Medical term:
mitochondrion
mitochondrion
[mi″to-kon´dre-ah] (pl. mitochon´dria) (Gr.)a small, spherical to rod-shaped, membrane-bounded cytoplasmic organelle, the principal sites of ATP synthesis; mitochondria also contain enzymes of the citric acid cycle and ones for fatty acid oxidation, oxidative phosphorylation, and other biochemical pathways. They also contain DNA, RNA, and ribosomes; they replicate independently and synthesize some of their own proteins. adj., adj mitochon´drial.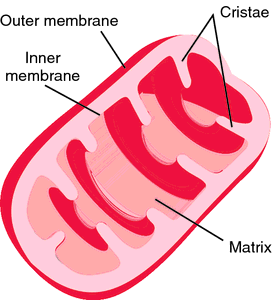

Mitochondrion. This organelle has a double membrane that unfolds and forms cristae. The membrane and cristae serve as attachment sites for oxidative enzymes. From Damjanov, 2000.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
mi·to·chon·dri·on
, pl.mi·to·chon·dri·a
(mī'tō-kon'drē-on, mī'to-kon'drē-ă),An organelle of the cell cytoplasm consisting of two sets of membranes, a smooth continuous outer coat and an inner membrane arranged in tubules or more often in folds that form platelike double membranes called cristae; mitochondria are the principal energy source of the cell and contain the cytochrome enzymes of terminal electron transport and the enzymes of the citric acid cycle, fatty acid oxidation, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Synonym(s): Altmann granule (2)
[G. mitos, thread, + chondros, granule, grits]
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
mitochondrion
(mī′tə-kŏn′drē-ən)n. pl. mitochon·dria (-drē-ə)
A spherical or elongated organelle in the cytoplasm of nearly all eukaryotic cells, containing genetic material and many enzymes important for cell metabolism, including those responsible for the conversion of food to usable energy.
mi′to·chon′dri·al (-drē-əl) adj.
The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
mi·to·chon·dri·on
, pl. mitochondria (mī'tō-kon'drē-ŏn, -ă)An organelle of the cell cytoplasm consisting of two sets of membranes, a smooth continuous outer coat and an inner membrane arranged in tubules or moreoften in folds that form platelike double membranes called cristae; mitochondria are the principal energy source of the cell and contain the cytochrome enzymes of terminal electron transport and the enzymes of the citric acid cycle, fatty acid oxidation, and oxidative phosphorylation.
[G. mitos, thread, + chondros, granule, grits]
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
mitochondrion
(pl. mitochondria) a subcellular, cylindrical organelle found in EUKARYOTES, of about 0.2–0.5 μm in length. Under the ELECTRON MICROSCOPE, the mitochondrion is seen to consist of a double membrane surrounding a matrix, with the inner membrane folded into projections called CRISTAE. The walls of the cristae are the site of ELECTRON TRANSPORT SYSTEMS producing ATP, while the reactions of the KREBS CYCLE take place within the matrix. Mitochondria have thus been named the ‘powerhouses’ of the cell and are especially prevalent in cells with a high energy requirement. Mitochondria are selfreplicating and contain DNA by which they can control the synthesis of some of their own proteins.Collins Dictionary of Biology, 3rd ed. © W. G. Hale, V. A. Saunders, J. P. Margham 2005
Altmann,
Richard, German histologist, 1852-1900.Altmann anilin-acid fuchsin stain - a mixture of picric acid, anilin, and acid fuchsin which stains mitochondria crimson against a yellow background.
Altmann fixative - a bichromate-osmic acid fixative.
Altmann-Gersh method - the method of rapidly freezing a tissue and dehydrating it in a vacuum.
Altmann granule - a granule that has an affinity for fuchsin. Synonym(s): fuchsinophil granule; mitochondrion
Altmann theory - a theory that protoplasm consists of granular particles that are clustered and enclosed in indifferent matter.
Medical Eponyms © Farlex 2012
mitochondrion
An organelle in the cytoplasm of cells, which produces most of the energy-rich molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in cells. It is produced by using oxygen to break down nutrient molecules (e.g. glucose). The number of mitochondria in a cell varies, it is greater in active cells, such as muscle and liver cells which need more ATP. Mitochondria are involved in other processes (e.g. apoptosis, cellular proliferation). Each mitochondrion contains DNA, RNA, ribosomes and granules. The DNA is distinct from that of the cell nucleus. Mitochondrial DNA is inherited only through the female. Mutations in mitochondrial DNA causes genetic disorders (e.g. Leber's hereditary optic atrophy). Plural: mitochondria.
Millodot: Dictionary of Optometry and Visual Science, 7th edition. © 2009 Butterworth-Heinemann
Latest Searches:
Voraxaze - Voranil - Voorhoeve - voodoo - VOO - Vontrol - von - vomitus - vomiturition - vomitory - vomitoria - vomito - vomitive - vomiting - vomit - vomica - vomerovaginalis - vomerovaginal - vomerorostralis - vomerorostral -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp