Medical term:
Neoral
cyclosporine
cyclosporine ophthalmic emulsion
Pharmacologic class: Polypeptide antibiotic
Therapeutic class: Immunosuppressant
Pregnancy risk category C
Respiratory: cough, dyspnea, Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, bronchospasm
FDA Box Warning
• Drug should be prescribed only by physicians experienced in managing systemic immunosuppressive therapy for indicated disease. At doses used for solid-organ transplantation, it should be prescribed only by physicians experienced in immunosuppressive therapy and management of organ transplant recipients. Patient should be managed in facility with adequate laboratory and medical resources. Physician responsible for maintenance therapy should have complete information needed for patient follow-up.
• Neoral may increase susceptibility to infection and neoplasia. In kidney, liver, and heart transplant patients, drug may be given with other immunosuppressants.
• Sandimmune should be given with adrenal corticosteroids but not other immunosuppressants. In transplant patients, increased susceptibility to infection and development of lymphoma and other neoplasms may result from increased immunosuppression.
• Sandimmune and Neoral aren't bioequivalent. Don't use interchangeably without physician supervision.
• In patients receiving Sandimmune soft-gelatin capsules and oral solution, monitor at repeated intervals (due to erratic absorption).
Action
Unclear. Thought to act by specific, reversible inhibition of immunocompetent lymphocytes in G0-G1 phase of cell cycle. Preferentially inhibits T lymphocytes; also inhibits lymphokine production. Ophthalmic action is unknown.
Availability
Capsules: 25 mg, 100 mg
Injection: 50 mg/ml
Oral solution: 100 mg/ml
Solution (ophthalmic): 0.05% (0.4 ml in 0.9 ml single-use vial)
Indications and dosages
➣ Psoriasis
Adults: Neoral only-1.25 mg/kg P.O. b.i.d. for 4 weeks. Based on patient response, may increase by 0.5 mg/kg/day once q 2 weeks, to a maximum dosage of 4 mg/kg/day.
➣ Severe active rheumatoid arthritis
Adults: Neoral only-1.25 mg/kg P.O. b.i.d. May adjust dosage by 0.5 to 0.75 mg/kg/day after 8 weeks and again after 12 weeks, to a maximum dosage of 4 mg/kg/day. If no response occurs after 16 weeks, discontinue therapy. Gengraf only-2.5 mg/kg P.O. daily given in two divided doses; after 8 weeks, may increase to a maximum dosage of 4 mg/kg/day.
➣ To prevent organ rejection in kidney, liver, or heart transplantation
Adults and children: Sandimmune only-Initially, 15 mg/kg P.O. 4 to 12 hours before transplantation, then daily for 1 to 2 weeks postoperatively. Reduce dosage by 5% weekly to a maintenance level of 5 to 10 mg/kg/day. Or 5 to 6 mg/kg I.V. as a continuous infusion 4 to 12 hours before transplantation.
➣ To increase tear production in patients whose tear production is presumed to be suppressed due to ocular inflammation associated with keratoconjunctivitis sicca
Adults: 1 drop in each eye b.i.d. given 12 hours apart
Off-label uses
• Aplastic anemia
• Atopic dermatitis
Contraindications
• Hypersensitivity to drug and any ophthalmic components
• Rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis in patients with abnormal renal function, uncontrolled hypertension, cancer (Gengraf, Neoral)
• Active ocular infections (ophthalmic use)
Precautions
Use cautiously in:
• hepatic impairment, renal dysfunction, active infection, hypertension
• herpes keratitis (ophthalmic use)
• pregnant or breastfeeding patients
• children younger than age 16 (safety and efficacy not established for ophthalmic use).
Administration
• For I.V. infusion, dilute as ordered with dextrose 5% in water or 0.9% normal saline solution. Administer over 2 to 6 hours.
• Mix Neoral solution with orange juice or apple juice to improve its taste.
• Dilute Sandimmune oral solution with milk, chocolate milk, or orange juice. Be aware that grapefruit and grapefruit juice affect drug metabolism.
• In postoperative patients, switch to P.O. dosage as tolerance allows.
• Be aware that Sandimmune and Neoral aren't bioequivalent. Don't use interchangeably.
• Before administering eyedrops, invert unit-dose vial a few times to obtain a uniform, white, opaque emulsion.
• Know that eyedrops can be used concomitantly with artificial tears, allowing a 15-minute interval between products.
Adverse reactions
CV: hypertension, chest pain, myocardial infarction
EENT: visual disturbances, hearing loss, tinnitus, rhinitis; (with ophthalmic use) ocular burning, conjunctival hyperemia, discharge, epiphora, eye pain, foreign body sensation, itching, stinging, blurring
GI: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal discomfort, gastritis, peptic ulcer, mouth sores, difficulty swallowing, anorexia, upper GI bleeding, pancreatitis
GU: gynecomastia, hematuria, nephrotoxicity, renal dysfunction, glomerular capillary thrombosis Hematologic: anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia
Metabolic: hyperglycemia, hypomagnesemia, hyperuricemia, hyperkalemia, metabolic acidosis
Musculoskeletal: muscle and joint pain
Respiratory: cough, dyspnea, Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, bronchospasm
Skin: acne, hirsutism, brittle fingernails, hair breakage, night sweats
Other: gum hyperplasia, flulike symptoms, edema, fever, weight loss, hiccups, anaphylaxis
Interactions
The following interactions pertain to oral and I.V. routes only.
Drug-drug. Acyclovir, aminoglycosides, amphotericin B, cimetidine, diclofenac, gentamicin, ketoconazole, melphalan, naproxen, ranitidine, sulindac, sulfamethoxazole, tacrolimus, tobramycin, trimethoprim, vancomycin: increased risk of nephrotoxicity
Allopurinol, amiodarone, bromocriptine, clarithromycin, colchicine, danazol, diltiazem, erythromycin, fluconazole, imipenem and cilastatin, itraconazole, ketoconazole, methylprednisolone, nicardipine, prednisolone, quinupristin/dalfopristin, verapamil: increased cyclosporine blood level
Azathioprine, corticosteroids, cyclophosphamide: increased immunosuppression Carbamazepine, isoniazid, nafcillin, octreotide, orlistat, phenobarbital, phenytoin, rifabutin, rifampin, ticlopidine: decreased cyclosporine blood level
Digoxin: decreased digoxin clearance
Live-virus vaccines: decreased antibody response to vaccine
Lovastatin: decreased lovastatin clearance, increased risk of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis
Potassium-sparing diuretics: increased risk of hyperkalemia
Drug-diagnostic tests. Alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, bilirubin, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, glucose, low-density lipoproteins: increased levels
Hemoglobin, platelets, white blood cells: decreased values
Drug-food. Grapefruit, grapefruit juice: decreased cyclosporine metabolism, increased cyclosporine blood level
High-fat diet: decreased drug absorption (Neoral)
Drug-herbs. Alfalfa sprouts, astragalus, echinacea, licorice: interference with immunosuppressant action St. John's wort: reduced cyclosporine blood level, possibly leading to organ rejection
Patient monitoring
• Observe patient for first 30 to 60 minutes of infusion. Monitor frequently thereafter.
• Monitor cyclosporine blood level, electrolyte levels, and liver and kidney function test results.
• Assess for signs and symptoms of hyperkalemia in patients receiving concurrent potassium-sparing diuretic.
Patient teaching
• Advise patient to dilute Neoral oral solution with orange or apple juice (preferably at room temperature) to improve its flavor.
• Instruct patient to use glass container when taking oral solution. Tell him not to let solution stand before drinking, to stir solution well and then drink all at once, and to rinse glass with same liquid and then drink again to ensure that he takes entire dose.
• Tell patient taking Neoral to avoid high-fat meals, grapefruit, and grapefruit juice.
• Advise patient to dilute Sandimmune oral solution with milk, chocolate milk, or orange juice to improve its flavor.
• Instruct patient to invert vial a few times to obtain a uniform, white, opaque emulsion before using eyedrops and to discard vial immediately after use.
• Inform patient that eyedrops can be used with artificial tears but to allow 15-minute interval between products.
• Caution patient not to wear contact lenses because of decreased tear production; however, if contact lenses are used, advise patient to remove them before administering eyedrops and to reinsert 15 minutes after administration.
• Inform patient that he's at increased risk for infection. Caution him to avoid crowds and exposure to illness.
• Instruct patient not to take potassium supplements, herbal products, or dietary supplements without consulting prescriber.
• Tell patient he'll need to undergo repeated laboratory testing during therapy.
• As appropriate, review all other significant and life-threatening adverse reactions and interactions, especially those related to the drugs, tests, foods, and herbs mentioned above.
cycloSPORINE†
(sye-kloe-spor-een) ,Gengraf
(trade name),Neoral
(trade name),SandIMMUNE
(trade name)Classification
Therapeutic: immunosuppressantsPharmacologic: polypeptides
†See for ophthalmic use
Indications
Action
Therapeutic effects
Pharmacokinetics
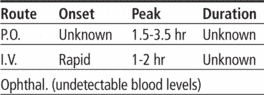
Time/action profile (blood levels)
| ROUTE | ONSET | PEAK | DURATION |
|---|---|---|---|
| PO | unknown† | 2–6 hr | unknown |
| IV | unknown | end of infusion | unknown |
Contraindications/Precautions
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Central nervous system
- posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (life-threatening)
- progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (life-threatening)
- seizures (life-threatening)
- tremor (most frequent)
- confusion
- flushing
- headache
- psychiatric problems
Cardiovascular
- hypertension (most frequent)
Gastrointestinal
- hepatotoxicity (life-threatening)
- diarrhea (most frequent)
- nausea (most frequent)
- vomiting (most frequent)
- abdominal discomfort
- anorexia
- pancreatitis
Genitourinary
- nephrotoxicity (most frequent)
Dermatologic
- hirsutism (most frequent)
- acne
- psoriasis
Fluid and Electrolyte
- hyperkalemia
- hypomagnesemia
Hematologic
- anemia
- leukopenia
- thrombocytopenia
Metabolic
- hyperlipidemia
- hyperuricemia
Neurologic
- hyperesthesia
- paresthesia
Miscellaneous
- gingival hyperplasia (most frequent)
- hypersensitivity reactions (most frequent)
- infections (including activation of latent viral infections such as BK virus-associated nephropathy) (most frequent)
- malignancy
Interactions
Drug-Drug interaction
Azithromycin,clarithomycin, allopurinol, amiodarone, bromocriptine, colchicine, danazol, digoxin, diltiazem, erythromycin, fluconazole, fluoroquinolones, imatinib, itraconazole, ketoconazole, voriconazole, metoclopramide, methylprednisolone, nefazodone, nicardipine, protease inhibitors, quinupristin/dalfopristin, verapamil, boceprevir, telaprevir, or hormonal contraceptives may ↑ serum levels and risk of toxicity.↑ immunosuppression with other immunosuppressants (cyclophosphamide, azathioprine, corticosteroids).Bosentan, carbamazepine, nafcillin, octreotide, orlistat, oxcarbazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, rifampin, rifabutin, or terbinafine, or ticlopidine may ↓ levels and effect.↑ risk of hyperkalemia with potassium-sparing diuretics, potassium supplements, or ACE inhibitors.May ↑ serum levels and risk of toxicity of aliskiren, ambrisentan, bosentan, colchicine, digoxin, etoposide, HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, methotrexate, nifedipine, repaglinide, sirolimus May ↓ antibody response to live-virus vaccines and ↑ risk of adverse reactions; avoid concurrent use.Concurrent use with tacrolimus should be avoided.↑ risk of renal dysfunction with ciprofloxacin, aminoglycosides, vancomycin, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, melphalan, amphotericin B, ketoconazole, colchicine, NSAIDS, cimetidine, ranitidine, or fibric acid derivatives Concomitant use with echinacea and melatonin may interfere with immunosuppression.Use with St. John’s wort may cause ↓ serum levels and organ rejection for transplant patients.Concurrent ingestion of grapefruit or grapefruit juice may ↑serum levels and should be avoided.Food ↓ absorption of microemulsion products (Neoral).Route/Dosage
Doses are adjusted on the basis of serum level monitoringPrevention of Transplant Rejection (Sandimmune)Availability (generic available)
Nursing implications
Nursing assessment
- Monitor serum creatinine level, intake and output ratios, daily weight, and BP during therapy. Report significant changes.
- Assess for any new signs or symptoms that may be suggestive of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML), an opportunistic infection of the brain caused by the Jakob Cruzfeldt (JC) virus, that may be fatal; withhold dose and notify health care professional promptly. PML symptoms may begin gradually (hemiparesis, apathy, confusion, cognitive deficiencies, and ataxia) and may include deteriorating renal function and renal graft loss.
- Monitor for signs and symptoms of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) (impaired consciousness, convulsions, visual disturbances including blindness, loss of motor function, movement disorders and psychiatric disturbances, papilloedema, visual impairment). Usually reversible with discontinuation of cyclosporine. Occurs more often in patients with liver transplant than kidney transplant.
- Prevention of Transplant Rejection: Assess for symptoms of organ rejection throughout therapy.
- Intravenous: Monitor patient for signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity (wheezing, dyspnea, flushing of face or neck) continuously during at least the first 30 min of each treatment and frequently thereafter. Oxygen, epinephrine, and equipment for treatment of anaphylaxis should be available with each IV dose.
- Arthritis: Assess pain and limitation of movement prior to and during administration.
- Prior to initiating therapy, perform a physical exam including BP on 2 occasions to determine baseline. Monitor BP every 2 wk during initial 3 mo, then monthly if stable. If hypertension occurs, dose should be reduced.
- Psoriasis: Assess skin lesions prior to and during therapy.
- Lab Test Considerations: Measure serum creatinine, BUN, CBC, magnesium, potassium, uric acid, and lipids at baseline, every 2 wk during initial therapy, and then monthly if stable. Nephrotoxicity may occur; report significant increases.
- May cause hepatotoxicity; monitor for ↑ AST, ALT, alkaline phosphatase, amylase, and bilirubin.
- May cause ↑ serum potassium and uric acid levels and ↓ serum magnesium levels.
- Serum lipid levels may be ↑.
Evaluate serum cyclosporine levels periodically during therapy. Dose may be adjusted daily, in response to levels, during initiation of therapy. Guidelines for desired serum levels will vary among institutions.
Potential Nursing Diagnoses
Chronic pain (Indications)Risk for infection (Side Effects)
Implementation
- Do not confuse cycloSPORINE with cyclophosphamide or cycloSERINE. Do not confuse Sandimmune with Sandostatin.
- Given with other immunosuppressive agents. Protect transplant patients from staff and visitors who may carry infection. Maintain protective isolation as indicated.
- Microemulsion products (Neoral) and other products (Sandimmune) are not interchangeable.
- Oral: Draw up oral solution in the pipette provided with the medication. Mix oral solution with milk, chocolate milk, apple juice, or orange juice, preferably at room temperature. Stir well and drink at once. Use a glass container and rinse with more diluent to ensure that total dose is taken. Administer oral doses with meals. Wipe pipette dry; do not wash after use.
Intravenous Administration
- pH: No Data.
- Intermittent Infusion: Diluent: Dilute each 1 mL (50 mg) of IV concentrate immediately before use with 20–100 mL of D5W or 0.9% NaCl for injection. Solution is stable for 24 hr in D5W. In 0.9% NaCl, it is stable for 6 hr in a polyvinylchloride container and 12 hr in a glass container at room temperature.Concentration: 2.5 mg/mL.
- Rate: Infuse slowly over 2–6 hr via infusion pump.
- Continuous Infusion: May be administered over 24 hr.
- Y-Site Compatibility: alemtuzumab, alfentanil, amikacin, aminocaproic acid, aminophylline, amphotericin B lipid complex, anidulafungin, argatroban, ascorbic acid, atracurium, atropine, azathioprine, aztreonam, benztropine, bivalirudin, bleomycin, bumetanide, buprenorphine, butorpohanol, calcium chloride, calcium gluconate, carboplatin, carmustine, caspofungin, cefazolin, cefoperazone, cefotaxime, cefotetan, cefoxitin, ceftaroline, ceftazidime, ceftriaxone, cefuroxime, chloramphenicol, chlorpromazine, cisplatin, clindamycin, cyclophosphamide, cytarabine, dactinomycin, daptomycin, dexamethasone, dexmedetomidine, dexrazoxane, digoxin, diltiazem, diphenhydramine, dobutamine, docetaxel, dopamine, doripenem, doxacurium, doxarubicin hydrochloride, doxorubicin liposomal, doxycycline, enalaprilat, ephedrine, epinephrine, epirubicin, epoetin alfa, ertapenem, erythromycin, esmolol, etoposide, etoposide phosphate, famotidine, fenoldopam, fentanyl, fluconazole, fludarabine, fluorouracil, folic acid, foscarnet, furosemide, ganciclovir, gemcitabine, gentamicin, glycopyrrolate, granisetron, heparin, hetastarch, hydrocortisone, hydromorphone, ifosfamide, imipenem/cilastatin, indomethacin, irinotecan, isoproterenol, ketorolac, labetalol, leucovorin calcium, levofloxacin, lidocaine, linezolid, lorazepam, mannitol, mechlorethamine, meperidine, meropenem, metaraminol, methotrexate, methyldopate, methylprednisolone, metoclopramide, metoprolol, metronidazole, micafungin, midazolam, milrinone, mitoxantrone, morphine, moxifloxacin, multivitamins, nafcillin, naloxone, nesiritide, nicardipine, nitroglycerin, nitroprusside, norepinephrine, octreotide, ondansetron, oxacillin, oxaliplatin, oxytocin, paclitaxel, palonosetron, pamidronate, pancuronium, papaverine, pemetrexed, penicillin G,, pentamidine, pentazocine, phentolamine, phenylephrine, phytonadione, piperacillin/tazobactam, potassium acetate, potassium chloride, prochlorperazine, promethazine, propofol, propranolol, protamine, pyridoxime, quinupristin/dalfopristin, ranitidine, sargramostim, sodium acetate, sodium bicarbonate, streptokinase, succinylcholine, sufentanil, tacrolimus, teniposide, theophylline, thiamine, thiotepa, ticarcillin/clavulanate, tigecycline, tirofiban, tobramycin, tolazoline, vancomycin, vasopressin, vecuronium, verapamil, vinblastine, vincristine, vinorelbine, zoledronic acid
- Y-Site Incompatibility: amphotericin B cholesteryl, amphotericin B liposome, cyanocobalamin, dantrolene, diazepam, diazoxide, idarubicin, pentobarbital, phenobarbital, phenytoin, rituximab, trastuzumab, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, voriconazole
Patient/Family Teaching
- Instruct patient to take medication at the same time each day with meals, as directed. Do not skip doses or double up on missed doses. Take missed doses as soon as remembered within 12 hr. Do not discontinue medication without advice of health care professional.
- Reinforce the need for lifelong therapy to prevent transplant rejection. Review symptoms of rejection for transplanted organ, and stress need to notify health care professional immediately if they occur.
- Instruct patients and/or parents to notify health care professional if diarrhea develops; decreases absorption of cyclosporine and can result in rejection.
- Instruct patient to avoid grapefruit and grapefruit juice to prevent interaction with cyclosporine.
- Advise patient of common side effects (nephrotoxicity, increased BP, hand tremors, increased facial and body hair, gingival hyperplasia). Advise patients that if hair growth is excessive, depilatories or waxing can be used.
- Teach patient the correct method for monitoring BP. Instruct patient to notify health care professional of significant changes in BP or if hematuria, increased frequency, cloudy urine, decreased urine output, fever, sore throat, tiredness, or unusual bruising occurs.
- Instruct patient on proper oral hygiene. Meticulous oral hygiene and dental examinations for teeth cleaning and plaque control every 3 mo will help decrease gingival inflammation and hyperplasia.
- Instruct patient to notify health care professional of all Rx or OTC medications, vitamins, or herbal products being taken and consult health care professional before taking other Rx, OTC, or herbal products or receiving any vaccinations while taking this medication.
- Advise patient to notify health care professional if pregnancy is planned or suspected, or if breast feeding.
- Emphasize the importance of follow-up exams and lab tests.
Evaluation/Desired Outcomes
- Prevention of rejection of transplanted tissues.
- Decrease in severity of pain.
- Increased ease of joint movement.
- Decrease in progression of psoriasis.
Neoral®
Cyclosporine for microemulsion Immunology An immunosuppressant for reducing organ rejection in kidney, liver, heart transplants; to manage severe, active rheumatoid arthritis unresponsive to MTX; to manage adult, nonimmunocompromised Pts with severe, recalcitrant, plaque psoriasis who are unresponsive to one or more systemic therapies–ie, PUVA, retinoids, or MTX--or in Pts for whom either systemic therapies are contraindicated or cannot be tolerated. See Immunosuppression.Latest Searches:
Voraxaze - Voranil - Voorhoeve - voodoo - VOO - Vontrol - von - vomitus - vomiturition - vomitory - vomitoria - vomito - vomitive - vomiting - vomit - vomica - vomerovaginalis - vomerovaginal - vomerorostralis - vomerorostral -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp