Medical term:
lymph
lymph
[limf]a transparent, usually slightly yellow, often opalescent liquid found within the lymphatic vessels, and collected from tissues in all parts of the body and returned to the blood via the lymphatic system. It is about 95 per cent water; the remainder consists of plasma proteins and other chemical substances contained in the blood plasma, but in slightly smaller percentage than in plasma. Its cellular component consists chiefly of lymphocytes.
The body contains three main kinds of fluid: blood, tissue fluid, and lymph. The blood consists of the blood cells and platelets, the plasma, or fluid portion, and a variety of chemical substances dissolved in the plasma. When the plasma, without its solid particles and some of its dissolved substances, seeps through the capillary walls and circulates among the body tissues, it is known as tissue fluid. When this fluid is drained from the tissues and collected by the lymphatic system, it is called lymph. The lymphatic system eventually returns the lymph to the blood, where it again becomes plasma. This movement of fluid through the body is described under circulatory system.
The body contains three main kinds of fluid: blood, tissue fluid, and lymph. The blood consists of the blood cells and platelets, the plasma, or fluid portion, and a variety of chemical substances dissolved in the plasma. When the plasma, without its solid particles and some of its dissolved substances, seeps through the capillary walls and circulates among the body tissues, it is known as tissue fluid. When this fluid is drained from the tissues and collected by the lymphatic system, it is called lymph. The lymphatic system eventually returns the lymph to the blood, where it again becomes plasma. This movement of fluid through the body is described under circulatory system.
lymph node any of the accumulations of lymphoid tissue organized as definite lymphoid organs along the course of lymphatic vessels (see accompanying illustration); they consist of an outer cortical and an inner medullary part. Lymph nodes are the main source of lymphocytes of the peripheral blood and, as part of the reticuloendothelial system, serve as a defense mechanism by removing noxious agents such as bacteria and toxins, and probably play a role in antibody formation. Sometimes called, incorrectly, lymph gland. Called also lymph or lymphatic follicle and lymphatic nodule.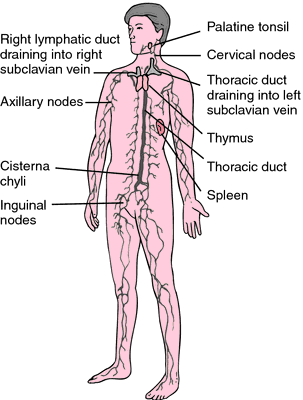

Location of clusters of superficial lymph nodes. From Applegate, 2000.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
lymph
(limf), [TA]A clear, transparent, sometimes faintly yellow and slightly opalescent fluid that is collected from the tissues throughout the body, flows in the lymphatic vessels (through the lymph nodes), and is eventually added to the venous blood circulation. Lymph consists of a clear liquid portion, varying numbers of white blood cells (chiefly lymphocytes), and a few red blood cells.
Synonym(s): lympha [TA]
[L. lympha, clear spring water]
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
lymph
(lĭmf)n.
1. A clear, watery, sometimes faintly yellowish fluid derived from body tissues that contains white blood cells and circulates throughout the lymphatic system, returning to the venous bloodstream through the thoracic duct. Lymph acts to remove bacteria and certain proteins from the tissues, transport fat from the small intestine, and supply mature lymphocytes to the blood.
2. Archaic A spring or stream of pure, clear water.
The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
lymph
(limf) [TA]A clear, sometimes faintly yellow and slightly opalescent fluid that is collected from the tissues throughout the body, flows in the lymphatic vessels, and through the lymph nodes, and is eventually added to the venous blood circulation. Lymph consists of a clear liquid portion, varying numbers of white blood cells (chiefly lymphocytes), and a few red blood cells.
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
lymph
Tissue fluids drained by the lymph vessels and returned to the large veins. Lymph varies in character in different parts of the body. Lymph from the tissues contains large numbers of white cells, mainly LYMPHOCYTES, and is usually clear. Lymph from the intestines is milky, especially after a meal, because of the large number of fat globules which it contains. Fat-laden lymph is called CHYLE.Collins Dictionary of Medicine © Robert M. Youngson 2004, 2005
lymph
the INTERSTITIAL FLUID found in the LYMPHATIC SYSTEM and around the tissues of vertebrates, with a total volume of around 20 litres in an adult human. Although its composition varies with location in the body, lymph is typically a clear, transparent fluid (95% water) which, like blood, will clot when removed from lymph vessels since it contains similar clotting agents to blood (except platelets). Lymph also contains protein, glucose and salts with large numbers of LEUCOCYTES, mainly LYMPHOCYTES.Collins Dictionary of Biology, 3rd ed. © W. G. Hale, V. A. Saunders, J. P. Margham 2005
Lymph
The almost colourless fluid that bathes body tissues and is found in the lymphatic vessels that drain the tissues of the fluid that filters across the blood vessel walls from blood. Lymph carries antibodies and lymphocytes (white blood cells that help fight infection) that have entered the lymph nodes from the blood.
Mentioned in: Bejel, Elephantiasis, Laryngeal Cancer, Lung Cancer, Non-Small Cell, Lymphedema, Lymphocytopenia, Lymphogranuloma Venereum, Salivary Gland Tumors
Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights reserved.
lymph
(limf) [TA]A clear, sometimes faintly yellow, and slightly opalescent fluid collected from tissues throughout the body, flows in the lymphatic vessels, and through the lymph nodes, and is eventually added to the venous blood circulation.
Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions © Farlex 2012
Patient discussion about lymph
Q. tender protuding lymph node lump rt. arm pit aprox. 1/2" dia. any concerns or recommend treatment necessary?
A. lymph nodes can flare up any time you get infected in the armpit and all the area that it drains. i had it several times and it went away in the same manner that it came. i think that sometimes it caused because of a blockade done by deodorant. so i try to use this Chinese salt stone that doesn't contain aluminum.
More discussions about lymphThis content is provided by iMedix and is subject to iMedix Terms. The Questions and Answers are not endorsed or recommended and are made available by patients, not doctors.
lymph
[limf]a transparent, usually slightly yellow, often opalescent liquid found within the lymphatic vessels, and collected from tissues in all parts of the body and returned to the blood via the lymphatic system. It is about 95 per cent water; the remainder consists of plasma proteins and other chemical substances contained in the blood plasma, but in slightly smaller percentage than in plasma. Its cellular component consists chiefly of lymphocytes.
The body contains three main kinds of fluid: blood, tissue fluid, and lymph. The blood consists of the blood cells and platelets, the plasma, or fluid portion, and a variety of chemical substances dissolved in the plasma. When the plasma, without its solid particles and some of its dissolved substances, seeps through the capillary walls and circulates among the body tissues, it is known as tissue fluid. When this fluid is drained from the tissues and collected by the lymphatic system, it is called lymph. The lymphatic system eventually returns the lymph to the blood, where it again becomes plasma. This movement of fluid through the body is described under circulatory system.
The body contains three main kinds of fluid: blood, tissue fluid, and lymph. The blood consists of the blood cells and platelets, the plasma, or fluid portion, and a variety of chemical substances dissolved in the plasma. When the plasma, without its solid particles and some of its dissolved substances, seeps through the capillary walls and circulates among the body tissues, it is known as tissue fluid. When this fluid is drained from the tissues and collected by the lymphatic system, it is called lymph. The lymphatic system eventually returns the lymph to the blood, where it again becomes plasma. This movement of fluid through the body is described under circulatory system.
lymph node any of the accumulations of lymphoid tissue organized as definite lymphoid organs along the course of lymphatic vessels (see accompanying illustration); they consist of an outer cortical and an inner medullary part. Lymph nodes are the main source of lymphocytes of the peripheral blood and, as part of the reticuloendothelial system, serve as a defense mechanism by removing noxious agents such as bacteria and toxins, and probably play a role in antibody formation. Sometimes called, incorrectly, lymph gland. Called also lymph or lymphatic follicle and lymphatic nodule.

Location of clusters of superficial lymph nodes. From Applegate, 2000.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
lymph
(limf), [TA]A clear, transparent, sometimes faintly yellow and slightly opalescent fluid that is collected from the tissues throughout the body, flows in the lymphatic vessels (through the lymph nodes), and is eventually added to the venous blood circulation. Lymph consists of a clear liquid portion, varying numbers of white blood cells (chiefly lymphocytes), and a few red blood cells.
Synonym(s): lympha [TA]
[L. lympha, clear spring water]
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
Latest Searches:
Voraxaze - Voranil - Voorhoeve - voodoo - VOO - Vontrol - von - vomitus - vomiturition - vomitory - vomitoria - vomito - vomitive - vomiting - vomit - vomica - vomerovaginalis - vomerovaginal - vomerorostralis - vomerorostral -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp