Medical term:
hypophyseal
pituitary
[pĭ-tu´ĭ-tar″e]1. pertaining to the pituitary gland.
2. pituitary gland.
3. a preparation of the pituitary glands of animals, used therapeutically.
pituitary gland an endocrine gland located at the base of the brain in a small recess of the sphenoid bone called the sella turcica. It is attached by the hypophyseal stalk to the hypothalamus and is divided into an anterior lobe (the adenohypophysis) and a posterior lobe (the neurohypophysis), which differ in embryological function and origin. Called also hypophysis.
The adenohypophysis originates from epithelial tissue. The adenohypophysis secretes six important hormones: growth hormone, thyroid-stimulating hormone or thyrotropin, adrenocorticotropic hormone or corticotropin, prolactin, follicle-stimulating hormone, and luteinizing hormone. Most of these hormones are tropic hormones, which regulate the growth, development, and proper functioning of other endocrine glands and are of vital importance to the growth, maturation, and reproduction of the individual. Secretion of the anterior pituitary hormones is controlled by releasing and inhibiting hormones produced by the hypothalamus. Information gathered by the nervous system about the well-being of an individual is collected in the hypothalamus and used to control the secretion of hormones by the pituitary gland. The hypothalamic releasing and inhibiting hormones are transported to the pituitary gland by way of the hypothalamic-hypophyseal portal system in which the hypothalamic venules connect with the capillaries of the anterior pituitary.
The neurohypophysis originates from neural tissue; it stores and secretes two hormones, oxytocin and vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone). These hormones are synthesized in the cell bodies of neurons located in the hypothalamus and transported along the axons to the terminals located in the neurohypophysis and are released in response to neural stimulation.
Surgical removal of part or all of the pituitary gland is called hypophysectomy and is usually done for treatment of a pituitary tumor. Because of its influence on the adrenal cortex and other endocrine glands, removal of the pituitary gland has widespread effects on the body. See hypophysectomy.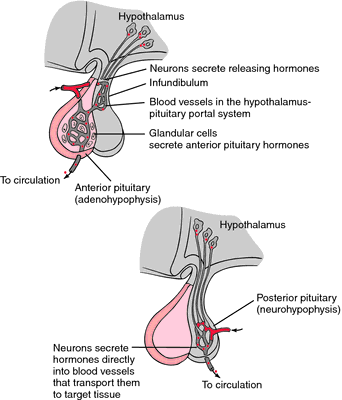
The adenohypophysis originates from epithelial tissue. The adenohypophysis secretes six important hormones: growth hormone, thyroid-stimulating hormone or thyrotropin, adrenocorticotropic hormone or corticotropin, prolactin, follicle-stimulating hormone, and luteinizing hormone. Most of these hormones are tropic hormones, which regulate the growth, development, and proper functioning of other endocrine glands and are of vital importance to the growth, maturation, and reproduction of the individual. Secretion of the anterior pituitary hormones is controlled by releasing and inhibiting hormones produced by the hypothalamus. Information gathered by the nervous system about the well-being of an individual is collected in the hypothalamus and used to control the secretion of hormones by the pituitary gland. The hypothalamic releasing and inhibiting hormones are transported to the pituitary gland by way of the hypothalamic-hypophyseal portal system in which the hypothalamic venules connect with the capillaries of the anterior pituitary.
The neurohypophysis originates from neural tissue; it stores and secretes two hormones, oxytocin and vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone). These hormones are synthesized in the cell bodies of neurons located in the hypothalamus and transported along the axons to the terminals located in the neurohypophysis and are released in response to neural stimulation.
Surgical removal of part or all of the pituitary gland is called hypophysectomy and is usually done for treatment of a pituitary tumor. Because of its influence on the adrenal cortex and other endocrine glands, removal of the pituitary gland has widespread effects on the body. See hypophysectomy.

The pituitary gland and its relationship to the hypothalamus.
posterior pituitary neurohypophysis.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
hy·po·phy·si·al
(hī'pō-fiz'ē-ăl),Relating to a hypophysis.
Synonym(s): hypophyseal
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
Latest Searches:
Voraxaze - Voranil - Voorhoeve - voodoo - VOO - Vontrol - von - vomitus - vomiturition - vomitory - vomitoria - vomito - vomitive - vomiting - vomit - vomica - vomerovaginalis - vomerovaginal - vomerorostralis - vomerorostral -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp