Medical term:
prisms
prism
[priz″әm]a solid of glass, plastic, or a similar substance with a triangular or polygonal cross section, which splits up a ray of light into its constituent colors and turns or deflects light rays toward its base. Prisms are used to correct deviations of the eyes, since they alter the apparent situation of objects.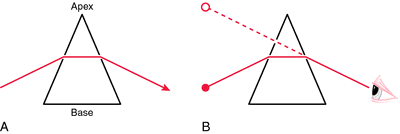

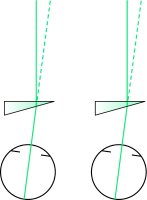
A, Light is deviated by the prism toward its base. B, The observer views an object through the prism and the object appears displaced toward its apex. From Stein et al., 2000.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
prism
(prizm),A transparent solid with sides that converge at an angle, which deflects a ray of light toward the thickest portion (the base) and splits white light into its component colors; in spectacles, a prism corrects ocular muscle imbalance.
[G. prisma]
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
PRISM
Platelet Receptor Inhibition in ischaemic Syndrome Management. A trial that compared a composite end point (death, acute MI and refractory ischaemia at 48 hours) in patients with unstable angina who were already receiving aspirin, and managed with either heparin or tirofiban, a nonpeptide inhibitor of platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor.Results
Tirofibran reduced mortality, but not acute MIs or refractory ischaemia.
Segen's Medical Dictionary. © 2012 Farlex, Inc. All rights reserved.
PRISM
Cardiology A clinical trial–Platelet Receptor Inhibition in Ischemic Syndrome Management which compared the composite end point–Death, MI, and refractory ischemia at 48 hrs of Pts with unstable angina–who were already receiving aspirin, who were managed with either heparin–H or tirofiban–T–a specific, nonpeptide inhibitor of platelet gpIIb/IIIa receptor. See Tirofiban.
McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine. © 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
prism
(prizm)A transparent solid, with sides that converge at an angle, that deflects a ray of light toward the thickest portion (the base) and splits white light into its component colors; in spectacles, a prism corrects ocular muscle imbalance.
[G. prisma]
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
prism
A transparent body (e.g. plastic, glass) bounded by two inclined plane surfaces, which intersect in a straight line called the apex, and form an angle called the prism angle. The face opposite the apex is called the base. It is an optical element used to deviate light (towards the base of the prism). The angle of deviation d of a prism in air is given by the following formula
achromatic prism A prism that deviates light without dispersion. It consists of two prisms, usually one of crown glass and the other of flint, of equal angular dispersions and mounted so that the apex of one is against the base of the other.
prism adaptation See vergence adaptation; prism adaptation test.
aligning prism See associated heterophoria.
prism ballast lens See ballast.
prism bar Clinical device consisting of a series of prisms of increasing strengths arranged in a convenient mount for rapid positioning in front of an eye. It can be used with the cover test or even to measure fusional responses when determining the zone of clear, single, binocular vision if rotary prisms are not available.
base-in prism; base-out prism See base setting.
bi-prism See Fresnel's bi-prism.
prism binoculars See binoculars.
compensating prism See associated heterophoria; relieving prism.
prism
cover test See cover test.
Crete's p . See rotary prism.
prism dioptre See prism dioptre.
dissociating prism A prism which, when placed in front of an eye, produces dissociation.
double prism See Fresnel's bi-prism.
double prism test See double prism test.
Dove prism An isosceles reflecting prism used to invert the image in an optical system. Light enters one side, is then refracted onto the base surface where it is internally reflected and refracted again through the other side.
erecting prism A prism designed to invert an image in an optical system with no change of size or shape. Examples: Dove prism, Porro prism. Syn. inverting prism. See erector.
Fresnel Press-On prism A trade name for a thin disc of transparent plastic consisting of one flat surface which can adhere to a clean lens surface when pressed in place, and another surface on which are incorporated small prismatic elements laid parallel to one another. Large optical effects can thus be provided in a much thinner and lighter form. These Press-On Fresnel prisms can be cut to any desired shape and are used commonly in orthoptics treatment. See Fresnel lens; orthoptics.
Herschel prism See rotary prism.
induced prism Prismatic effect created when the patient's visual axis does not pass through the optical centre of an ophthalmic lens. The amount of prism power is given by Prentice's law. See correction induced convergence; Prentice's law.
inverting p . See prism, erecting.
lacrimal prism See tear meniscus.
minimum deviation of a prism The deviation of light rays from their original path is minimum when light passes symmetrically through a prism so that the incident and emergent angles are equal (Fig. P15). See angle of deviation; prism.
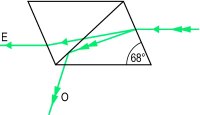
Nicol prism An optical device for producing a beam of plane polarized light. It is made from a piece of calcite crystal cut diagonally in half with the two halves cemented together. Incident light is split into ordinary and extraordinary linearly polarized rays in the prism: the ordinary ray reaches the interface and is totally reflected, while the extraordinary ray is transmitted (Fig. P16). See analyser; birefringence; polarizer.
ophthalmic prism A prism used in the correction or in the measurement of a deviation of the eyes. The power of such a prism is usually only a few prism dioptres. The power of a thin prism in air, represented by the angle of deviation d, is given by the approximate formula
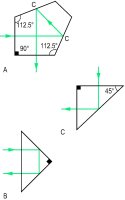
penta prism See Fig. P18.
polarizing prism A prism made from doubly refracting material. Example: quartz. See analyzer; polarized light; polarizer.
Porro prism A combination prism consisting of two 90º totally reflecting prisms arranged at right angles to each other. It is used in optical systems, such as binoculars to invert the image and provide a shorter displacement. It is the most common erecting prism.
prism power See prism power.
reflecting prism A prism in which light is internally reflected at one or more of the plane surfaces before emerging. This happens when the angle of incidence at the surface is greater than the critical angle (Fig. P18). Syn. total reflecting prism. See total reflection.
prism reflex test See Krimsky's method.
relieving prism An ophthalmic prism prescribed to relieve symptoms caused by an uncompensated heterophoria. Syn. compensating prism.
Risley prism See rotary prism.
rotary prism A pair of identical thin prisms mounted one in front of the other, so that they can be rotated by equal amounts in opposite directions to give a resultant power in a single meridian. The power can vary from zero when the apex of one prism coincides with the base of the other, to the sum of the powers of the two prisms when the apices coincide. The Risley prism is a very common type of rotary prism. It is used to determine the limits of the zone of clear, single, binocular vision and also in some stereoscopes (e.g. variable prism stereoscope). Other types of rotary prisms are those of Crete and Herschel. Syn. variable prism. See base setting; variable prism stereoscope.
tear prism See tear meniscus.
total reflecting prism See reflecting prism.
version prism's See yoke prisms.
Wollaston prism Two right-angled prisms of equal angle made of a double refracting crystal such as quartz or calcite cemented together by their hypotenuse faces to form a rectangular unit. The optical axis of the crystal in one prism is perpendicular to that in the other prism and both axes are also perpendicular to the direction of the incident light. A beam of unpolarized light incident on a Wollaston prism will emerge as two diverging beams which are oppositely polarized and almost free of dispersion. This prism is used in some types of keratometers (e.g. Javal-Schiotz). Syn. Wollaston polarizer.
yoke prism's Two prisms, one in front of each eye, of equal deviation and direction (e.g. 2 ΧBU, OU). The apparent view moves towards the apex of the prisms. These are sometimes prescribed in the management of nystagmus, in visual training, for the bedridden (BD prisms) and in some cases of physical disability. (Fig. P19) Note: also spelt yoked prisms. Syn. version prisms.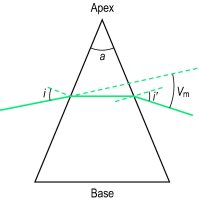






d = i + i′ − a
where i is the angle of incidence, i′ the angle of emergence and a the prism angle (Fig. P15). See vergence adaptation; base setting; prism dioptre; prism power; minimum deviation of a prism; ophthalmic prism; recumbent spectacles; spectroscope.achromatic prism A prism that deviates light without dispersion. It consists of two prisms, usually one of crown glass and the other of flint, of equal angular dispersions and mounted so that the apex of one is against the base of the other.
prism adaptation See vergence adaptation; prism adaptation test.
aligning prism See associated heterophoria.
prism ballast lens See ballast.
prism bar Clinical device consisting of a series of prisms of increasing strengths arranged in a convenient mount for rapid positioning in front of an eye. It can be used with the cover test or even to measure fusional responses when determining the zone of clear, single, binocular vision if rotary prisms are not available.
base-in prism; base-out prism See base setting.
bi-prism See Fresnel's bi-prism.
prism binoculars See binoculars.
compensating prism See associated heterophoria; relieving prism.
prism
cover test See cover test.
Crete's p . See rotary prism.
prism dioptre See prism dioptre.
dissociating prism A prism which, when placed in front of an eye, produces dissociation.
double prism See Fresnel's bi-prism.
double prism test See double prism test.
Dove prism An isosceles reflecting prism used to invert the image in an optical system. Light enters one side, is then refracted onto the base surface where it is internally reflected and refracted again through the other side.
erecting prism A prism designed to invert an image in an optical system with no change of size or shape. Examples: Dove prism, Porro prism. Syn. inverting prism. See erector.
Fresnel Press-On prism A trade name for a thin disc of transparent plastic consisting of one flat surface which can adhere to a clean lens surface when pressed in place, and another surface on which are incorporated small prismatic elements laid parallel to one another. Large optical effects can thus be provided in a much thinner and lighter form. These Press-On Fresnel prisms can be cut to any desired shape and are used commonly in orthoptics treatment. See Fresnel lens; orthoptics.
Herschel prism See rotary prism.
induced prism Prismatic effect created when the patient's visual axis does not pass through the optical centre of an ophthalmic lens. The amount of prism power is given by Prentice's law. See correction induced convergence; Prentice's law.
inverting p . See prism, erecting.
lacrimal prism See tear meniscus.
minimum deviation of a prism The deviation of light rays from their original path is minimum when light passes symmetrically through a prism so that the incident and emergent angles are equal (Fig. P15). See angle of deviation; prism.
Nicol prism An optical device for producing a beam of plane polarized light. It is made from a piece of calcite crystal cut diagonally in half with the two halves cemented together. Incident light is split into ordinary and extraordinary linearly polarized rays in the prism: the ordinary ray reaches the interface and is totally reflected, while the extraordinary ray is transmitted (Fig. P16). See analyser; birefringence; polarizer.
ophthalmic prism A prism used in the correction or in the measurement of a deviation of the eyes. The power of such a prism is usually only a few prism dioptres. The power of a thin prism in air, represented by the angle of deviation d, is given by the approximate formula
d = (n − 1) a
where n is the index of refraction of the prism and a the prism angle. Example: if the prism angle is equal to 10º and the index of refraction of the prism is 1.523, the deviation will be equal to 5.23º or 9.12 Χ. (Fig. P17). See prism dioptre; prism power.penta prism See Fig. P18.
polarizing prism A prism made from doubly refracting material. Example: quartz. See analyzer; polarized light; polarizer.
Porro prism A combination prism consisting of two 90º totally reflecting prisms arranged at right angles to each other. It is used in optical systems, such as binoculars to invert the image and provide a shorter displacement. It is the most common erecting prism.
prism power See prism power.
reflecting prism A prism in which light is internally reflected at one or more of the plane surfaces before emerging. This happens when the angle of incidence at the surface is greater than the critical angle (Fig. P18). Syn. total reflecting prism. See total reflection.
prism reflex test See Krimsky's method.
relieving prism An ophthalmic prism prescribed to relieve symptoms caused by an uncompensated heterophoria. Syn. compensating prism.
Risley prism See rotary prism.
rotary prism A pair of identical thin prisms mounted one in front of the other, so that they can be rotated by equal amounts in opposite directions to give a resultant power in a single meridian. The power can vary from zero when the apex of one prism coincides with the base of the other, to the sum of the powers of the two prisms when the apices coincide. The Risley prism is a very common type of rotary prism. It is used to determine the limits of the zone of clear, single, binocular vision and also in some stereoscopes (e.g. variable prism stereoscope). Other types of rotary prisms are those of Crete and Herschel. Syn. variable prism. See base setting; variable prism stereoscope.
tear prism See tear meniscus.
total reflecting prism See reflecting prism.
version prism's See yoke prisms.
Wollaston prism Two right-angled prisms of equal angle made of a double refracting crystal such as quartz or calcite cemented together by their hypotenuse faces to form a rectangular unit. The optical axis of the crystal in one prism is perpendicular to that in the other prism and both axes are also perpendicular to the direction of the incident light. A beam of unpolarized light incident on a Wollaston prism will emerge as two diverging beams which are oppositely polarized and almost free of dispersion. This prism is used in some types of keratometers (e.g. Javal-Schiotz). Syn. Wollaston polarizer.
yoke prism's Two prisms, one in front of each eye, of equal deviation and direction (e.g. 2 ΧBU, OU). The apparent view moves towards the apex of the prisms. These are sometimes prescribed in the management of nystagmus, in visual training, for the bedridden (BD prisms) and in some cases of physical disability. (Fig. P19) Note: also spelt yoked prisms. Syn. version prisms.

Fig. P15 Prism (a, prism angle; i, angle of incidence = i′, angle of emergence; Vm, angle of minimum deviation)

Fig. P16 Nicol prism (O, ordinary ray; E, extraordinary ray)

Fig. P17 A line of stars seen through a prism base down

Fig. P18 Examples of reflecting prisms (A, penta prism, with surfaces C coated with silver or aluminium; B and C, in which the surfaces reflect light by total internal reflection)

Fig. P19 Yoke prisms
| Table P10 Approximate deviation of thin ophthalmic prisms of various apical angles and of two different refractive indices | ||||||||
| deviation | ||||||||
| apical angle in degrees (º) | spectacle crown glass (n 5 1.523) | extra dense flint glass (n 5 1.70) | ||||||
| degrees (º) | Χ | degrees (º) | Χ | |||||
| 1 | 0.52 | 0.91 | 0.70 | 1.22 | ||||
| 2 | 1.05 | 1.84 | 1.40 | 2.45 | ||||
| 3 | 1.57 | 2.75 | 2.10 | 3.67 | ||||
| 4 | 2.09 | 3.66 | 2.80 | 4.90 | ||||
| 5 | 2.61 | 4.57 | 3.50 | 6.12 | ||||
| 6 | 3.14 | 5.49 | 4.20 | 7.35 | ||||
| 7 | 3.66 | 6.40 | 4.90 | 8.57 | ||||
| 8 | 4.18 | 7.31 | 5.60 | 9.80 | ||||
| 9 | 4.71 | 8.24 | 6.30 | 11.02 | ||||
| 10 | 5.23 | 9.15 | 7.00 | 12.25 | ||||
| 11 | 5.75 | 10.06 | 7.70 | 13.47 | ||||
| 12 | 6.28 | 10.99 | 8.40 | 14.70 | ||||
Millodot: Dictionary of Optometry and Visual Science, 7th edition. © 2009 Butterworth-Heinemann
Latest Searches:
ViaScint - viannia - Vianain - Vialetto - vial - Viadur - Viactiv - Viactin - viable - viability - VHDL - VHD - VFl - VFib - Vfend - VFC - Vexol - vexans - vexabilis - Vetuss -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp