Medical term:
Dexair
dexamethasone
[dek″sah-meth´ah-sōn]dexamethasone
dexamethasone sodium phosphate
Pharmacologic class: Glucocorticoid
Therapeutic class: Anti-inflammatory
Pregnancy risk category C
Action
Unclear. Reduces inflammation by suppressing polymorphonuclear leukocyte migration, reversing increased capillary permeability, and stabilizing leukocyte lysosomal membranes. Also suppresses immune response (by reducing lymphatic activity), stimulates bone marrow, and promotes protein, fat, and carbohydrate metabolism.
Availability
Elixir: 0.5 mg/5 ml
Intravitreal implant: 0.7 mg
Oral solution: 0.5 mg/5 ml, 1 mg/ml
Solution for injection (sodium phosphate): 4 mg/ml, 10 mg/ml, 20 mg/ml, 24 mg/ml
Tablets: 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 0.75 mg, 1 mg, 1.5 mg, 2 mg, 4 mg, 6 mg
Indications and dosages
➣ Macular edema following branch retinal vein occlusion or central retinal vein occlusion; noninfectious uveitis affecting posterior segment of eye
Adults: 0.7 mg by intravitreal implant
➣ Allergic and inflammatory conditions
Adults: 0.75 to 9 mg/day (dexamethasone) P.O. as a single dose or in divided doses; in severe cases, much higher dosages may be needed. Dosage requirements vary and must be individualized based on disease and patient response.
➣ Cerebral edema
Adults: Initially, 10 mg (sodium phosphate) I.V., followed by 4 mg I.M. q 6 hours. Then reduce dosage gradually over 5 to 7 days.
➣ Suppression test for Cushing's syndrome
Adults: 1 mg P.O. at 11 P.M. or 0.5 mg P.O. q 6 hours for 48 hours (with urine collection testing, as ordered)
Off-label uses
• Acute altitude sickness
• Bacterial meningitis
• Bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants
• Hirsutism
• Suppression test for detection, diagnosis, or management of depression
Contraindications
• Hypersensitivity to drug, benzyl alcohol, bisulfites, EDTA, creatinine, polysorbate 80, or methylparaben
• Systemic fungal infections
• Active or suspected ocular or periocular infections, advanced glaucoma (intravitreal implant)
Precautions
Use cautiously in:
• renal insufficiency, cirrhosis, diabetes mellitus, diverticulitis, GI disease, cardiovascular disease, hypoprothrombinemia, hypothyroidism, myasthenia gravis, glaucoma, osteoporosis, infections, underlying immunosuppression, psychotic tendencies
• pregnant or breastfeeding patients
• children.
Administration
• Give P.O. dose with food or milk.
• When giving I.M., inject deep into gluteal muscle; rotate sites as needed.
• For I.V. use, drug may be given undiluted as a single dose over 1 minute or added to dextrose or I.V. saline solutions and given as an intermittent infusion at prescribed rate.
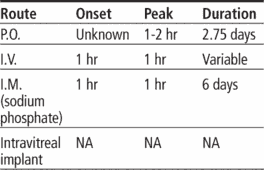
Adverse reactions
CNS: headache, malaise, vertigo, psychiatric disturbances, increased intracranial pressure, seizures
CV: hypotension, thrombophlebitis, myocardial rupture after recent myocardial infarction, thromboembolism
EENT: cataracts; elevated intraocular pressure (IOP), conjunctival hemorrhage (with intravitreal implant)
GI: nausea, vomiting, abdominal distention, dry mouth, anorexia, peptic ulcer, bowel perforation, pancreatitis, ulcerative esophagitis
Metabolic: decreased carbohydrate tolerance, hyperglycemia, cushingoid appearance (moon face, buffalo hump), decreased growth (in children), latent diabetes mellitus, sodium and fluid retention, negative nitrogen balance, adrenal suppression, hypokalemic alkalosis
Musculoskeletal: muscle wasting, muscle pain, osteoporosis, aseptic joint necrosis, tendon rupture, long bone fractures
Skin: diaphoresis, angioedema, erythema, rash, pruritus, urticaria, contact dermatitis, acne, decreased wound healing, bruising, skin fragility, petechiae
Other: facial edema, weight gain or loss, increased susceptibility to infection, hypersensitivity reactions
Interactions
Drug-drug. Barbiturates, phenytoin, rifampin: decreased dexamethasone effects
Digoxin: increased risk of digoxin toxicity
Ephedrine: increased dexamethasone clearance
Estrogen, hormonal contraceptives: blocking of dexamethasone metabolism
Fluoroquinolones: increased risk of tendon rupture
Itraconazole, ketoconazole: increased dexamethasone blood level and effects
Live-virus vaccines: decreased antibody response to vaccine, increased risk of adverse reactions
Loop and thiazide diuretics: additive hypokalemia
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: increased risk of GI adverse effects
Somatrem, somatropin: decreased response to these drugs
Drug-diagnostic tests. Calcium, potassium: decreased levels
Cholesterol, glucose: increased levels
Nitroblue tetrazolium test: false-negative result
Drug-herbs. Echinacea: increased immune-stimulating effect
Ginseng: potentiation of immunemodulating response
Drug-behaviors. Alcohol use: increased risk of gastric irritation and GI ulcers
Patient monitoring
• Monitor blood glucose level closely in diabetic patients receiving drug orally.
• Monitor hemoglobin and potassium levels.
• Assess for occult blood loss.
☞ In long-term therapy, never discontinue drug abruptly. Dosage must be tapered gradually.
• Monitor patient for increased IOP after intravitreal injection.
Patient teaching
☞ Instruct patient to immediately report sudden weight gain, swelling of face or limbs, excessive nervousness or sleep disturbances, excessive body hair growth, vision changes, difficulty breathing, muscle weakness, persistent abdominal pain, or change in stool color.
• Tell patient to take oral drug with or after meals.
• Advise patient to report vision changes and if eye becomes red, sensitive to light, or painful after intravitreal implant, to promptly report this to ophthalmologist.
• Inform patient that drug makes him more susceptible to infection. Advise him to avoid crowds and exposure to illness.
☞ Caution patient not to stop taking drug abruptly.
• As appropriate, review all other significant and life-threatening adverse reactions and interactions, especially those related to the drugs, tests, herbs, and behaviors mentioned above.
dex·a·meth·a·sone
(dek'să-meth'ă-sōn),dexamethasone
(dĕk′sə-mĕth′ə-sōn′, -zōn′)dex·a·meth·a·sone
(DM) (dek'să-meth'ă-sōn)dexamethasone
A synthetic CORTICOSTEROID drug used for its anti-inflammatory action and for its value in reducing OEDEMA of the brain. It is also used to treat severe inflammatory and allergic disorders, shock, congenital adrenal hyperplasia, vomiting caused by chemotherapy, and for the diagnosis of Cushing's disease. The drug is on the WHO official list. Brand names are Decadron and Dexsol. The drug is also used in various combinations.antiinflammatory drug
dex·a·meth·a·sone
(dek'să-meth'ă-sōn)Latest Searches:
Voraxaze - Voranil - Voorhoeve - voodoo - VOO - Vontrol - von - vomitus - vomiturition - vomitory - vomitoria - vomito - vomitive - vomiting - vomit - vomica - vomerovaginalis - vomerovaginal - vomerorostralis - vomerorostral -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp