Medical term:
Lorazepam
lorazepam
[lor-az´ĕ-pam]lorazepam
Pharmacologic class: Benzodiazepine
Therapeutic class: Anxiolytic
Controlled substance schedule IV
Pregnancy risk category D
Action
Unknown. Thought to depress CNS at limbic system and disrupt neurotransmission in reticular activating system.
Availability
Injection: 2 mg/ml, 4 mg/ml
Solution (concentrated): 2 mg/ml
Tablets: 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 2 mg
Indications and dosages
➣ Anxiety
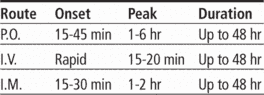
Adults: 2 to 3 mg P.O. daily in two or three divided doses. Maximum dosage is 10 mg daily.
➣ Insomnia
Adults: 2 to 4 mg P.O. at bedtime
➣ Premedication before surgery (as antianxiety agent, sedative-hypnotic, or amnestic)
Adults: 0.05 mg/kg (not to exceed 4 mg) deep I.M. injection at least 2 hours before surgery, or 0.044 mg/kg (not to exceed 2 mg) I.V. 15 to 20 minutes before surgery. For greater amnestic effect, give up to 0.05 mg/kg (not to exceed 4 mg) I.V. 15 to 20 minutes before surgery.
➣ Status epilepticus
Adults: 4 mg I.V. given slowly (no faster than 2 mg/minute). If seizures continue or recur after 10 to 15 minutes, repeat dose. If seizure control isn't established after second dose, other measures should be used. Don't exceed 8 mg in 12 hours.
Dosage adjustment
• Elderly or debilitated patients
Off-label uses
• Acute alcohol withdrawal syndrome
Contraindications
• Hypersensitivity to drug, other benzodiazepines, polyethylene or propylene glycol, or benzyl alcohol
• Acute angle-closure glaucoma
• Coma or CNS depression
• Hepatic or renal failure
Precautions
Use cautiously in:
• hepatic or renal impairment
• history of suicide attempt, drug abuse, depressive disorder, or psychosis
• elderly patients
• pregnant or breastfeeding patients.
Administration
• For I.V. use, dilute with equal volume of compatible diluent, such as normal saline solution or dextrose 5% in water. Keep resuscitation equipment and oxygen at hand.
☞ Give each 2 mg of I.V. dose slowly, over 2 to 5 minutes. Don't exceed rate of 2 mg/minute.
• Don't give parenteral form to children younger than age 18.
Adverse reactions
CNS: amnesia, agitation, ataxia, depression, disorientation, dizziness, drowsiness, headache, incoordination, asthenia
CV (with too rapid I.V. administration): hypotension, bradycardia, tachycardia, apnea, cardiac arrest, cardiovascular collapse
EENT: blurred vision, diplopia, nystagmus
GI: nausea, abdominal discomfort
Other: increased or decreased appetite
Interactions
Drug-drug. CNS depressants (including antidepressants, antihistamines, benzodiazepines, sedative-hypnotics): additive CNS depression
Hormonal contraceptives: increased lorazepam clearance
Drug-herbs. Chamomile, hops, kava, skullcap, valerian: increased CNS depression
Drug-behaviors. Alcohol use: increased CNS depression
Smoking: increased metabolism and decreased efficacy of lorazepam
Patient monitoring
☞ During I.V. administration, monitor ECG and cardiovascular and respiratory status.
• Monitor vital signs closely.
• Evaluate for amnesia.
• Watch closely for CNS depression. Institute safety precautions as needed to prevent injury.
☞ Monitor for signs and symptoms of overdose (such as confusion, hypotension, coma, and labored breathing).
• Assess liver function tests and CBC.
Patient teaching
• Tell patient and family about drug's possible CNS effects. Recommend appropriate safety precautions.
• Explain that with long-term use, drug must be discontinued slowly (typically over 8 to 12 weeks).
• Instruct patient to avoid alcohol, because it increases drowsiness and other CNS effects.
• Caution patient to avoid smoking, because it speeds drug breakdown in body.
• Advise female patient to inform prescriber if she is pregnant or breastfeeding.
• As appropriate, review all other significant and life-threatening adverse reactions and interactions, especially those related to the drugs, herbs, and behaviors mentioned above.
lorazepam
(lôr-ăz′ə-păm′)lorazepam
Neuropharmacology A benzodiazepine anxiolytic, antidepressant, sedative, hypnoticlorazepam
A benzodiazepine tranquillizer drug similar to diazepam). A brand name is Ativan.Latest Searches:
Voraxaze - Voranil - Voorhoeve - voodoo - VOO - Vontrol - von - vomitus - vomiturition - vomitory - vomitoria - vomito - vomitive - vomiting - vomit - vomica - vomerovaginalis - vomerovaginal - vomerorostralis - vomerorostral -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp