Medical term:
Levaquin
levofloxacin
Pharmacologic class: Fluoroquinolone
Therapeutic class: Anti-infective
Pregnancy risk category C
FDA Box Warning
Fluoroquinolones for systemic use are associated with an increased risk of tendinitis and tendon rupture in all ages. This risk is further increased in patients usually over age 60, with concomitant use of corticosteroids, and in kidney, heart, and lung transplant recipients.
Action
Inhibits the enzyme DNA gyrase in susceptible gram-negative and gram-positive aerobic and anaerobic bacteria, interfering with bacterial DNA synthesis
Availability
Ophthalmic solution: Quixin-0.5% (5 mg/ml), Iquix-1.5%
Premixed solution for injection: 250 mg/50 ml, 500 mg/100 ml, 750 mg/150 ml
Solution for injection (concentrated): 500 mg/20 ml
Tablets: 250 mg, 500 mg, 750 mg
Indications and dosages
➣ Acute bacterial exacerbation of chronic bronchitis
Adults: 500 mg I.V. or P.O. q 24 hours for 7 days
➣ Community-acquired pneumonia
Adults: 500 mg I.V. or P.O. q 24 hours for 7 to 14 days, or 750 mg I.V. or P.O. q 24 hours for 5 days
➣ Nosocomial pneumonia caused by methicillin-susceptible strains of Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Serratia marcescens, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, or Streptococcus pneumoniae; complicated skin and skin-structure infections
Adults: 750 mg I.V. or P.O. q 24 hours for 7 to 14 days
➣ Acute bacterial sinusitis caused by S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, or Moraxella catarrhalis
Adults: 500 mg I.V. or P.O. q 24 hours for 10 to 14 days or 750 mg P.O. or I.V. q 24 hours for 5 days
➣ Uncomplicated skin and skin-structure infections
Adults: 500 mg I.V. or P.O. q 24 hours for 7 to 10 days
➣ Complicated urinary tract infections; acute pyelonephritis caused by E. coli
Adults: 250 mg I.V. or P.O. q 24 hours for 10 days or 750 mg P.O. or I.V. q 24 hours for 5 days
➣ Uncomplicated urinary tract infections
Adults: 250 mg I.V. or P.O. q 24 hours for 3 days
➣ Chronic bacterial prostatitis
Adults: 500 mg I.V. or P.O. q 24 hours for 28 days.
➣ Conjunctivitis
Adults and children ages 1 and older: One or two drops of 0.5% ophthalmic solution into affected eye q 2 hours while awake on days 1 and 2 (up to eight times daily); then one or two drops q 4 hours while awake on days 3 through 7 (up to four times daily)
➣ Corneal ulcers
Adults and children ages 6 and older: On days 1 to 3, one or two drops of 1.5% ophthalmic solution instilled into affected eye(s) q 30 minutes to 1 hour while awake and q 4 to 6 hours after retiring; thereafter, one or two drops q 1 to 4 hours while awake until treatment completion
➣ Inhalational anthrax (postexposure)
Adults and children ages 6 months and older weighing more than 50 kg (110 lb): 500 mg P.O. or I.V. q 24 hours for 60 days
Children ages 6 months and older weighing less than 50 kg (110 lb): 8 mg/kg P.O. or I.V., not to exceed 250 mg/dose q 12 hours for 60 days
Dosage adjustment
• Renal impairment
Contraindications
• Hypersensitivity to drug, its components, or other quinolones
Precautions
Use cautiously in:
• bradycardia, acute myocardial ischemia, prolonged QTc interval, cirrhosis, renal impairment, underlying CNS disease, uncorrected hypocalcemia
• elderly patients
• pregnant or breastfeeding patients
• children younger than age 18 (except in ophthalmic use).
Administration
• Be aware that oral and I.V. dosages are identical.
• Give parenteral form by I.V. route only. Drug isn't for I.M., subcutaneous, intrathecal, or intraperitoneal use.
• To prepare I.V. infusion, use compatible solution, such as 0.9% sodium chloride injection, dextrose 5% and 0.9% sodium chloride injection, dextrose 5% in water, or dextrose 5% in lactated Ringer's solution.
• Infuse over 60 to 90 minutes, depending on dosage. Don't infuse with other drugs.
☞ Avoid rapid or bolus I.V. administration, because this may cause severe hypotension
• Flush I.V. line before and after infusion.
• Give oral doses 2 hours before or after sucralfate, iron, antacids containing magnesium or aluminum, or multivitamins with zinc.
• Give oral form without regard to food, but don't give with milk or yogurt alone.
• Be aware that the two ophthalmic preparations have different indications.
Adverse reactions
CNS: dizziness, headache, insomnia, seizures
CV: chest pain, palpitations, hypotension
EENT: photophobia, sinusitis, pharyngitis
GI: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, flatulence, pseudomembranous colitis
GU: vaginitis
Hematologic: lymphocytopenia
Metabolic: hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia
Musculoskeletal: back pain, tendon rupture, tendinitis
Skin: photosensitivity
Other: altered taste, reaction and pain at I.V. site, hypersensitivity reactions including Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Interactions
Drug-drug. Antacids containing aluminum or magnesium, didanosine (tablets), iron salts, sucralfate, zinc salts: decreased levofloxacin absorption
Cimetidine: interference with levofloxacin elimination
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: increased risk of CNS stimulation and seizures
Drug-diagnostic tests. Glucose: increased or decreased level
Lymphocytes: decreased count
EEG: abnormal findings
Drug-food. Concurrent tube feedings, milk, yogurt: impaired levofloxacin absorption
Drug-herbs. Dong quai, St. John's wort: phototoxicity
Fennel: decreased levofloxacin absorption
Drug-behaviors. Sun exposure: phototoxicity
Patient monitoring
• Check vital signs, especially blood pressure. Too-rapid infusion can cause hypotension.
• Closely monitor patients with renal insufficiency.
• Monitor blood glucose level closely in diabetic patients.
☞ Assess for severe diarrhea, which may indicate pseudomembranous colitis.
☞ Watch for hypersensitivity reaction. Discontinue drug immediately if rash or other signs or symptoms occur.
☞ Watch for signs and symptoms of tendinitis or tendon rupture.
Patient teaching
☞ Tell patient to stop taking drug and contact prescriber if he experiences signs or symptoms of hypersensitivity reaction (rash, hives, or other skin reactions) or severe diarrhea (which may indicate pseudomembranous colitis).
☞ Instruct patient to stop taking drug and notify prescriber immediately if tendon pain, swelling, or inflammation occurs.
• Instruct patient not to take with milk, yogurt, multivitamins containing zinc or iron, or antacids containing aluminum or magnesium.
• Teach patient proper use of eye drops. Tell him to avoid touching applicator tip to eye, finger, or any other object.
• Caution patient to avoid driving and other activities that require mental alertness until CNS effects of drug are known.
• As appropriate, review all other significant and life-threatening adverse reactions and interactions, especially those related to the drugs, tests, foods, herbs, and behaviors mentioned above.
levofloxacin
(le-voe-flox-a-sin) ,Levaquin
(trade name)Classification
Therapeutic: anti infectivesPharmacologic: fluoroquinolones
Indications
- Urinary tract infections, including cystitis, pyelonephritis, and prostatitis,
- Respiratory tract infections, including acute sinusitis, acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis, community-acquired pneumonia, and nosocomial pneumonia,
- Uncomplicated and complicated skin and skin structure infections.
Action
Therapeutic effects
- Staphylococcus aureus,
- Staphylococcus epidermidis,
- Staphylococcus saprophyticus,
- Streptococcus pyogenes,
- Streptococcus pneumoniae,
- Enterococcus faecalis,
- Bacillus anthracis.
- Escherichia coli,
- Klebsiella pneumoniae,
- Enterobacter cloacae,
- Proteus mirabilis,
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa,
- Serratia marcescens,
- Haemophilus influenzae,
- Moraxella catarrhalis.
- Chlamydophylia pneumoniae,
- Legionella pneumoniae,
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and Yersinia pestis
Pharmacokinetics
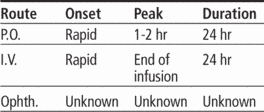
Time/action profile (blood levels)
| ROUTE | ONSET | PEAK | DURATION |
| PO | rapid | 1–2 hr | 24 hr |
| IV | rapid | end of infusion | 24 hr |
Contraindications/Precautions
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Central nervous system
- elevated intracranial pressure (including pseudotumor cerebri) (life-threatening)
- seizures (life-threatening)
- agitation
- anxiety
- confusion
- depression
- dizziness
- drowsiness
- hallucinations
- headache
- insomnia
- nightmares
- paranoia
- tremor
Cardiovascular
- torsade de pointes (life-threatening)
- QT interval prolongation
Gastrointestinal
- hepatotoxicity (life-threatening)
- pseudomembranous colitis (life-threatening)
- nausea (most frequent)
- abdominal pain
- diarrhea
- vomiting
Genitourinary
- vaginitis
Dermatologic
- stevens-johnson syndrome (life-threatening)
- photosensitivity
- rash
Endocrinologic
- hyperglycemia
- hypoglycemia
Local
- phlebitis at IV site
Neurologic
- peripheral neuropathy
Musculoskeletal
- arthralgia
- tendinitis
- tendon rupture
Miscellaneous
- hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis (life-threatening)
Interactions
Drug-Drug interaction
Concurrent use of amiodarone, disopyramide, procainamide, quinidine, dofetilide, or sotalol ↑ risk of torsade de pointes in susceptible individuals (avoid concurrent use).↑ serum theophylline levels and may lead to toxicity.Administration withantacids, iron salts, bismuth subsalicylate, sucralfate, and zinc salts ↓ absorption.May ↑ the effects of warfarin.Serum levels may be ↓ by antineoplastic agents.Cimetidine may interfere with elimination.Probenecid ↓ renal elimination.May ↑ the risk of nephrotoxicity from cyclosporine.Concurrent therapy with corticosteroids may ↑ the risk of tendon rupture.Absorption is impaired by concurrent enteral feeding (because of metal cations).Route/Dosage
Renal Impairment
Oral Intravenous (Adults) Normal renal function dosing of 750 mg/day: CCr 20–49 mL/min—750 mg q 48 hr; CCr 10–19 mL/min—750 mg initially, then 500 mg q 48 hr; Normal renal function dosing of 500 mg/day: CCr 20–49 mL/min—500 mg initially then 250 mg q 24 hr; CCr 10–19 mL/min—500 mg initially then 250 mg q 48 hr. Normal renal function dosing of 250 mg/day: CCr 10–19 mL/min—250 mg q 48 hr.Availability (generic available)
Nursing implications
Nursing assessment
- Assess for infection (vital signs; appearance of wound, sputum, urine, and stool; WBC; urinalysis; frequency and urgency of urination; cloudy or foul-smelling urine) at beginning of and during therapy.
- Obtain specimens for culture and sensitivity before initiating therapy. First dose may be given before receiving results.
- Observe patient for signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis (rash, pruritus, laryngeal edema, wheezing). Discontinue drug and notify physician or other health care professional immediately if these problems occur. Keep epinephrine, an antihistamine, and resuscitation equipment close by in case of an anaphylactic reaction.
- Monitor bowel function. Diarrhea, abdominal cramping, fever, and bloody stools should be reported to health care professional promptly as a sign of pseudomembranous colitis. May begin up to several weeks following cessation of therapy.
- Assess for rash periodically during therapy. May cause Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Discontinue therapy if severe or if accompanied with fever, general malaise, fatigue, muscle or joint aches, blisters, oral lesions, conjunctivitis, hepatitis and/or eosinophilia.
- Assess for signs and symptoms of peripheral neuropathy (pain, burning, tingling, numbness, and/or weakness or other alterations of sensation including light touch, pain, temperature, position sense, and vibratory sensation) periodically during therapy. Symptoms may be irreversible; discontinue levofloxacin if symptoms occur.
- Lab Test Considerations: May cause ↑ serum AST, ALT, LDH, bilirubin, and alkaline phosphatase.
- May also cause ↑ or ↓ serum glucose.
Potential Nursing Diagnoses
Risk for infection (Patient/Family Teaching)Implementation
- Do not confuse levofloxacin with levetiracetam.
- Oral: May be administered without regard to meals. Products or foods containing calcium, magnesium, aluminum, iron, zinc should not be ingested for 4 hr before and 2 hr after administration.
Intravenous Administration
- pH: 3.8–5.8.
- Intermittent Infusion: Diluent: Dilute to a with 0.9% NaCl, D5W, D5/0.9% NaCl, D5/0.45% NaCl, or D5/LR. Concentration: 5 mg/mL. Also available in premixed bottles and flexible containers with D5W, which need no further dilution. Discard unused solution. Diluted solution is stable for 72 hr at room temperature and 14 days if refrigerated.
- Rate: Administer by infusion over at least 60 min for 250–mg or 500–mg doses and over 90 min for 750–mg dose. Avoid rapid bolus injection to prevent hypotension.
- Y-Site Compatibility: alemtuzumab, alfentanil, amifostine, amikacin, aminocaproic acid, aminophylline, ampicillin, ampicillin/sulbactam, anidulafungin, argatroban, atracurium, aztreonam, bivalirudin, bleomycin, bumetanide, buprenorphine, busulfan, butorphanol, caffeine citrate, calcium gluconate, carboplatin, carmustine, caspofungin, cefepime, cefotetan, ceftaroline, ceftazidime, ceftriaxone, cefuroxime, chlorpromazine, cisatracurium, cisplatin, clindamycin, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, cytarabine, dacarbazine, dactomycin, daptomycin, dexamethasone, dexmedetomidine, dexrazoxane, digoxin, diltiazem, diphenhydramine, dobutamine, docetaxel, dolasetron, dopamine, doripenem, doxacurium, doxycycline, droperidol, enalaprilat, ephedrine, epinephrine, epirubicin, eptifibatide, ertapenem, erythromycin, esmolol, etoposide, etoposide phosphate, famotidine, fenoldopam, fentanyl, filgrastim, floxuridine, fluconazole, fludarabine, foscarnet, fosphenytoin, gemcitabine, gentamicin, granisetron, haloperidol, hydrocortisone, hydromorphone, idarubicin, ifosfamide, imipenem/cilastatin, irinotecan, isoproterenol, labetalol, leucovorin, levorphanol, lidocaine, linezolid, mannitol, mechlorethamine, meperidine, mesna, methylprednisolone, metoclopramide, metronidazole, midazolam, milrinone, mitomycin, mitoxantrone, mivacurium, mycohpenolate, nalbuphine, naloxone, nesiritide, octreotide, ondansetron, oxacillin, oxaliplatin, oxytocin, paclitaxel, palonosetron, pamidronate, pancuronium, pemetrexed, penicillin G sodium, pentamidine, phenylephrine, plicamycin, potassium acetate, potassium chloride, promethazine, propranolol, quinapristin/dalfopristin, ranitidine, remifentanil, rocuronium, sargramostim, sodium acetate, sodium bicarbonate, succinylcholine, sufentanil, tacrolimus, teniposide, theophylline, thiotepa, ticarcillin/clavulanate, tigecycline, tirofiban, tobramycin, topotecan, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, vancomycin, vasopressin, vecuronium, verapamil, vinblastine, vincristine, vinorelbine, voriconazole, zidovudine, zoledronic acid
- Y-Site Incompatibility: acyclovir, alprostadil, amiodarone, amphotericin B colloidal, amphotericin B lipid complex, amphotericin B liposome, cefazolin, cefoperazone, cefoxitin, daunorubicin hydrochloride, diazepam, drotrecogin, fluorouracil, furosemide, ganciclovir, heparin, inamrinone, indomethacin, ketorolac, methotrexate, micafungin, nitroglycerin, nitroprusside, pantoprazole, pentobarbital, phenytoin, piperacillin/tazobactam, prochlorperazine, propofol, rituximab, streptozocin, telavancin, thiopental, trastuzumab
Patient/Family Teaching
- Instruct patient to take medication as directed at evenly spaced times and to finish drug completely, even if feeling better. Take missed doses as soon as possible, unless almost time for next dose. Do not double doses. Advise patient that sharing of this medication may be dangerous.
- Advise patients to notify health care professional immediately if they are taking theophylline.
- Encourage patient to maintain a fluid intake of at least 1500–2000 mL/day to prevent crystalluria.
- Advise patient that antacids or medications containing calcium, magnesium, aluminum, iron, or zinc will decrease absorption and should not be taken within 4 hr before and 2 hr after taking this medication.
- May cause dizziness and drowsiness. Caution patient to avoid driving or other activities requiring alertness until response to medication is known.
- Advise patient to notify health care professional of any personal or family history of QTc prolongation or proarrhythmic conditions such as recent hypokalemia, significant bradycardia, or recent myocardial ischemia or if fainting spells or palpitations occur. Patients with this history should not receive levofloxacin.
- Advise patient to stop taking levofloxacin and notify health care professional immediately if signs and symptoms of peripheral neuropathy occur.
- Caution patient to use sunscreen and protective clothing to prevent phototoxicity reactions during and for 5 days after therapy. Notify health care professional if a sunburn-like reaction or skin eruption occurs.
- Advise patient to report signs of superinfection (furry overgrowth on the tongue, vaginal itching or discharge, loose or foul-smelling stools).
- Advise patient to notify health care professional of all Rx or OTC medications, vitamins, or herbal products being taken and to consult with health care professional before taking other medications.
- Instruct patient to notify health care professional if fever and diarrhea develop, especially if stool contains blood, pus, or mucus. Advise patient not to treat diarrhea without consulting health care professional.
- Instruct patient to notify health care professional immediately if rash, jaundice, signs of hypersensitivity, or tendon (shoulder, hand, Achilles, and other) pain, swelling, or inflammation occur. If tendon symptoms occur, avoid exercise and use of the affected area. Increased risk in >65 yr old, kidney, heart and lung transplant recipients, and patients taking corticosteroids concurrently. Therapy should be discontinued.
Evaluation/Desired Outcomes
- Resolution of the signs and symptoms of bacterial infection. Time for complete resolution depends on organism and site of infection.
- Avoidance of signs and symptoms of inhalational anthrax (postexposure treatment).
- Prevention and treatment of plague.
Levaquin
(lĕv′ə-kwĭn′)Levaquin®
Levofloxacin, see there.Latest Searches:
Voraxaze - Voranil - Voorhoeve - voodoo - VOO - Vontrol - von - vomitus - vomiturition - vomitory - vomitoria - vomito - vomitive - vomiting - vomit - vomica - vomerovaginalis - vomerovaginal - vomerorostralis - vomerorostral -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp