Medical term:
hematomas
hematoma
[he″mah-to´mah]A localized collection of extravasated blood, usually clotted, in an organ, space, or tissue; contusions (bruises) and black eyes are familiar forms that are seldom serious. Hematomas can occur almost anywhere on the body; they are almost always present with a fracture and are especially serious when they occur inside the skull, where they may produce local pressure on the brain. In minor injuries the blood is absorbed unless infection develops.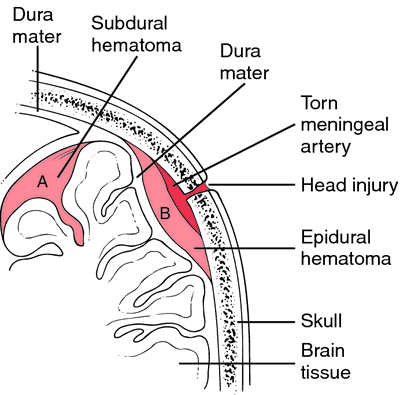
Cranial Hematoma. The two most common kinds of cranial hematomas are epidural and subdural (dural refers to the dura mater). Epidural hematoma occurs between the dura mater and the skull. It is most often caused by a heavy blow to the head that damages the upper surface of the dura mater. Blood seeps into the surrounding tissue, forming a tumorlike mass or hematoma. Since the skull is rigid, the hematoma presses inward against the brain; if the pressure continues, the brain can be affected. An epidural hematoma is the result of rupture of a relatively large meningeal artery, so that there is a rapid leakage of blood, causing increased intracranial pressure that can be fatal in a short period of time.
A subdural hematoma occurs beneath the dura mater, between the tough casing and the more delicate membranes covering the tissue of the brain, the pia-arachnoid. This kind of injury is more often caused by the head striking an immovable object, such as the floor, than by a blow from a moving object. There may be no severe head injury or fracture. A blow to the head can cause the brain to move violently, tearing blood vessels and forming a swelling that may include fluid from the brain tissue. A chronic subdural hematoma may remain and increase in size. (See also head injury.)
A subdural hematoma occurs beneath the dura mater, between the tough casing and the more delicate membranes covering the tissue of the brain, the pia-arachnoid. This kind of injury is more often caused by the head striking an immovable object, such as the floor, than by a blow from a moving object. There may be no severe head injury or fracture. A blow to the head can cause the brain to move violently, tearing blood vessels and forming a swelling that may include fluid from the brain tissue. A chronic subdural hematoma may remain and increase in size. (See also head injury.)
Symptoms. The most common symptoms of epidural hematoma occur within a few hours after injury. There can be a sudden or gradual loss of consciousness, partial or full paralysis on the side opposite the injury, and dilation of the pupil of the eye on the same side as the injury.
The symptoms of chronic subdural hematoma are similar to those of a brain tumor, and may come and go. There may be subtle personality changes, or the patient may become confused, weak in various parts of the body, vague, and drowsy. Subdural hematoma occasionally occurs in babies as a result of birth injury. Unless the injury is discovered and treated at an early stage, the child's mental and physical development may be retarded, and spastic paralysis can occur. Early surgery is usually successful in preventing permanent symptoms and disabilities.
The symptoms of chronic subdural hematoma are similar to those of a brain tumor, and may come and go. There may be subtle personality changes, or the patient may become confused, weak in various parts of the body, vague, and drowsy. Subdural hematoma occasionally occurs in babies as a result of birth injury. Unless the injury is discovered and treated at an early stage, the child's mental and physical development may be retarded, and spastic paralysis can occur. Early surgery is usually successful in preventing permanent symptoms and disabilities.
Treatment. Prompt surgery is the only treatment for epidural hematoma. The clotted blood is removed by a combination of suction and irrigation methods through openings made in the skull, and the bleeding is controlled. The same surgery is used for subdural hematomas.
Septal Hematoma. Injury to the nose sometimes causes hematoma of the nasal septum. Its symptoms include nasal obstruction and headache. The condition may be treated by incision and drainage or may clear up spontaneously in a few weeks. If the hematoma becomes infected, an abscess may result, requiring drainage and treatment with antibiotics.

Subdural and epidural hematoma. A, Subdural hematoma. As a result of trauma to the head, small ruptured blood vessels leak blood into the space under the dura mater. The hematoma forms between the dura mater and the arachnoid membrane. B, Epidural hematoma. The result of a head injury that tears a large meningeal artery, causing the collection of a large amount of blood above the dura mater. The large epidural hematoma compresses brain tissue. If not relieved, subdural and epidural hematomas can be fatal.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
he·ma·to·ma
(hē'mă-tō'mă, hem-ă-),A localized mass of extravasated blood that is relatively or completely confined within an organ or tissue, a space, or a potential space; the blood is usually clotted (or partly clotted), and, depending on its duration, may manifest various degrees of organization and decolorization.
[hemato- + G. -oma, tumor]
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
hematoma
(hē′mə-tō′mə)n. pl. hemato·mas or hemato·mata (-mə-tə)
A localized swelling filled with blood resulting from a break in a blood vessel.
The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
hematoma
A tumor-like mass produced by coagulated blood in a cavity. See Cerebral hematoma, Epidural hematoma.McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine. © 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
he·ma·to·ma
(hē'mă-tō'mă)A localized mass of extravasated blood that is relatively or completely confined within an organ or tissue, a space, or a potential space; the blood is usually clotted, and, depending on how long it has been there, may manifest various degrees of organization and decolorization.
Synonym(s): haematoma.
Synonym(s): haematoma.
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
Hematoma
A localized collection of blood that accumulates in an organ, tissue, or body space as the result of leakage from a broken blood vessel. Hematomas sometimes develop within the nasal cartilage when the nose is fractured.
Mentioned in: Atherectomy, Bone Marrow Aspiration and Biopsy, Computed Tomography Scans, Face Lift, Joint Fluid Analysis, Nasal Trauma, Pelvic Exam, Shaken Baby Syndrome
Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights reserved.
haematoma
A swelling containing blood. It may result from injury (e.g. black eye) or from some blood disease, such as leukaemia. Note: also spelt hematoma.
Millodot: Dictionary of Optometry and Visual Science, 7th edition. © 2009 Butterworth-Heinemann
he·ma·to·ma
(hē'mă-tō'mă)Localized mass of extravasated blood relatively or completely confined within an organ or space; blood usually clots.
Synonym(s): haematoma.
Synonym(s): haematoma.
[hemato- + G. -oma, tumor]
Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions © Farlex 2012
Patient discussion about Hematoma
Q. What is hematoma?
A. "hem" means blood, it's a very common bruise - when you fall off your bicycles, you get hit. if you don't cut yourself too in the process- blood vessels usually get ripped and blood flows to that area. this causes a red/blue color. after a couple of weeks it'll change color to green and then yellow. this is the blood cells disintegrate.
More discussions about HematomaThis content is provided by iMedix and is subject to iMedix Terms. The Questions and Answers are not endorsed or recommended and are made available by patients, not doctors.
Latest Searches:
Voraxaze - Voranil - Voorhoeve - voodoo - VOO - Vontrol - von - vomitus - vomiturition - vomitory - vomitoria - vomito - vomitive - vomiting - vomit - vomica - vomerovaginalis - vomerovaginal - vomerorostralis - vomerorostral -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp