Medical term:
epithelial
epithelial
[ep″ĭ-the´le-al]pertaining to or composed of epithelium.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
ep·i·the·li·al
(ep'i-thē'lē-ăl),Relating to or consisting of epithelium.
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
epithelial
adjective Referring to epithelium, which lines internal and external surfaces of the body.Segen's Medical Dictionary. © 2012 Farlex, Inc. All rights reserved.
ep·i·the·li·al
(ep'i-thē'lē-ăl)Relating to or consisting of epithelium.
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
epithelium
(ep?i-the'le-um) ('le-a) plural.epithelia [ epi- + Gr. thele, nipple, teat + -ium (2)]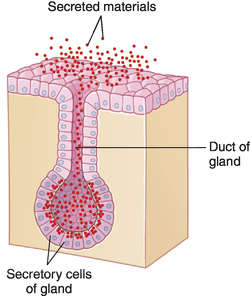
GLANDULAR EPITHELIUM: (Orig. mag. ×430)
The layer of cells forming the epidermis of the skin and the surface layer of mucous and serous membranes. The cells rest on a basement membrane and lie in close approximation with little intercellular material between them. They are devoid of blood vessels. The epithelium may be simple, consisting of a single layer, or stratified, consisting of several layers. Cells making up the epithelium may be flat (squamous), cube-shaped (cuboidal), or cylindrical (columnar). Modified forms of epithelium include ciliated, pseudostratified, glandular, and neuroepithelium. The epithelium may include goblet cells, which secrete mucus. Stratified squamous epithelium may be keratinized for a protective function or abnormally keratinized in pathological response. Squamous epithelium is classified as endothelium, which lines the blood vessels and the heart, and mesothelium, which lines the serous cavities. Epithelium serves the general functions of protection, absorption, and secretion, and specialized functions such as movement of substances through ducts, production of germ cells, and reception of stimuli. Its ability to regenerate is excellent; it may replace itself as frequently as every 24 hr. See: illustration; skinepithelial (-al), adjective
ciliated epithelium
Epithelium with hairlike processes on the surface that wave actively only in one direction. This type is present in the respiratory tract and fallopian tubes.
columnar epithelium
Epithelium composed of cylindrical cells.
cuboidal epithelium
Epithelium consisting of cube-shaped or prismatic cells with height about equal to their width.
germinal epithelium
1. Epithelium that covers the surface of the genital ridge of the urogenital folds of an embryo. It gives rise to the seminiferous tubules of the testes and the surface layer of the ovary. It was once thought to produce the germ cells (spermatozoa and ova).
2. The epithelium that covers the surface of a mature mammalian ovary.
glandular epithelium
Epithelium consisting of secretory cells.
junctional epithelium
A band of nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium that attaches both to the gingiva (on one side) and the crown of the tooth (on the other). Synonym: epithelial attachment; gingival cuff
laminated epithelium
Stratified epithelium.mesenchymal epithelium
Squamous epithelium that lines the subarachnoid and subdural cavities, the chambers of the eye, and the perilymphatic spaces of the ear.
pavement epithelium
Epithelium consisting of flat, platelike cells in a single layer.
pigmented epithelium
Epithelium containing pigment granules.
pseudostratified epithelium
Epithelium in which the bases of cells rest on the basement membrane but the distal ends of some do not reach the surface. Their nuclei lie at different levels, giving the appearance of stratification.
reduced enamel epithelium
Combined epithelial layers of the enamel organ, which form a protective layer over the enamel crown as it erupts and then become the primary epithelial attachment surrounding the tooth.
squamous epithelium
The flat form of epithelial cells.
stratified epithelium
Epithelium with the cells in layers; mitosis takes place in the lowest layer. Synonym: laminated epithelium
sulcular epithelium
The nonkeratinized epithelium that lines the gingival sulcus.
transitional epithelium
A form of stratified epithelium in which the cuboidal cells adjust to mechanical changes such as stretching and recoiling. This type of tissue is found only in the urinary system (renal pelvis, ureter, bladder, and a part of the urethra).
Medical Dictionary, © 2009 Farlex and Partners
ep·i·the·li·al
(ep'i-thē'lē-ăl)Relating to or consisting of epithelium.
Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions © Farlex 2012
Word not found in the Dictionary and Encyclopedia. Did you mean:
- epithelialize
- epithelialise
Latest Searches:
Voraxaze - Voranil - Voorhoeve - voodoo - VOO - Vontrol - von - vomitus - vomiturition - vomitory - vomitoria - vomito - vomitive - vomiting - vomit - vomica - vomerovaginalis - vomerovaginal - vomerorostralis - vomerorostral -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp