cord
[kord] any long, cylindrical, flexible structure; called also chord, chorda, and funiculus.
spermatic cord the structure extending from the abdominal inguinal ring to the testis, comprising the pampiniform plexus, nerves, ductus deferens, testicular artery, and other vessels.
spinal cord see spinal cord.
tethered cord a congenital anomaly resulting from defective closure of the neural tube; the conus medullaris is abnormally low and tethered by a short, thickened filum terminale, fibrous bands, intradural lipoma, or some other intradural abnormality. Surgical correction in infancy or early childhood is necessary to prevent progressive neurological deficit in the lower limb and bladder dysfunction.
umbilical cord see umbilical cord.
vocal c's see vocal cords.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
cord
(kōrd), [TA] Avoid the misspelling chord.1. In anatomy, any long ropelike structure, composed of several to many longitudinally oriented fibers, vessels, ducts, or combinations thereof.
See also: chorda.
2. In histopathology, a line of tumor cells only one cell in width.
Synonym(s): fasciculus (2) [TA], funiculus [TA], funicle
[L. chorda, a string]
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
cord
(kôrd)n. also chord Anatomy A long ropelike structure, such as a nerve or tendon: a spinal cord.
cord′er n.
The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
cord
ENT See Fixed vocal cord, Spinal cord, Vocal cord Obstetrics See Umbilical cord. McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine. © 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
cord
(kōrd) [TA] 1. anatomy Any long, ropelike structure. A small, cordlike structure composed of several to many longitudinally oriented fibers, vessels, ducts, or combinations thereof.
Synonym(s): fasciculus (2) [TA] , funiculus [TA] , funicle.
2. histopathology A line of tumor cells only one cell in width.
[L. chorda, a string]
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
cord
(kord) [Gr. khorde] 1. A stringlike structure.
2. The umbilical cord.
3. A firm, elongated structure consistent with a thrombosed vein, esp. in the extremities, where it may be felt on palpation.
nuchal cord
The condition in which the umbilical cord is found wrapped around the neck of the fetus during delivery. If the cord cannot be unwrapped easily, or if there is more than one loop, the cord should be clamped and cut before delivery continues.
splenic cord
A spongelike cord in the red pulp of the spleen composed of macrophages and dendritic cells. The macrophages phagocytize pathogens, cell debris, and cells that are old, abnormal, or damaged, esp. red blood cells. Phagocytosis may be increased when the spleen is enlarged (splenomegaly). Synonym: cords of Billroth
spermatic cord
The cord by which the testis is connected to the abdominal inguinal ring. It surrounds the ductus deferens, blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves supplying the testis and epididymis. These are enclosed in the cremasteric fascia, which forms an investing sheath.
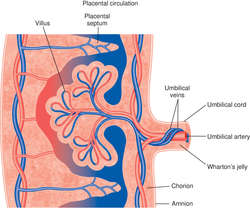

UMBILICAL CORD
umbilical cord
The attachment connecting the fetus with the placenta. It contains two arteries and one vein surrounded by a gelatinous substance (Wharton's jelly). The umbilical arteries carry blood from the fetus to the placenta, where nutrients are obtained and carbon dioxide and oxygen are exchanged; this oxygenated blood returns to the fetus through the umbilical vein. See:
illustrationThe umbilical cord is surgically severed after the birth of the child. To give the infant a better blood supply, the cord should not be cut or tied until the umbilical vessels have ceased pulsating. However, in preterm infants, the cord should be clamped and cut before pulsation ceases to avoid maternal-newborn transfusion and reduce the risk of hypovolemia, polycythemia, and hyperbilirubinemia.
The stump of the severed cord atrophies and leaves a depression on the abdomen of the child (the navel, umbilicus, or belly button).
Willis cord
See: Willis, ThomasMedical Dictionary, © 2009 Farlex and Partners
cord
(kōrd) [TA] In anatomy, any long ropelike structure, composed of several to many longitudinally oriented fibers, vessels, ducts, or combinations thereof.
[L. chorda, a string]
Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions © Farlex 2012
Patient discussion about cord
Q. How can I fix my vocal cords? Please I am in need of desperate help.
A. rest, which means no talking,
Q. what does c4-5 mild central disk bulging impinging upon cervical cord without spinal stenosis or distortion of the cord . mild righ neural foraminal narrowing from uncovertebral joint hypertropy mean
A. Well this basically means there is a very small narrowing of the cervical (your neck area) spinal canal (where the spinal cord is), however the narrowing does not cause any damage to the spinal cord, therefore probably does not cause any major symptoms involving the nerves. The c4-5 bulging part refers to the part in between the two cervical vertebras c4 and c5, in which the disc (a part in the spinal cord) is sliding a bit side-ways, but again, it does not seem to be causing any trouble.
More discussions about cordThis content is provided by iMedix and is subject to iMedix Terms. The Questions and Answers are not endorsed or recommended and are made available by patients, not doctors.
