Medical term:
acromegaly
acromegaly
[ak″ro-meg´ah-le]excessive enlargement of the limbs due to thickening of bones and soft tissues, caused by hypersecretion of growth hormone, usually from a tumor of the pituitary gland. In adults whose bone growth has stopped, the bones most affected are those of the face, jaw, hands, and feet (see accompanying illustration).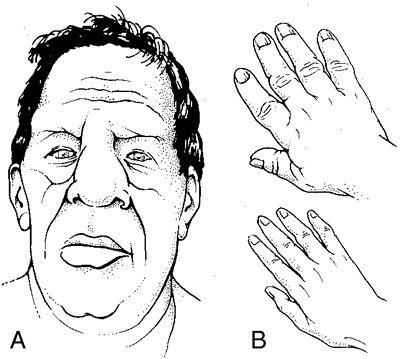 Gradual enlargement of paranasal sinuses, prominence of nose and supraorbital ridges, prognathism, widely separated teeth, and an underbite are part of the coarsening of facial features. Early signs include increased metabolism and strength and profuse sweating. Later joint pain, weakness, and sometimes diabetes mellitus and visual disturbances are seen. In children overproduction of growth hormone stimulates growth of long bones and results in gigantism. Surgical treatment includes removal of the tumor or the pituitary gland (transsphenoidal hypophysectomy), pituitary irradiation, or a combination of the two. Drug therapy with the dopamine receptor agonist bromocriptine may be used as adjuvant therapy in conjunction with either surgery or radiation.
Gradual enlargement of paranasal sinuses, prominence of nose and supraorbital ridges, prognathism, widely separated teeth, and an underbite are part of the coarsening of facial features. Early signs include increased metabolism and strength and profuse sweating. Later joint pain, weakness, and sometimes diabetes mellitus and visual disturbances are seen. In children overproduction of growth hormone stimulates growth of long bones and results in gigantism. Surgical treatment includes removal of the tumor or the pituitary gland (transsphenoidal hypophysectomy), pituitary irradiation, or a combination of the two. Drug therapy with the dopamine receptor agonist bromocriptine may be used as adjuvant therapy in conjunction with either surgery or radiation.

Appearance in acromegaly: A, facial appearance; B, acromegalic hand (upper) and normal hand (lower). From Dorland's, 2000.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
ac·ro·meg·a·ly
(ak'rō-meg'ă-lē), [MIM*102200]A disorder marked by progressive enlargement of peripheral parts of the body, especially the head, face, hands, and feet, resulting from excessive secretion of somatotropin; organomegaly and metabolic disorders occur; diabetes mellitus may develop.
Synonym(s): acromegalia
[acro- + G. megas, large]
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
acromegaly
(ăk′rō-mĕg′ə-lē)n.
A chronic disorder caused by overproduction of human growth hormone usually by the pituitary gland, characterized by enlargement of the bones of the extremities and the skull and often by the development of complications such as diabetes, hypertension, and osteoarthritis.
ac′ro·me·gal′ic (-mĭ-găl′ĭk) adj. & n.
The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
acromegaly
A disease caused by excess growth hormone (GH) by anterior pituitary or extrapituitary origin that occurs after the closure of epiphyseal plates after puberty. Excess GH production that precedes the closure of the epiphyseal growth plates results in gigantism in afflicted children and adolescentsAetiology
Secretion of GH by anterior pituitary; GH-releasing hormone by hypothalamic tumours; ectopic GH production by small-cell carcinoma of lung, carcinoids, islet cell tumours, adrenal adenomas or other endocrine tumours.
Clinical findings
Coarsened, enlarged facies, lips, tongue, nose, jaw, hands, feet, supraorbital ridge and frontal bones, widely spaced teeth, bone proliferation in extremities, soft tissue thickening, hyperhidrosis, macroglossia, headache, amenorrhoea, impotence, somnolence, moodiness, glucose intolerance, cardiomegaly with heart failure (acromegalic heart disease), hypertension, carpal tunnel syndrome, sleep apnoea.
Management
Surgery—endonasal transphenoidal excision of the pituitary tumour; medical—somatostatin analogues (e.g., octreotide, lanreotide, which inhibit growth hormone production); in unresponsive cases dopamine agonists may work.
Segen's Medical Dictionary. © 2012 Farlex, Inc. All rights reserved.
acromegaly
Endocrinology A disease of adults due to excess hGH secretion of anterior pituitary or extrapituitary origin, or due to excess secretion of GH-RH by hypothalamic tumors or ectopic hGH production by small cell carcinoma of the lungs, carcinoids, islet cell tumors, adrenal adenomas or other 'endocrine' tumors Clinical Coarsened, enlarged facies, lips, nose, jaw, hands, feet, and frontal bones, widely spaced teeth, bone proliferation in extremities, soft tissue thickening, hyperhidrosis, macroglossia, headache, amenorrhea, impotence, somnolence, moodiness, glucose intolerance, HTN, heart disease, carpal tunnel syndrome, sleep apnea. See Giantism. See Acromegaloidism.McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine. © 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
ac·ro·meg·a·ly
(ak'rō-meg'ă-lē)A disorder marked by progressive enlargement of the head, face, hands, and feet, due to excessive secretion of somatotropin; organomegaly and metabolic disorders occur; diabetes mellitus may develop.
[acro- + G. megas, large]
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
acromegaly
A serious disorder resulting from overproduction of growth hormone by the pituitary gland during adult life, after the growing ends of the bones (the epiphyses) have fused and the normal growth process is complete. The condition is usually the result of a benign tumour of the pituitary gland. There is no change in body height, but gradual enlargement of the jaw, tongue, nose, ribs, hands and feet occurs. There is also CUTIS VERTICIS GYRATA. If excessive growth hormone production occurs before the epiphyses have fused the result is gigantism. Acromegaly is treated by removing the cause.Collins Dictionary of Medicine © Robert M. Youngson 2004, 2005
acromegaly
a chronic disease characterized by enlargement of the head, hands and feet, causing gigantism. It is caused by over-secretion of growth hormones from the anterior PITUITARY GLAND.Collins Dictionary of Biology, 3rd ed. © W. G. Hale, V. A. Saunders, J. P. Margham 2005
Acromegaly
A rare disease resulting from excessive growth hormone caused by a benign tumor. If such a tumor develops within the first 10 years of life, the result is gigantism (in which growth is accelerated) and not acromegaly. Symptoms include coarsening of the facial features, enlargement of the hands, feet, ears, and nose, jutting of the jaw, and a long face.
Mentioned in: Growth Hormone Tests, Thyroid Function Tests
Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights reserved.
ac·ro·meg·a·ly
(ak'rō-meg'ă-lē) [MIM*102200]Disorder marked by progressive enlargement of peripheral body parts due to excessive secretion of somatotropin; organomegaly and metabolic disorders occur; diabetes mellitus may develop.
Synonym(s): hyperpituitarism.
[acro- + G. megas, large]
Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions © Farlex 2012
Latest Searches:
Voraxaze - Voranil - Voorhoeve - voodoo - VOO - Vontrol - von - vomitus - vomiturition - vomitory - vomitoria - vomito - vomitive - vomiting - vomit - vomica - vomerovaginalis - vomerovaginal - vomerorostralis - vomerorostral -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp