Medical term:
Umbilical
umbilical
[um-bil´ĭ-kal]pertaining to the umbilicus.
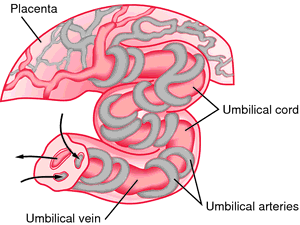
umbilical cord the structure that connects the fetus and placenta; it is the lifeline of the fetus in the uterus throughout pregnancy. About 2 weeks after conception, the umbilical cord and the placenta are sufficiently developed to begin their functions. Through two arteries and a vein in the cord, nourishment and oxygen pass from the blood vessels in the placenta to the fetus, and waste products pass from the fetus to the placenta. Soon after birth, the umbilical cord is clamped or tied and then cut. The part that is attached to the placenta, still in the uterus, is expelled with the placenta. The stump that remains attached to the baby's abdomen is about 2 inches (5 cm) long. After a few days it falls off naturally.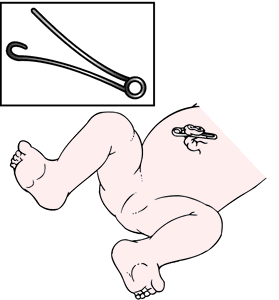

Clamping the umbilical cord.

Umbilical cord with umbilical vein and umbilical arteries. From McKinney, 2000.
umbilical hernia protrusion of abdominal contents through the abdominal wall at the umbilicus, the defect in the abdominal wall and protruding intestine being covered with skin and subcutaneous tissue. Called also exomphalos and exumbilication.
During the growth of the fetus, the intestines grow more rapidly than the abdominal cavity. For a period, a portion of the intestines of the unborn child usually lies outside the abdomen in a sac within the umbilical cord. Normally, the intestines return to the abdomen, and the defect is closed by the time of birth. Occasionally the abdominal wall does not close solidly, and umbilical hernia results. This defect is more likely to be seen in premature infants and in girls rather than boys. It usually closes by itself. Coughing, crying, and straining temporarily cause the sac to enlarge, but the hernia never bursts and digestion is not affected. If the defect in the abdominal wall has not repaired itself by the time the child is 2 years old, surgery to correct the condition (herniorrhaphy) can then be performed.
Umbilical hernia should be distinguished from omphalocele, in which the intestines protrude directly into the umbilical cord and are covered only by a thin membrane. Omphalocele is a surgical emergency that must be treated immediately after birth.
During the growth of the fetus, the intestines grow more rapidly than the abdominal cavity. For a period, a portion of the intestines of the unborn child usually lies outside the abdomen in a sac within the umbilical cord. Normally, the intestines return to the abdomen, and the defect is closed by the time of birth. Occasionally the abdominal wall does not close solidly, and umbilical hernia results. This defect is more likely to be seen in premature infants and in girls rather than boys. It usually closes by itself. Coughing, crying, and straining temporarily cause the sac to enlarge, but the hernia never bursts and digestion is not affected. If the defect in the abdominal wall has not repaired itself by the time the child is 2 years old, surgery to correct the condition (herniorrhaphy) can then be performed.
Umbilical hernia should be distinguished from omphalocele, in which the intestines protrude directly into the umbilical cord and are covered only by a thin membrane. Omphalocele is a surgical emergency that must be treated immediately after birth.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
um·bil·i·cal
(ŭm-bil'i-kăl),Relating to the umbilicus.
Synonym(s): omphalic
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
umbilical
(ŭm-bĭl′ĭ-kəl)adj.
1. Of, relating to, or resembling a navel or an umbilical cord.
2. Located near the central area of the abdomen.
n. Aerospace
An umbilical cord.
um·bil′i·cal·ly adv.
The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
umbilical
adjective Referring to the umbilicus.Pronunciation
Medspeak-UK: pronounced, umm bih LIE cull
Medspeak-US: pronounced, I
Segen's Medical Dictionary. © 2012 Farlex, Inc. All rights reserved.
um·bil·i·cal
(ŭm-bil'i-kăl)Relating to the umbilicus.
Synonym(s): omphalic.
Synonym(s): omphalic.
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
Umbilical
Referring to the opening in the abdominal wall where the blood vessels from the placenta enter.
Mentioned in: Abdominal Wall Defects
Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights reserved.
Latest Searches:
Voraxaze - Voranil - Voorhoeve - voodoo - VOO - Vontrol - von - vomitus - vomiturition - vomitory - vomitoria - vomito - vomitive - vomiting - vomit - vomica - vomerovaginalis - vomerovaginal - vomerorostralis - vomerorostral -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp