Medical term:
lymphadenopathy
lymphadenopathy
[lim-fad″ĕ-nop´ah-the]disease of the lymph nodes; called also adenopathy.
angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy (angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy with dysproteinemia (AILD)) a systemic disorder resembling lymphoma characterized by fever, night sweats, weight loss, generalized lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, macropapular rash, polyclonal hypergammaglobulinemia, and Coombs'-positive hemolytic anemia. It is considered to be a nonmalignant hyperimmune reaction to chronic antigenic stimulation; there is proliferation of B cells accompanied by profound deficiency of T cells. The disease follows a progressive but extremely variable course: some patients survive for a long period without chemotherapy; in other patients, overwhelming infections rapidly lead to death
dermatopathic lymphadenopathy regional lymph node enlargement associated with melanoderma and other dermatoses marked by chronic erythroderma.
immunoblastic lymphadenopathy angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy.
lymphadenopathy syndrome a condition occurring in immunocompromised individuals, characterized by unexplained lymphadenopathy for 3 or more months that involves extrainguinal sites, which on biopsy reveal nonspecific lymphoid hyperplasia. See also AIDS-related complex.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
lym·phad·e·nop·a·thy
(lim-fad'ĕ-nop'ă-thē),1. Any disease process affecting a lymph node or lymph nodes.
2. The appearance of enlarged lymph nodes found on a radiologic examination of any kind.
[lymphadeno- + G. pathos, suffering]
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
lymphadenopathy
(lĭm-făd′n-ŏp′ə-thē, lĭm′fə-dn-)n. pl. lymphadenopa·thies
An enlargement of the lymph nodes, usually associated with disease.
The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
lymphadenopathy
A generic term for lymph node enlargement of any aetiology, benign or malignant.Lymphadenopathy, aetiology
Infection
• Viral—Infectious mononucleosis, CMV, HIV.
• Bacterial—Typhoid, TB, syphilis, Yersinia.
Malignancy
• Lymphoproliferative—especially lymphoma
• Metastases.
Storage
Lipid storage, Niemann-Pick, sphingomyelia.
Drugs
Phenytoin, allopurinol, isoniazid.
Immune
Automimmune, rheumatoid arthritis, sarcoid, GVHD.
Benign hyperplasia, Langerhans cell histiocytosis.
Segen's Medical Dictionary. © 2012 Farlex, Inc. All rights reserved.
lymphadenopathy
Enlarged lymph nodes, follicular hypertrophy, swollen lymph glands Hematology Enlargement of lymph nodes of any etiology; the differential diagnostic considerations are multiple and divided into reactive patterns; benign lymphadenopathy is characterized by1. Variability of the follicle–germinal center size;.
2. Lack of capsular or fat invasion;.
3. Mitotic activity confined to the germinal center;.
4. Cortical localization and inhomogeneous distribution of the follicles. See Angiography lymphadenopathy, Benign lymphadenopathy, Dermatopathic lymphadenopathy, Phenytoin lymphadenopathy, Shotty lymphadenopathy.
McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine. © 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
lym·phad·e·nop·a·thy
(lim-fad'ĕ-nop'ă-thē)Any disease process affecting a lymph node or lymph nodes.
[G. lympha spring water +aden gland + G. pathos, suffering]
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
lymphadenopathy
(lim″fad″ĕ-nop′ă-thē) [ lymph- + adenopathy]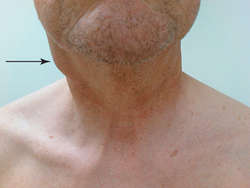
CERVICAL LYMPHADENOPATHY: Squamous cell carcinoma of the neck
Enlargement of lymph nodes (LN), typically to greater than 1.5 cm. The increased size is caused by activation and proliferation of lymphocytes and phagocytic white blood cells within the node or by invasion of the node by tumor. Most often, lymphadenopathy is found in nodes involved in local, regional, or systemic infections; it results occasionally from cancers. Lymphadenopathy may also be found in an array of other, less common illnesses, including thyroiditis, thyrotoxicosis, autoimmune diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis), sarcoidosis, and drug reactions (e.g., phenytoin). See: illustration
Enlarged LNs may be tender or not; tenderness often is present when lymph nodes swell rapidly (e.g., in response to infections, hypersensitivity reactions, or some fulminant lymphomas). Rock-hard, enlarged, and immobile LNs are typical of metastatic cancer, whereas rubbery LNs are found in lymphomas. LNs that do not resolve spontaneously within 4 to 6 weeks, or for which no obvious explanation exists, usually are sampled by biopsy or aspiration.
dermatopathic lymphadenopathy
Widespread lymphadenopathy secondary to various skin disorders.
See: table| Category | Examples | Location | Age of patient | Texture | Size | Associated signs or symptoms | Diagnostic tests | Necessity for biopsy or aspirate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial infection | Strep throat; cat scratch disease | Angle of the jaw; axilla, neck | Child or preteen; any | Relatively soft and tender; relatively soft and tender | 1 sq. cm; > 1 cm | Fever, sore throat, tonsillar exudate, malaise, headache, difficulty swallowing; may have fever, night sweats, weight loss | Can be diagnosed clinically; antibody blood tests | No; not usually |
| Granuloma | Tuberculosis; sarcoidosis | Neck, chest; hilum of the lung and other locations | Any; usually adults | Relatively soft and tender; rubbery | > 1 cm; > 1 cm, sometimes massive | May have fever, night sweats, weight loss, productive sputum; cough, shortness of breath, may have systemic illness, or be asymptomatic | Tuberculin (purified protein derivative), interferon blood test, sputum for acid-fast bacilli; blood for ACE levels | Occasionally; often |
| Metastatic cancer | Breast cancer | Axilla next to the breast | Adults | Stone | Especially likely if > 2 cm | Lump in the breast | Mammography, ultrasound, other imaging techniques | Yes |
| Lymphoma | Hodgkin lymphoma | Chest, neck, axilla, groin, or all of these | Young adult | Rubbery | > 1 cm | May have fever, night sweats, weight loss, enlarged spleen | Radiologic imaging | Yes |
| Viral infection | Mononucleosis; HIV/AIDS | Head and neck, spleen; generalized | Young adult; any, but most often young adult or adult | Rubbery; firm | About 1 cm; variable | May have fever, night sweats, weight loss; fever, night sweats, weight loss, or symptoms of opportunistic infection | Tests for Epstein-Barr virus, heterophile antibody; antibody blood tests | No; not usually |
Medical Dictionary, © 2009 Farlex and Partners
lymphadenopathy
Any disease process affecting a LYMPH NODE. Also known as lymphadenosis.Collins Dictionary of Medicine © Robert M. Youngson 2004, 2005
lymphadenopathy
An enlargement of a lymph gland. The preauricular lymph node located 1 cm in front of the external ear drains the orbital region and is sometimes involved with eyelid and conjunctival infection (e.g. adult inclusion conjunctivitis, follicular conjunctivitis). Syn. adenopathy (although strictly speaking this term refers to the enlargement of any gland).
Millodot: Dictionary of Optometry and Visual Science, 7th edition. © 2009 Butterworth-Heinemann
lym·phad·e·nop·a·thy
(lim-fad'ĕ-nop'ă-thē)1. Any disease process affecting lymph nodes.
2. The appearance of enlarged lymph nodes found on x-rays.
[G. lympha spring water + aden gland + G. pathos, suffering]
Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions © Farlex 2012
Patient discussion about lymphadenopathy
Q. my friend ate a bar of chocolate and now her left neck gland is swollen any ideas why? no other symptoms
A. it can be an infection -just like brandon said- or although this is rare, it can also be an allergic reaction.
if it is an infection, you can usually find such other infection symptoms like : fever, pain in that swollen area, increased white blood cells (in blood work test), etc.
if it is an allergy, usually it will fade away itself in couple of days, or you can just try to consume anti-allergic drugs, such as : loratadine and maybe combined with dexamethasone.
Good luck, and stay healthy always..
More discussions about lymphadenopathyif it is an infection, you can usually find such other infection symptoms like : fever, pain in that swollen area, increased white blood cells (in blood work test), etc.
if it is an allergy, usually it will fade away itself in couple of days, or you can just try to consume anti-allergic drugs, such as : loratadine and maybe combined with dexamethasone.
Good luck, and stay healthy always..
This content is provided by iMedix and is subject to iMedix Terms. The Questions and Answers are not endorsed or recommended and are made available by patients, not doctors.
Latest Searches:
Voraxaze - Voranil - Voorhoeve - voodoo - VOO - Vontrol - von - vomitus - vomiturition - vomitory - vomitoria - vomito - vomitive - vomiting - vomit - vomica - vomerovaginalis - vomerovaginal - vomerorostralis - vomerorostral -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp