implant
1. (im-plant´) to insert or graft material, such as tissue or radioactive material, into intact tissues or a body cavity; see also transplant.
2. (im´plant) any material inserted or grafted into the body.
cochlear implant see cochlear implant.
dental implant a prosthetic tooth with an anchoring structure surgically implanted beneath the mucosal or periosteal layer or in the bone.
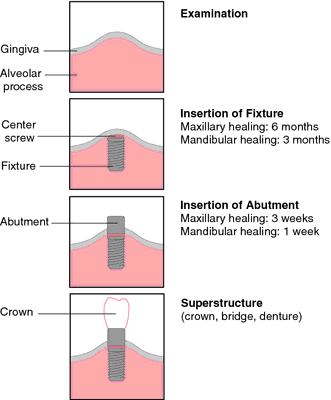
Sequence of treatment with osseointegrated dental implants. From Darby and Walsh, 1995.
penile implant penile prosthesis.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
im·plant
(im'plant), 1. To graft or insert.
See also: graft, transplant, prosthesis.
2. A surgically inserted or imbedded graft or device; also, a zone of cells or tissue transferred from another site through a developmental error or neoplastic process.
See also: graft, transplant, prosthesis.
[L. im-, in, + planto, pp. -atus, to plant, fr. planta, a sprout, shoot]
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
implant
(ĭm-plănt′)v. im·planted, im·planting, im·plants
v.tr. Medicine a. To insert or embed (an object or a device) surgically: implant a drug capsule; implant a pacemaker.
b. To graft or insert (a tissue) within the body.
v.intr. Embryology To become attached to and embedded in the uterine lining. Used of a fertilized egg.
n. (ĭm′plănt′) Something implanted, especially a surgically implanted tissue or device: a dental implant; a subcutaneous implant.
im·plant′a·ble adj.
The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
implant
Audiology
See Cochlear implant.
Breast
A pliable silicone shell filled with saline (formerly with silicone gel) and placed between the skin and pectoral muscle o cosmetically enhance the breasts.
Dentistry
A titanium device—e.g., Brånemark system, Nobelpharma—which is surgically placed in the mandible or maxilla and allowed to “fuse” for 3 to 6 months to the bone (osseointegration), which serves as an anchor for attaching artificial teeth.
Medspeak
Any device placed into a surgically or naturally formed cavity of the human body and intended to remain there for a period of 30 days or more.
Oncology
See Tumour implant.
Pathology
(1) A generic term for a secondary tumour nodule, often understood to mean a mass that is not contiguous with the primary neoplasm, which is most common on the free surface of the peritoneum.
The term as used in surgical pathology is semantically problematic as it implies implantation of a primary lesion elsewhere in the peritoneal cavity, usually of the ovary, and ignores the possible origin of such implants from “renegade” embryonic rests in the peritoneal cavity and/or a multicentric origin of the lesions.
(2) A cluster of epithelial cells in the peritoneal cavity in patients with epithelial ovarian neoplasms that are of either borderline (i.e., of uncertain malignant potential) or frankly malignant (e.g., serous, mucinous cystadenocarcinoma).
Radiation oncology
A small amount of radioisotope sealed in a needle, seed, wire, or catheter, which is placed directly within or near a tumour to deliver brachytherapy.
Surgery
noun A device that is inserted to preserve or maintain a function (e.g., a hip or knee prosthesis), or to preserve, enhance or alter a contour (e.g., a breast or chin implant).
verb To surgically place such a device in its appropriate site.Segen's Medical Dictionary. © 2012 Farlex, Inc. All rights reserved.
implant
A material that is not original to its location. See Baerveldt glaucoma implant, Bioimplant, Dental implant, Molteno implant, Penile implant, Silicone implant, Visual implant Audiology See Cochlear implant Breast surgery A silicone shell shaped in the form of a breast and filled with saline or silicone gel Dentistry A titanium device–eg, Brånemark system, Nobelpharma that is surgically placed in the mandible or maxilla, allowed to 'fuse' in 3 to 6 months to the bone–osseointegration, which serves as an anchor for attaching artificial teeth Oncology Tumor implant, see there Surgery noun A device that is inserted to preserve or maintain a function–eg, a hip or knee prosthesis, or to preserve, enhance or alter a contour–eg, a breast or chin implant verb To surgically place such a device in its appropriate site. See Breast implant, Permanent adjustable implant. McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine. © 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
im·plant
(im-plant) 1. To graft or insert.
2. Material inserted or grafted into tissues.
See also: graft, transplant
3. dentistry a graft or insert set in or onto the alveolar recess prepared for its insertion.
See also: implant denture
4. orthopedics A metallic or plastic device employed in joint reconstruction.
[L. im-, in, + planto, pp. -atus, to plant, fr. planta, a sprout, shoot]
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
implant
(im'plant?) [ ¹in- + plant] An object inserted into the body, e.g., a piece of tissue, a tooth, a pellet of medicine, a tube or needle containing a radioactive substance, liquid and solid plastic materials used to augment tissues or to fill in areas traumatically or surgically removed, artificial joints, and/or for other therapeutic purposes. See: mammaplasty, augmentation
auditory brainstem implant
An auditory prosthesis that bypasses the cochlea and auditory nerve and partially restores hearing by directly stimulating the cochlear nucleus complex. This type of implant helps those with retrocochlear deafness. The implant electrode is inserted directly into the auditory brainstem and is used for those who cannot benefit from cochlear implants because of lesions of the cochlea and/or auditory nerve. It has been used to treat patients who have undergone surgical excision of an acoustic neuroma. Synonym: brainstem implant
bone implant
An implant to repair bone or to cover implanted objects such as artificial hips or tooth implants.
brain implant
Any substance, tissue, or object placed surgically in the brain.
brainstem implant
Auditory brainstem implant.breast implant
A surgically inserted object used to change the size and/or contour of the breast or chest wall, either using the patient's own tissue, e.g., a pedicle graft, or a prosthesis.
cochlear implant
An electrical device that receives sound and transmits the resulting signal to electrodes implanted in the cochlea. That signal stimulates the cochlea so that hearing-impaired persons can perceive sound.
CAUTION!
Cochlear implants increase the likelihood of meningitis. Patients with cochlear implants should be vaccinated against pneumococcus and Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib). 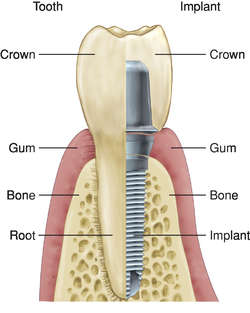

DENTAL IMPLANT
dental implant
In dentistry, a prosthetic device in any of several shapes. It is implanted into oral tissues beneath the mucosa or the periosteal layer, or within the bone to support or hold a fixed or removable prosthesis. Synonym: tooth implant See: illustration
CAUTION!
Ultrasonic devices should not be used on dental implants. endosteal implant
A dental prosthesis that is partially submerged and anchored within the bone. The blade form and the cylinder form are the two types of endosteal implants used. The cylinder form, which is most common, consists of a screw, a small titanium cylinder, and an abutment surgically inserted into the bone. The blade form consists of one or more abutments. In both forms, the prosthetic device is placed on the abutment(s).
interstitial implant
An implant consisting of an applicator containing a radioactive source directly into a tumor to deliver a high radiation dose while sparing the surrounding tissues.
intracavitary implant
An implant consisting of an applicator containing a radioactive source directly into a hollow organ to deliver a high radiation dose to the organ while sparing the surrounding tissues.
radioactive implant
See: brachytherapy; interstitial implant; intracavitary implantstaple implant
Transosteal implant.subperiosteal implant
A prosthesis for edentulous patients who cannot wear dentures (e.g., because of mandibular atrophy). The implant consists of a metal framework that rests on the residual ridge beneath the periosteum but does not penetrate the mandible.
tooth implant
Dental implant.transosteal implant
A rarely used type of dental prosthesis that completely penetrates the mandible. Its use is complicated by infection and a high rate of implant failure. Synonym: staple implant
wafer implant
A slowly dissolving polymer impregnated with chemotherapeutic drugs. It is placed into the tissue space from which a cancer has been removedto deliver a strong dose of chemotherapy to any residual cancer cells that escaped the resection.
Medical Dictionary, © 2009 Farlex and Partners
Implant
A fixture with one end implanted into the bone and the other end covered with a crown, often to serve as a stable abutment for a bridge or denture.
Mentioned in: Tooth Replacements and Restorations
Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights reserved.
im·plant
(im-plant) 1. To graft or insert.
2. (īm'plant) A surgically inserted or imbedded graft or device; also, a zone of cells or tissue transferred from another site through a developmental error or neoplastic process.
See also: prosthesis
[L. im-, in, + planto, pp. -atus, to plant, fr. planta, a sprout, shoot]
Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions © Farlex 2012
Patient discussion about implant
Q. Does anyone know if its possible to get breast implants if i have an implanted defibrillator? I have hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. I'm 27 and in great health, I workout 6 days a week and I have no further symptoms.
A. Thanks for your help. In fact I have an appointment with my cardiologist in a couple of weeks and if he says its OOK I will definitely consult it with the plastic surgeon as well. However I always try to do some additional research on my own and get second opinions.
Ince again,
Thanks!
Q. Do any of you with FM have silicone breast implants, or have you ever had them? How about saline? My silicone implants expired on the surgeon's shelf before they went in my body. Both implants ruptured and disintegrated within 5 years of implantation. I was diagnosed with FM shortly after 2 surgeries to remove silicone goo. Just wondering if anyone else has made the connection. Thank you!
A. As far as I know several studies failed to prove there is a connection between rupture of breast implants and fibromyalgia, as did the FDA conclude. Indeed I heard about one study that found this connection, but it seemed like a very problematic one.
You can read about this subject here (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Breast_implants#Claims_of_systemic_illness_and_disease)
Q. I have hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and an ICD. Is it possible to get breast implants with an ICD? I have no further symptoms: I workout and run 6 days a week, in good shape and only 27 years old.
A. Some medical equipment can damage your ICD If you are visiting your doctor , tell him or her that you have an ICD BEFORE they do any testing or treatment.i'm pretty sure they'll find a creative way to do the implant.any way- before doing any procedure- ask the cardiologist that handles you about it.
More discussions about implantThis content is provided by iMedix and is subject to iMedix Terms. The Questions and Answers are not endorsed or recommended and are made available by patients, not doctors.

