Medical term:
Triderm
triamcinolone
[tri″am-sin´o-lōn]a prednisolone derivative used in replacement therapy for adrenocortical insufficiency and as an antiinflammatory and immunosuppressant in a wide variety of disorders; administered orally in the form of the acetonide, diacetate, and hexacetonide esters.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
triamcinolone
(trī′ăm-sĭn′ə-lōn′)n.
A synthetic glucocorticoid, C21H27FO6, used, usually in acetal or acetate forms, in the treatment of a wide variety of inflammatory and allergic conditions.
The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
triamcinolone
A CORTICOSTEROID drug used to treat inflammatory disorders, ASTHMA, THROMBOCYTOPENIA and some forms of LEUKAEMIA. Brand names are Adcortyl, Adcortyl in Orabase, Kenalog, Lederspan and Nasacort. Triamcinolone is also an ingredient is a range of preparations for external use.Collins Dictionary of Medicine © Robert M. Youngson 2004, 2005
antiinflammatory drug
A drug which inhibits or suppresses most inflammatory responses of an allergic, bacterial, traumatic or anaphylactic origin, as well as being immunosuppressant. They include the corticosteroids (e.g. betamethasone, dexamethasone, fluorometholone, hydrocortisone acetate, loteprednol etabonate, prednisolone, rimexolone, triamcinolone). They are sometimes combined with an antibiotic drug (e.g. betamethasone combined with neomycin or sulfacetamide, dexamethasone combined with neomycin or polymyxin B). Corticosteroids have side effects, such as enhancing the activity of herpes simplex virus, fungal overgrowth, raising intraocular pressure or cataract formation.There are other antiinflammatory drugs that are non-steroidal (NSAID) and have little toxicity. They act mainly by blocking prostaglandin synthesis. These include diclofenac sodium, flurbiprofen sodium, indomethacin, ketorolac, nepafenac and oxyphenbutazone. See immunosuppressants; steroid.
chalazion
A chronic inflammatory lipogranuloma due to retention of the secretion (such as blocked ducts) of a meibomian gland in the tarsus of an eyelid. It is characterized by a gradual painless swelling of the gland without marked inflammatory signs and sometimes astigmatism which is induced by the cyst pressing on the cornea (Fig. C5). Small chalazia may disappear spontaneously but large ones usually have to be incised and curetted (i.e. removal of the pus with a scraper) through a tarsal incision. Resolution may also occur after local injection of a corticosteroid drug (e.g. dexamethasone or triamcinolone). Syn. meibomian cyst (although it is not a true cyst because its walls are made of granulomatous tissue and not lined with epithelium). See internal hordeolum.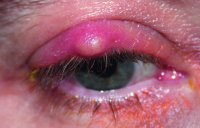


Fig. C5 Upper eyelid chalazion
Millodot: Dictionary of Optometry and Visual Science, 7th edition. © 2009 Butterworth-Heinemann
Latest Searches:
Voraxaze - Voranil - Voorhoeve - voodoo - VOO - Vontrol - von - vomitus - vomiturition - vomitory - vomitoria - vomito - vomitive - vomiting - vomit - vomica - vomerovaginalis - vomerovaginal - vomerorostralis - vomerorostral -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp