receptive to touch or contact.
taste hair
Gustatory hair.terminal hair
The long, coarse, pigmented hair of the adult.
twisted hair
Congenitally deformed hair that is short, brittle, and coiled.
Medical Dictionary, © 2009 Farlex and Partners
hair
The filamentary keratin secretion of follicles in the skin. The outer layer, or cuticle, of each hair is made of overlapping flat cells arranged like roofing slates. Below this is the thick cortex of horny cells and the core of softer rectangular cells. The hair colour comes from pigment cells (melanocytes) of uniform colour present in differing concentration. Very curly hair comes from curved follicles.Collins Dictionary of Medicine © Robert M. Youngson 2004, 2005
hair
- (in plants) a filamentous outgrowth from an epidermal cell that may have a secretory function (in glands), an absorbing function (in root hairs), or a function in trapping and preventing air movement of the leaf surface, so lowering the rate of TRANSPIRATION.
- (in animals) a filamentous structure of mammalian skin formed of cornified epidermal cells that multiply in the hair follicle.
Collins Dictionary of Biology, 3rd ed. © W. G. Hale, V. A. Saunders, J. P. Margham 2005
hair
(hār) [TA] 1. One of the fine, keratinized filamentous epidermal growths arising from the skin of the body of mammals except the palms, soles, and flexor surfaces of the joints.
2. One of the fine, hairlike processes of the auditory cells of the labyrinth, and of other sensory cells, called auditory or sensory hair.
[A.S. haer]
Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions © Farlex 2012
Patient discussion about hair
Q. i am 12 and my hair is falling out what do i do? there is like a hair ball in my tub
A. First of all you are going through puberty and the hormonal levels in your body are changing, this could cause accelerated hair loss that will go away. However, if you feel like you are having severe hair loss you should go and get blood tests for the evaluation of several vitamin defficiencies (B12, Folic acid and Iron), that can be the reason. Soemtimes a lack in our nutrition can be the reason for losing hair.
Q. What medications cause hair loss? I have RA, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, allergies and depression for which I take medication. Which of these cause hair loss?
A. any one of them can, you need to ask your pharmacist about it
Q. I went to a new hair dresser a to get my highlights done. and I think something is terribly wrong with my scalp. After washing the color away I already felt my scalp is tender, so he put some natural mask on my hair which he said will make it soft and nice, and calm the roots. A couple of days has past now and I still feel as though my scalp is a bit burning, and I think I am losing more hair than normally. So I am a “BIT” bit panicking here. Did he damage my scalp? How can I make the burning feeling go away? My friend said it is probably an allergic reaction to the active materials in the coloring or the natural mask, but I am usually not allergic to anything. Should I see a doctor?HELP!!!!
A. because of a very amusing story i'll tell someday - i know i'm allergic to P-Phenylenediamine or CPPD Black Rubber Mix that hair dyes sometime have. i also felt a burning sensation and lost some hair(that grew back ..) so i looked for alternative hair dyes and found some..just google hypoallergenic hair dyes. i recommend going to see a dermatologist just to be safe and get tested to see if you are really allergic.
More discussions about hairThis content is provided by iMedix and is subject to iMedix Terms. The Questions and Answers are not endorsed or recommended and are made available by patients, not doctors.

