Medical term:
Cardizem
diltiazem hydrochloride
Pharmacologic class: Calcium channel blocker
Therapeutic class: Antianginal, antiarrhythmic (class IV), antihypertensive
Pregnancy risk category C
Action
Inhibits calcium from entering myocardial and vascular smooth-muscle cells, thereby depressing myocardial and smooth-muscle contraction and decreasing impulse formation and conduction velocity. As a result, systolic and diastolic pressures decrease.
Availability
Capsules (extended-release, sustained-release): 60 mg, 90 mg, 120 mg, 180 mg, 240 mg, 300 mg, 360 mg, 420 mg
Injection: 5 mg/ml in 10-ml vials, 100-mg Monovial
Tablets: 30 mg, 60 mg, 90 mg, 120 mg
Indications and dosages
➣ Angina pectoris and vasospastic (Prinzmetal's) angina; hypertension; supraventricular tachyarrhythmias; atrial flutter or fibrillation
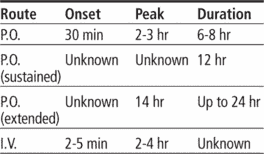
Adults: 30 to 90 mg P.O. three to four times daily (tablets), or 60 to 120 mg P.O. b.i.d. (sustained-release), or 180 to 240 mg P.O. once daily (extended-release), adjusted after 14 days as needed, up to a total daily dosage of 360 mg. Or 0.25 mg/kg by I.V. bolus over 2 minutes; if response is inadequate after 15 minutes, may give 0.35 mg/kg over 2 minutes; may follow with continuous I.V. infusion at 10 mg/hour (at a range of 5 to 15 mg/hour) for up to 24 hours.
Dosage adjustment
• Severe hepatic or renal impairment
• Elderly patients
Off-label uses
• Unstable angina, coronary artery bypass graft surgery
• Tardive dyskinesia
• Migraine
• Hyperthyroidism
• Raynaud's phenomenon
Contraindications
• Hypersensitivity to drug
• Atrial flutter or fibrillation associated with shortened refractory period (Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, with I.V. use)
• Recent myocardial infarction or pulmonary congestion
• Cardiogenic shock, concurrent I.V. beta-blocker therapy, ventricular tachycardia, neonates (with I.V. use, because of benzyl alcohol in syringe formulation)
• Sick sinus syndrome, second- or third-degree atrioventricular block (except in patients with ventricular pacemakers)
• Hypotension (systolic pressure below 90 mm Hg)
Precautions
Use cautiously in:
• severe hepatic or renal impairment, heart failure
• history of serious ventricular arrhythmias
• concurrent use of I.V. diltiazem and I.V. beta blockers
• elderly patients
• pregnant or breastfeeding patients
• children (safety not established).
Administration
• When giving I.V., dilute in dextrose 5% in water or normal saline solution.
• Give I.V. bolus dose over 2 minutes; a second bolus may be given after 15 minutes.
• Administer continuous I.V. infusion at a rate of 5 to 15 mg/hour.
☞ When giving by continuous I.V. infusion, make sure emergency equipment is available and that patient has continuous ECG monitoring with frequent blood pressure monitoring.
• Don't crush tablets or sustained-release capsules; they must be swallowed whole.
• Withhold dose if systolic blood pressure falls below 90 mm Hg, diastolic pressure is below 60 mm Hg, or apical pulse is slower than 60 beats/minute.
Adverse reactions
CNS: headache, abnormal dreams, anxiety, confusion, dizziness, drowsiness, nervousness, psychiatric disturbances, asthenia, paresthesia, syncope, tremor
CV: peripheral edema, bradycardia, chest pain, hypotension, palpitations, tachycardia, arrhythmias, heart failure
EENT: blurred vision, tinnitus, epistaxis
GI: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, dyspepsia, dry mouth
GU: urinary frequency, dysuria, nocturia, polyuria, gynecomastia, sexual dysfunction
Hematologic: anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia
Metabolic: hyperglycemia
Musculoskeletal: joint stiffness, muscle cramps
Respiratory: cough, dyspnea
Skin: rash, dermatitis, flushing, diaphoresis, photosensitivity, pruritus, urticaria, erythema multiforme
Other: unpleasant taste, gingival hyperplasia, weight gain, decreased appetite, Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Interactions
Drug-drug. Beta-adrenergic blockers, digoxin, disopyramide, phenytoin: bradycardia, conduction defects, heart failure
Carbamazepine, cyclosporine, quinidine: decreased diltiazem metabolism, increased risk of toxicity
Cimetidine, ranitidine: increased blood level and effects of diltiazem
Fentanyl, nitrates, other antihypertensives, quinidine: additive hypotension
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, imipramine, sirolimus, tacrolimus: increased blood levels of these drugs
Lithium: decreased lithium blood level, reduced antimanic control
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: decreased antihypertensive effect of diltiazem
Theophylline: increased theophylline effects
Drug-diagnostic tests. Hepatic enzymes: increased levels
Drug-food. Grapefruit juice: increased blood level and effects of diltiazem
Drug-behaviors. Acute alcohol ingestion: additive hypotension
Patient monitoring
• Check blood pressure and ECG before starting therapy, and monitor closely during dosage adjustment period. Withhold dose if systolic pressure is below 90 mm Hg.
☞ Monitor for signs and symptoms of heart failure and worsening arrhythmias.
• Supervise patient during ambulation.
Patient teaching
• Instruct patient to swallow extended-release capsules whole and not to crush or chew them.
• Advise patient to change position slowly to minimize light-headedness and dizziness.
• Caution patient to avoid driving and other hazardous activities until he knows how drug affects concentration and alertness.
• As appropriate, review all other significant and life-threatening adverse reactions and interactions, especially those related to the drugs, tests, foods, and behaviors mentioned above.
Cardizem
(kär′dĭ-zĕm′)Cardizem®
Diltiazem, see there.Latest Searches:
Voraxaze - Voranil - Voorhoeve - voodoo - VOO - Vontrol - von - vomitus - vomiturition - vomitory - vomitoria - vomito - vomitive - vomiting - vomit - vomica - vomerovaginalis - vomerovaginal - vomerorostralis - vomerorostral -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp