Medical term:
lympha
lymph
[limf]a transparent, usually slightly yellow, often opalescent liquid found within the lymphatic vessels, and collected from tissues in all parts of the body and returned to the blood via the lymphatic system. It is about 95 per cent water; the remainder consists of plasma proteins and other chemical substances contained in the blood plasma, but in slightly smaller percentage than in plasma. Its cellular component consists chiefly of lymphocytes.
The body contains three main kinds of fluid: blood, tissue fluid, and lymph. The blood consists of the blood cells and platelets, the plasma, or fluid portion, and a variety of chemical substances dissolved in the plasma. When the plasma, without its solid particles and some of its dissolved substances, seeps through the capillary walls and circulates among the body tissues, it is known as tissue fluid. When this fluid is drained from the tissues and collected by the lymphatic system, it is called lymph. The lymphatic system eventually returns the lymph to the blood, where it again becomes plasma. This movement of fluid through the body is described under circulatory system.
The body contains three main kinds of fluid: blood, tissue fluid, and lymph. The blood consists of the blood cells and platelets, the plasma, or fluid portion, and a variety of chemical substances dissolved in the plasma. When the plasma, without its solid particles and some of its dissolved substances, seeps through the capillary walls and circulates among the body tissues, it is known as tissue fluid. When this fluid is drained from the tissues and collected by the lymphatic system, it is called lymph. The lymphatic system eventually returns the lymph to the blood, where it again becomes plasma. This movement of fluid through the body is described under circulatory system.
lymph node any of the accumulations of lymphoid tissue organized as definite lymphoid organs along the course of lymphatic vessels (see accompanying illustration); they consist of an outer cortical and an inner medullary part. Lymph nodes are the main source of lymphocytes of the peripheral blood and, as part of the reticuloendothelial system, serve as a defense mechanism by removing noxious agents such as bacteria and toxins, and probably play a role in antibody formation. Sometimes called, incorrectly, lymph gland. Called also lymph or lymphatic follicle and lymphatic nodule.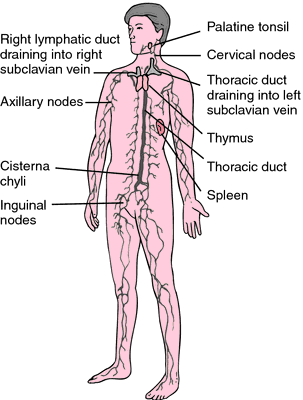

Location of clusters of superficial lymph nodes. From Applegate, 2000.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
lymph
(limf), [TA]A clear, transparent, sometimes faintly yellow and slightly opalescent fluid that is collected from the tissues throughout the body, flows in the lymphatic vessels (through the lymph nodes), and is eventually added to the venous blood circulation. Lymph consists of a clear liquid portion, varying numbers of white blood cells (chiefly lymphocytes), and a few red blood cells.
Synonym(s): lympha [TA]
[L. lympha, clear spring water]
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
lymph
[limf]a transparent, usually slightly yellow, often opalescent liquid found within the lymphatic vessels, and collected from tissues in all parts of the body and returned to the blood via the lymphatic system. It is about 95 per cent water; the remainder consists of plasma proteins and other chemical substances contained in the blood plasma, but in slightly smaller percentage than in plasma. Its cellular component consists chiefly of lymphocytes.
The body contains three main kinds of fluid: blood, tissue fluid, and lymph. The blood consists of the blood cells and platelets, the plasma, or fluid portion, and a variety of chemical substances dissolved in the plasma. When the plasma, without its solid particles and some of its dissolved substances, seeps through the capillary walls and circulates among the body tissues, it is known as tissue fluid. When this fluid is drained from the tissues and collected by the lymphatic system, it is called lymph. The lymphatic system eventually returns the lymph to the blood, where it again becomes plasma. This movement of fluid through the body is described under circulatory system.
The body contains three main kinds of fluid: blood, tissue fluid, and lymph. The blood consists of the blood cells and platelets, the plasma, or fluid portion, and a variety of chemical substances dissolved in the plasma. When the plasma, without its solid particles and some of its dissolved substances, seeps through the capillary walls and circulates among the body tissues, it is known as tissue fluid. When this fluid is drained from the tissues and collected by the lymphatic system, it is called lymph. The lymphatic system eventually returns the lymph to the blood, where it again becomes plasma. This movement of fluid through the body is described under circulatory system.
lymph node any of the accumulations of lymphoid tissue organized as definite lymphoid organs along the course of lymphatic vessels (see accompanying illustration); they consist of an outer cortical and an inner medullary part. Lymph nodes are the main source of lymphocytes of the peripheral blood and, as part of the reticuloendothelial system, serve as a defense mechanism by removing noxious agents such as bacteria and toxins, and probably play a role in antibody formation. Sometimes called, incorrectly, lymph gland. Called also lymph or lymphatic follicle and lymphatic nodule.

Location of clusters of superficial lymph nodes. From Applegate, 2000.
node
[nōd]a small mass of tissue in the form of a swelling, knot, or protuberance, either normal or pathological. adj., adj no´dal.
node of Aschoff and Tawara atrioventricular node.
atrioventricular node (AV node) a collection of cardiac fibers at the base of the interatrial septum that transmits the cardiac impulse initiated by the sinoatrial node.
Bouchard's n's cartilaginous and bony enlargements of the proximal interphalangeal joints of the fingers in degenerative joint disease; such nodes on the distal joints are called Heberden's nodes.
Delphian node a lymph node encased in the fascia in the midline just above the thyroid isthmus, so called because it is exposed first at operation and, if diseased, is indicative of disease of the thyroid gland.
Flack's node sinoatrial node.
Heberden's n's nodular protrusions on the phalanges at the distal interphalangeal joints of the fingers in osteoarthritis. Similar nodes on the proximal joints are called bouchard's nodes.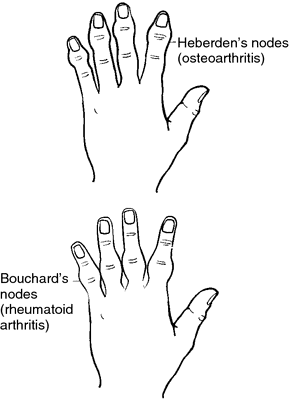

Comparison of Heberden's nodes (seen in patients with osteoarthritis) with Bouchard's nodes (seen in patients with rheumatoid arthritis). From Copstead and Banasik, 2000.
hemal n's nodes with a rich content of erythrocytes within sinuses, found near large blood vessels along the ventral side of the vertebrae and near the spleen and kidneys in various mammals, especially ruminants, having functions probably like those of the spleen; their presence in humans is doubtful.
Keith's node (Keith-Flack node) sinoatrial node.
Legendre's n's Bouchard's nodes.
lymph node see lymph node.
Osler's n's small, raised, swollen, tender areas, bluish or sometimes pink or red, due to inflammation around the site of lodgement of small infected emboli in distal arterioles; they occur commonly in the pads of the fingers or toes, in the palms, or in the soles and are practically pathognomonic for subacute bacterial endocarditis.
Parrot's n's bony nodes on the outer table of the skull of infants with congenital syphilis.
n's of Ranvier constrictions of myelinated nerve fibers at regular intervals at which the myelin sheath is absent and the axon is enclosed only by Schwann cell processes.
SA node sinoatrial node.
Schmorl's node an irregular or hemispherical bone defect in the upper or lower margin of the body of a vertebra into which the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disk herniates.
sentinel node
1. the first lymph node to receive drainage from a tumor; used to determine whether there is lymphatic metastasis in certain types of cancer. If this node is negative for malignancy, others “upstream” from it are usually also negative.
2. signal n.
signal node an enlarged supraclavicular lymph node; often the first sign of a malignant abdominal tumor.
singer's n's vocal cord nodules.
sinoatrial node a collection of atypical muscle fibers in the wall of the right atrium where the rhythm of cardiac contraction is usually established; therefore also referred to as the pacemaker of the heart. Called also SA node.
syphilitic node a swelling on a bone due to syphilitic periostitis.
node of Tawara atrioventricular node.
teacher's n's vocal cord nodules.
Troisier's node (Virchow's node) sentinel node.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
lymph node
(limf nōd), [TA]One of numerous round, oval, or bean-shaped bodies located along the course of lymphatic vessels, varying greatly in size (1-25 mm in diameter) and usually presenting a depressed area, the hilum, on one side through which blood vessels enter and efferent lymphatic vessels emerge. The structure consists of a fibrous capsule and internal trabeculae supporting lymphoid tissue and lymph sinuses; lymphoid tissue is arranged in nodules in the cortex and cords in the medulla of a node, with afferent vessels entering at many points of the periphery.
Synonym(s): nodus lymphoideus [TA], lymphonodus ☆ , nodus lymphaticus ☆ , lymph gland, lymphaden, lymphoglandula
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
lymph node
n.
Any of the small bodies located along the vessels of the lymphatic system (in humans notably in the neck, armpits, and groin) that filter bacteria and foreign particles from lymph fluid. During infection, lymph nodes may become swollen with activated lymphocytes. Also called lymph gland.
The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
lymph node
(limf nōd) [TA]One of numerous round, oval, or bean-shaped bodies located along the course of lymphatic vessels, varying greatly in size (1-25 mm in diameter) and usually presenting a depressed area, the hilum, on one side through which afferent lymphatic vessels enter and efferent lymphatic vessels emerge. The structure consists of a fibrous capsule and internal trabeculae supporting lymphoid tissue and lymph sinuses; lymphoid tissue is arranged in nodules in the cortex and cords in the medulla of a node, with afferent vessels entering at many points of the periphery.
Synonym(s): nodus lymphaticus [TA] , nodus lymphoideus [TA] , lymph gland, lymphoglandula, lymphonodus.
Synonym(s): nodus lymphaticus [TA] , nodus lymphoideus [TA] , lymph gland, lymphoglandula, lymphonodus.
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012

LYMPH NODE
lymph node
A small encapsulated lymphoid organ that filters lymph. Lymph nodes are found at junctions or branches along the lymphatics. They provide sites where immune responses can be generated through the interaction of antigens, macrophages, dendritic cells and lymphocytes. See: illustration; immune response; inflammation; lymph; lymphocyteLymph nodes are 0.1-2.5 cm long kidney-shaped aggregates of lymphocytes and macrophages embedded in a meshwork reticulum composed of thin collagen fibers. At each lymph node, an artery enters through a surface indentation (the hilum) alongside an exiting vein and an exiting (efferent) lymphatic vessel; a number of afferent lymphatic vessels enter the lymph node at other sites. Inside lymph nodes, lymph slowly flows through endothelial sinuses lined by lymphocytes and macrophages. Macrophages remove macromolecules, particles, debris, and microorganisms from the lymph stream. Lymphocytes and antibodies move through the walls of the sinuses and into the passing lymph, while dendritic cells pass from the lymph into the lymphatic follicles, carrying antigens from the body's epithelia and from infected tissues. In the cortical region of the lymph node, the sinuses wind around lymphatic follicles, which are ovoid germinal centers packed with differentiating and proliferating B lymphocytes and surrounded by loose T lymphocytes. Lymphocytes and antibodies also enter and exit blood capillaries throughout the lymph node. Lymph nodes are most numerous in the neck, mediastinum, abdominal mesenteries, pelvis, the proximal limbs (the axillae and the groin), and along the posterior abdominal wall. Inside the chest and trunk, lymph nodes tend to be found along the veins near viscera.
See also: node
Medical Dictionary, © 2009 Farlex and Partners
lymph node
orlymphatic node
a mass of lymphoid tissue, important in producing antibodies containing macrophages which remove foreign bodies from the lymph. It is present only in mammals and birds.Collins Dictionary of Biology, 3rd ed. © W. G. Hale, V. A. Saunders, J. P. Margham 2005
Lymph node
A small mass of tissue in the form of a knot or protuberance. Lymph nodes are the primary sources of lymph fluid, which serve in the body's defense by removing toxic fluids and bacteria.
Mentioned in: Chronic Fatigue Syndrome, Lumpectomy, Lung Cancer, Non-Small Cell
Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights reserved.
lymph node
(limf nōd) [TA]One of numerous round, oval, or bean-shaped bodies located along the course of lymphatic vessels, varying greatly in size and usually presenting a depressed area, the hilum.
Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions © Farlex 2012
Patient discussion about lymph node
Q. tender protuding lymph node lump rt. arm pit aprox. 1/2" dia. any concerns or recommend treatment necessary?
A. lymph nodes can flare up any time you get infected in the armpit and all the area that it drains. i had it several times and it went away in the same manner that it came. i think that sometimes it caused because of a blockade done by deodorant. so i try to use this Chinese salt stone that doesn't contain aluminum.
More discussions about lymph nodeThis content is provided by iMedix and is subject to iMedix Terms. The Questions and Answers are not endorsed or recommended and are made available by patients, not doctors.
Latest Searches:
Voraxaze - Voranil - Voorhoeve - voodoo - VOO - Vontrol - von - vomitus - vomiturition - vomitory - vomitoria - vomito - vomitive - vomiting - vomit - vomica - vomerovaginalis - vomerovaginal - vomerorostralis - vomerorostral -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp