neu·ro·path·ic
(nū'rō-path'ik), Relating in any way to neuropathy.
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
neu·ro·path·ic
(nūr'ō-path'ik) Relating in any way to neuropathy.
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
neuropathy
(noo-rop'a-the) [ neuro- + -pathy] Any disease of the nerves. neuropathic (noor?o-path'ik), adjective See: table; polyneuropathy.
AIDS peripheral neuropathy
Direct infection of peripheral nerves by HIV, resulting in sensory and motor changes due to destruction of axons or their myelin covering. Acute or chronic inflammatory myelin damage may be the first sign of peripheral nerve involvement. Patients display gradual or abrupt onset of motor weakness and diminished or absent reflexes. Diagnostic biopsies of peripheral nerves show inflammatory changes and loss of myelin. Distal sensory neuropathy occurs in up to 30% of patients with AIDS, usually late in the disease. There is increased risk in older patients and those with diabetes mellitus, nutritional deficiencies, low CD4 cell counts, and vitamin B
12 deficiencies. Patients report sharp pain, numbness, or burning in the feet. Destruction of dorsal root ganglions and degeneration of central peripheral axons are seen on autopsy. Some older antiretroviral drugs (ddI, ddC, and d4T) also cause a reversible peripheral neuropathy in about 20% of patients. See: AIDS; Guillain-Barré syndrome; chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy
Treatment
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, opioids, gabapentin, anticonvulsants, and topical agents have all been used with variable success to treat the pain of AIDS-related sensory neuropathy. Acupuncture is not effective. Human nerve growth factor, which stimulates regeneration of damaged nerve fibers, is being studied, esp. to minimize the neuropathy that antiretroviral drugs cause.
ascending neuropathy
Neuropathy that ascends from the lower part of the body to the upper.
auditory neuropathy
Abbreviation: AN
Impaired hearing in children due to an absence of auditory evoked potentials, despite the presence of normal cochlear hair cell structure and function.
Synonym: auditory dyssynchronydescending neuropathy
Neuropathy that descends from the upper part of the body to the lower.
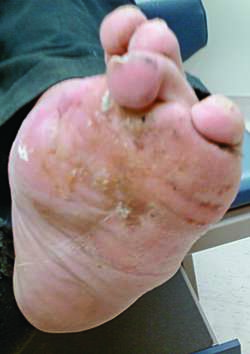

NEUROPATHIC FOOT DUE TO DIABETES
diabetic neuropathy
Damage to autonomic, motor, and/or sensory nerves due to metabolic or vascular derangements in patients with long-standing diabetes mellitus. In Western nations, diabetes is the most common cause of neuropathy. Symptoms usually include loss of sensation or unpleasant sensations in the feet, erectile dysfunction, focal motor deficits, gastroparesis, loss of the ability to maintain postural blood pressure, and diseases of cardiac innervation. Sensory loss in the feet may result in undetected injuries that become infected or gangrenous. Synonym: diabetic polyneuropathy See:
illustrationTreatment
Tight control of blood sugar levels may prevent some neuropathic symptoms in patients with diabetes mellitus.
dysthyroid optic neuropathy
Crowding of and damage to the optic nerve in patients with Grave's disease. It is characterized by loss of visual acuity and color vision, swelling of the optic disk, and compression of the optic nerve at the apex of the orbit. Synonym: apical crowding
entrapment neuropathy
Nerve entrapment syndrome.facial sensory neuropathy
Trigeminal neuralgia.focal neuropathy
Any nerve disease or injury, e.g., carpal tunnel syndrome or peroneal nerve palsy, that affects a single nerve.
generalized neuropathy
A rarely used synonym for polyneuropathy.
glue-sniffer's neuropathy
Malfunction of sensory and motor nerves due to inhaling toxic hydrocarbons. The lower extremities and trigeminal nerve are most often damaged.
interdigital neuropathy
See: Morton, Thomas Georgemultifocal motor neuropathy
An asymmetrical motor weakness occasionally found in middle-aged men.
optic neuropathy
Pathological injury to the optic nerves or the blood supply to them. Usually, only one eye is affected. Several forms have been described, including ischemic optic neuropathy, which, if prolonged, leads to blindness in the affected eye; optic neuritis due to acute demyelination of optic nerve fibers; infiltrative optic neuropathy, in which the optic nerve is compressed by a tumor or aneurysm; and optic neuropathy due to toxic nutritional factors, e.g., methanol or a combined nutritional and vitamin deficiency.
peripheral neuropathy
Any syndrome in which muscle weakness, paresthesias, impaired reflexes, and autonomic symptoms in the hands and feet are common. This syndrome occurs in patients with diabetes mellitus, renal or hepatic failure, alcoholism, or in those who take certain medications such as phenytoin and isoniazid.
plantar neuropathy
Any of several conditions in which nerves that supply sensation to the sole of the foot are injured or chronically compressed, resulting in burning and tingling sensations and difficulty standing, walking, or running.
subacute myelo-optic neuropathy
, subacute myelo-optico neuropathy Abbreviation: SMON
Neuropathy that usually begins with abdominal pain or diarrhea, followed by sensory and motor disturbances in the lower limbs, ataxia, impaired vision, and convulsions or coma. It is reported mostly in Japan and Australia. Most patients survive, but neurological disability remains. Many of those who have the disease have a history of taking drugs of the halogenated oxyquinoline group such as clioquinol (formerly called iodochlorhydroxyquin).
sural neuropathy
A relatively rare form of sensory neuropathy affecting the lateral ankle, typically associated with the wearing of poorly fitting work boots or shoes that compress the sural nerve.
tomaculous neuropathy
The presence of sausage-shaped areas of thickened myelin with secondary axon constriction in some cases of familial recurrent brachial neuropathy.
toxic-nutritional optic neuropathy
Bilateral visual impairment with central scotomas. This is usually associated with a toxic or nutritional disorder (e.g., the ingestion of methyl alcohol).
vibration-induced neuropathy
Hand-arm vibration syndrome.| Name | Affected nerve(s) | Affected part(s) | Affects sensation? | Affects movement? | Clinical features | Type of neuropathy |
|---|
| Bell’s palsy | Facial | Eye, nasolabial fold, lip (corner of the mouth) | Occasionally | Yes | Paralysis of the facial muscles, usually on just one side of the face | Inflammatory |
| Carpal tunnel syndrome | Median | Wrist and hand | Yes | Yes | Pain and numbness of the hand and wrist, often caused by repetitive movements or overuse such as typing, sawing, hammering, or polishing | Entrapment |
| Diabetic sensory neuropathy | Multiple | Feet, lower extremities; sometimes hands late in the course | Yes | No | Burning, stinging pain beginning in both feet, typically occurring after several years of poorly controlled diabetes. Can predispose to foot injury and infections. | Metabolic |
| Idiopathic brachial plexopathy (neuralgic amyotrophy; Parsonage-Turner syndrome; shoulder girdle syndrome) | Brachial | Shoulder | Yes | Yes | Pain in the shoulder, esp. after vigorous physical activity. Occasionally followed by shoulder girdle muscle atrophy | Entrapment |
| Meralgia paresthetica | Lateral femoral cutaneous | Thigh | Yes | No | Stinging pain in the anterolateral thigh. Usually found in obesity or in diabetes mellitus | Entrapment |
| Morton’s neuroma (interdigital neuropathy) | Interdigital nerves of the feet | Ball of foot | Yes | No | Pain often occurring between the web spaces of the 3rd and 4th toes during walking or standing | Entrapment |
| Piriformis syndrome | Sciatic | Buttock, with radiation into the leg | Yes | No | Buttock pain without back pain that is worsened by sitting and is relieved by walking | Entrapment/compression |
| Radial nerve palsy (musculospiral paralysis; Saturday night palsy) | Radial nerve (spiral groove entrapment) | Wrist, hand, and forearm | Yes | Yes | Temporary paralysis and numbness of the hand and arm, which may mimic a stroke. Caused by nerve compression, e.g., falling asleep on one’s side on a hard surface | Entrapment compression |
| Suprascapular neuropathy | Suprascapular | Back of the shoulder | Yes | Yes | Shoulder pain and muscular atrophy. Decreased ability to rotate or abduct the shoulder | Entrapment |
| Tarsal tunnel syndrome | Posterior tibial | Sole of the foot | Yes | No | Pain under the foot that is worsened by walking | Entrapment |
| Trigeminal neuralgia | Trigeminal | Cheek, nose, upper lip | Yes | No | Intense, repetitive facial pains that are often worsened by chewing, shaving, or toothbrushing, usually accompanied by spasm on the affected side of the face | Entrapment |
Medical Dictionary, © 2009 Farlex and Partners
neuropathy
[noo͡-rop´ah-the] any of numerous functional disturbances and pathologic changes in the peripheral nervous system. The etiology may be known (e.g., arsenical, diabetic, ischemic, or traumatic neuropathy) or unknown. encephalopathy and myelopathy are corresponding terms relating to involvement of the brain and spinal cord. The term is also used to designate noninflammatory lesions in the peripheral nervous system, in contrast to inflammatory lesions (neuritis). adj., adj neuropath´ic.
alcoholic neuropathy neuropathy due to thiamine deficiency in chronic alcoholism.
Denny-Brown's sensory neuropathy hereditary sensory radicular neuropathy.
diabetic neuropathy a complication of diabetes mellitus consisting of chronic symmetrical sensory polyneuropathy affecting first the nerves of the lower limbs and often affecting autonomic nerves. Pathologically, there is segmental demyelination of the peripheral nerves. An uncommon, acute form is marked by severe pain, weakness, and wasting of proximal and distal muscles, peripheral sensory impairment, and loss of tendon reflexes. With autonomic involvement there may be orthostatic hypotension, nocturnal diarrhea, retention of urine, impotence, and small diameter of the pupils with sluggish reaction to light.
entrapment neuropathy any of a group of neuropathies, such as carpal tunnel syndrome, caused by mechanical pressure on a peripheral nerve.
hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy (HMSN) any of a group of hereditary polyneuropathies involving muscle weakness, atrophy, sensory deficits, and vasomotor changes in the lower limbs. Some diseases in this group have been numbered: types I and II are varieties of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and type III is progressive hypertrophic neuropathy.
hereditary sensory neuropathy hereditary sensory radicular neuropathy.
hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy (HSAN) any of several inherited neuropathies that involve slow ascendance of lesions of the sensory nerves, resulting in pain, distal trophic ulcers, and a variety of autonomic disturbances. Types include hereditary sensory radicular neuropathy and familial dysautonomia.
hereditary sensory radicular neuropathy a dominantly inherited polyneuropathy characterized by signs of radicular sensory loss in both the upper and lower limbs; shooting pains; chronic, indolent, trophic ulceration of the feet; and sometimes deafness. Called also hereditary sensory neuropathy and Denny-Brown's sensory neuropathy or syndrome.
Leber's optic neuropathy a maternally transmitted disorder characterized by bilateral progressive optic atrophy, with onset usually at about the age of twenty. Degeneration of the optic nerve and papillomacular bundle results in progressive loss of central vision that may remit spontaneously. It is much more common in males. Called also Leber's disease and Leber's optic atrophy.
progressive hypertrophic neuropathy a slowly progressive familial disease beginning in early life, marked by hyperplasia of interstitial connective tissue, causing thickening of peripheral nerve trunks and posterior roots, and by sclerosis of the posterior columns of the spinal cord, with atrophy of distal parts of the legs and diminution of tendon reflexes and sensation. Called also Dejerine's disease and Dejerine-Sottas disease.
serum neuropathy a neurologic disorder, usually involving the cervical nerves or brachial plexus, occurring two to eight days after the injection of foreign protein, as in immunization or serotherapy for tetanus, diphtheria, or scarlet fever, and characterized by local pain followed by sensory disturbances and paralysis. Called also serum neuritis.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
neu·rop·a·thy
(nū-rop'ă-thē), 1. A classic term for any disorder affecting any segment of the nervous system.
2. In contemporary usage, a disease involving the cranial nerves or the peripheral or autonomic nervous system.
Synonym(s): neuritis (2) , neuropathia
[neuro- + G. pathos, suffering]
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
neuropathy
(no͝o-rŏp′ə-thē, nyo͝o-)n. pl. neuropa·thies Any of various diseases or abnormalities of the nervous system, especially of the peripheral nervous system.
neu′ro·path′ic (-rə-păth′ĭk) adj.
The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
neuropathy
A generic term for any disorder of peripheral nerves.
Aetiology
• Congenital (e.g., hereditary sensory radicular neuropathy or hypertrophic interstitial neuropathy)
• Traumatic—entrapment (e.g., carpal tunnel syndrome).
• Metabolic (e.g., due to amyloid or diabetes).
• Toxic (e.g., tobacco or alcohol-related amblyopia, cis-platinum, vincristine).
• Infectious (e.g., herpetic).Segen's Medical Dictionary. © 2012 Farlex, Inc. All rights reserved.
neuropathy
Neurology A disorder of peripheral nerves, which may be congenital–eg, hereditary sensory radicular neuropathy or hypertrophic interstitial neuropathy, traumatic–entrapment–eg, carpal tunnel syndrome, metabolic–eg, due to amyloid or DM, toxic–eg, tobacco or alcohol-related amblyopia, cis-platinum, vincristine, or infectious–eg, herpetic. See Alcoholic neuropathy, Autonomic neuropathy, Colchicine neuropathy, Diabetic neuropathy, Drug-related neuropathy, Dying back neuropathy, Entrapment neuropathy, Familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy, Giant axonal neuropathy, Hereditary motor & sensory neuropathy, Hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsies, Hereditary sensory neuropathy, Jamaican neuropathy, Leber hereditary optic neuropathy, Localized hypertrophic neuropathy, Motor neuropathy, Neck crack neuropathy, Nutcracker neuropathy, Optic neuropathy, Retrobulbar neuropathy, Subacute myelo-optic neuropathy, Thalidomide neuropathy. Cf Nerve dysfunction. McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine. © 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
neu·rop·a·thy
(nūr-op'ă-thē) 1. Any disorder affecting the nervous system.
2. In contemporary usage, a disease involving the cranial nerves, or the peripheral or autonomic nervous systems.
Synonym(s): neuritis (2) , neuropathia.
[neuro- + G. pathos, suffering]
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
neuropathy
(noo-rop'a-the) [ neuro- + -pathy] Any disease of the nerves. neuropathic (noor?o-path'ik), adjective See: table; polyneuropathy.
AIDS peripheral neuropathy
Direct infection of peripheral nerves by HIV, resulting in sensory and motor changes due to destruction of axons or their myelin covering. Acute or chronic inflammatory myelin damage may be the first sign of peripheral nerve involvement. Patients display gradual or abrupt onset of motor weakness and diminished or absent reflexes. Diagnostic biopsies of peripheral nerves show inflammatory changes and loss of myelin. Distal sensory neuropathy occurs in up to 30% of patients with AIDS, usually late in the disease. There is increased risk in older patients and those with diabetes mellitus, nutritional deficiencies, low CD4 cell counts, and vitamin B
12 deficiencies. Patients report sharp pain, numbness, or burning in the feet. Destruction of dorsal root ganglions and degeneration of central peripheral axons are seen on autopsy. Some older antiretroviral drugs (ddI, ddC, and d4T) also cause a reversible peripheral neuropathy in about 20% of patients. See: AIDS; Guillain-Barré syndrome; chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy
Treatment
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, opioids, gabapentin, anticonvulsants, and topical agents have all been used with variable success to treat the pain of AIDS-related sensory neuropathy. Acupuncture is not effective. Human nerve growth factor, which stimulates regeneration of damaged nerve fibers, is being studied, esp. to minimize the neuropathy that antiretroviral drugs cause.
ascending neuropathy
Neuropathy that ascends from the lower part of the body to the upper.
auditory neuropathy
Abbreviation: AN
Impaired hearing in children due to an absence of auditory evoked potentials, despite the presence of normal cochlear hair cell structure and function.
Synonym: auditory dyssynchronydescending neuropathy
Neuropathy that descends from the upper part of the body to the lower.


NEUROPATHIC FOOT DUE TO DIABETES
diabetic neuropathy
Damage to autonomic, motor, and/or sensory nerves due to metabolic or vascular derangements in patients with long-standing diabetes mellitus. In Western nations, diabetes is the most common cause of neuropathy. Symptoms usually include loss of sensation or unpleasant sensations in the feet, erectile dysfunction, focal motor deficits, gastroparesis, loss of the ability to maintain postural blood pressure, and diseases of cardiac innervation. Sensory loss in the feet may result in undetected injuries that become infected or gangrenous. Synonym: diabetic polyneuropathy See:
illustrationTreatment
Tight control of blood sugar levels may prevent some neuropathic symptoms in patients with diabetes mellitus.
dysthyroid optic neuropathy
Crowding of and damage to the optic nerve in patients with Grave's disease. It is characterized by loss of visual acuity and color vision, swelling of the optic disk, and compression of the optic nerve at the apex of the orbit. Synonym: apical crowding
entrapment neuropathy
Nerve entrapment syndrome.facial sensory neuropathy
Trigeminal neuralgia.focal neuropathy
Any nerve disease or injury, e.g., carpal tunnel syndrome or peroneal nerve palsy, that affects a single nerve.
generalized neuropathy
A rarely used synonym for polyneuropathy.
glue-sniffer's neuropathy
Malfunction of sensory and motor nerves due to inhaling toxic hydrocarbons. The lower extremities and trigeminal nerve are most often damaged.
interdigital neuropathy
See: Morton, Thomas Georgemultifocal motor neuropathy
An asymmetrical motor weakness occasionally found in middle-aged men.
optic neuropathy
Pathological injury to the optic nerves or the blood supply to them. Usually, only one eye is affected. Several forms have been described, including ischemic optic neuropathy, which, if prolonged, leads to blindness in the affected eye; optic neuritis due to acute demyelination of optic nerve fibers; infiltrative optic neuropathy, in which the optic nerve is compressed by a tumor or aneurysm; and optic neuropathy due to toxic nutritional factors, e.g., methanol or a combined nutritional and vitamin deficiency.
peripheral neuropathy
Any syndrome in which muscle weakness, paresthesias, impaired reflexes, and autonomic symptoms in the hands and feet are common. This syndrome occurs in patients with diabetes mellitus, renal or hepatic failure, alcoholism, or in those who take certain medications such as phenytoin and isoniazid.
plantar neuropathy
Any of several conditions in which nerves that supply sensation to the sole of the foot are injured or chronically compressed, resulting in burning and tingling sensations and difficulty standing, walking, or running.
subacute myelo-optic neuropathy
, subacute myelo-optico neuropathy Abbreviation: SMON
Neuropathy that usually begins with abdominal pain or diarrhea, followed by sensory and motor disturbances in the lower limbs, ataxia, impaired vision, and convulsions or coma. It is reported mostly in Japan and Australia. Most patients survive, but neurological disability remains. Many of those who have the disease have a history of taking drugs of the halogenated oxyquinoline group such as clioquinol (formerly called iodochlorhydroxyquin).
sural neuropathy
A relatively rare form of sensory neuropathy affecting the lateral ankle, typically associated with the wearing of poorly fitting work boots or shoes that compress the sural nerve.
tomaculous neuropathy
The presence of sausage-shaped areas of thickened myelin with secondary axon constriction in some cases of familial recurrent brachial neuropathy.
toxic-nutritional optic neuropathy
Bilateral visual impairment with central scotomas. This is usually associated with a toxic or nutritional disorder (e.g., the ingestion of methyl alcohol).
vibration-induced neuropathy
Hand-arm vibration syndrome.| Name | Affected nerve(s) | Affected part(s) | Affects sensation? | Affects movement? | Clinical features | Type of neuropathy |
|---|
| Bell’s palsy | Facial | Eye, nasolabial fold, lip (corner of the mouth) | Occasionally | Yes | Paralysis of the facial muscles, usually on just one side of the face | Inflammatory |
| Carpal tunnel syndrome | Median | Wrist and hand | Yes | Yes | Pain and numbness of the hand and wrist, often caused by repetitive movements or overuse such as typing, sawing, hammering, or polishing | Entrapment |
| Diabetic sensory neuropathy | Multiple | Feet, lower extremities; sometimes hands late in the course | Yes | No | Burning, stinging pain beginning in both feet, typically occurring after several years of poorly controlled diabetes. Can predispose to foot injury and infections. | Metabolic |
| Idiopathic brachial plexopathy (neuralgic amyotrophy; Parsonage-Turner syndrome; shoulder girdle syndrome) | Brachial | Shoulder | Yes | Yes | Pain in the shoulder, esp. after vigorous physical activity. Occasionally followed by shoulder girdle muscle atrophy | Entrapment |
| Meralgia paresthetica | Lateral femoral cutaneous | Thigh | Yes | No | Stinging pain in the anterolateral thigh. Usually found in obesity or in diabetes mellitus | Entrapment |
| Morton’s neuroma (interdigital neuropathy) | Interdigital nerves of the feet | Ball of foot | Yes | No | Pain often occurring between the web spaces of the 3rd and 4th toes during walking or standing | Entrapment |
| Piriformis syndrome | Sciatic | Buttock, with radiation into the leg | Yes | No | Buttock pain without back pain that is worsened by sitting and is relieved by walking | Entrapment/compression |
| Radial nerve palsy (musculospiral paralysis; Saturday night palsy) | Radial nerve (spiral groove entrapment) | Wrist, hand, and forearm | Yes | Yes | Temporary paralysis and numbness of the hand and arm, which may mimic a stroke. Caused by nerve compression, e.g., falling asleep on one’s side on a hard surface | Entrapment compression |
| Suprascapular neuropathy | Suprascapular | Back of the shoulder | Yes | Yes | Shoulder pain and muscular atrophy. Decreased ability to rotate or abduct the shoulder | Entrapment |
| Tarsal tunnel syndrome | Posterior tibial | Sole of the foot | Yes | No | Pain under the foot that is worsened by walking | Entrapment |
| Trigeminal neuralgia | Trigeminal | Cheek, nose, upper lip | Yes | No | Intense, repetitive facial pains that are often worsened by chewing, shaving, or toothbrushing, usually accompanied by spasm on the affected side of the face | Entrapment |
Medical Dictionary, © 2009 Farlex and Partners
neuropathy
Any NEURON disorder. Neuropathy occurs in CANCER, in DIABETES, in LEPROSY, in vitamin deficiency states, and may occur from genetic causes, from poisoning, from glue sniffing, from disorders of the AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM and from nerve pressure.Collins Dictionary of Medicine © Robert M. Youngson 2004, 2005
Neuropathy
A condition affecting the nerves supplying the arms and legs. Typically, the feet and hands are involved first. If sensory nerves are involved, numbness, tingling, and pain are prominent, and if motor nerves are involved, the patient experiences weakness.
Mentioned in: Adrenoleukodystrophy, Alcohol-Related Neurologic Disease, Charcot Marie Tooth Disease, Diabetic Foot Infections, Electrical Stimulation of the Brain, Optic Atrophy, Pain Management, Porphyrias
Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights reserved.
neu·rop·a·thy
(nūr-op'ă-thē) 1. Classic term for any disorder affecting any segment of nervous system.
2. In contemporary usage, disease involving the cranial nerves or the peripheral or autonomic nervous system.
Synonym(s): neuritis (2) .
[neuro- + G. pathos, suffering]
Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions © Farlex 2012
Patient discussion about neuropathy
Q. I am interested in finding info on Peripheral neuropathy and its symptoms. I wonder if I have it. I have restless leg syndrome discovered via a sleep clinic. A small tingling area developed in my back about 8 years ago. Nothing was disclosed to me about it and it progressed further up the back. I now wake up some nights with what I describe as left shoulder knot that makes left arm tingle and feel numb. Sometimes also goes down through to the left leg. It makes me feel jumpy and have trouble getting back to sleep. I rub Benyln on shoulder and take Tylenol. I eventually fall back to sleep. I do not have a family Dr. as she closed her practice and I must now visit walkin clinics. A stress test was recently done as I was having chest pain. Dr. thinks it's due to my Acid Reflux. HELP!
A. numbness and tingling can be symptoms of 25 possible cases. how i know? i just typed those symptoms in this symptom checker, and this is what i got:
http://www.healthline.com/symptomsearch?addterm=Tingling
about neuropathy- as i recall (and i could be wrong here), in most cases it's a symptom that something cause. your nervous system usually don't just shut off with no reason.
Q. is neurontin a safe drug for a 75 year old person?i have leg and foot pain and swelling.are there bad effects
A. Neruontin active substance is Gabapentin, an anti-epileptic medication. it is also given in some other conditions such as diabetic neuropathy. i guess that's the reason you got it. one of it's side effects is swelling of the hands, feet, ankles, or lower legs. i know i got that myself...and the advise to every side effect you encounter is the same- tell your Dr. about it. he might be able to change medication or reduce it in some level.
Q. My blood sugars are usually in the range of 180 (when I first get up) to about 240 in evening.. normal? I have been told I have Diabetes Type II. one doctor put me on metformin.. then that doc retired. Next doc said I don't need metformin. But I have noticed by checking blood sugars at home, they seem a little high. Also have been having some sweating, headaches, and some pain in feet and weird burning in feet.. Is that from high blood sugar? What is high? Should I tell my doc what my readings are? Do you think I need to get on a medication? I am trying diet modification and some exercise (I have a bad back and can't do much exercise or walking)... just don't want to get damage to my body from high blood sugars. thanks
A. Your readings does describe diabetes, and metformin is considered as the first line treatment for diabetes, however, giving diet and exercise a chance before starting meds was considered a legitimate approach before. I think that informing your doctor is a very good idea. The complaints your describe may result from diabetes, although not necessarily.
Take care,
More discussions about neuropathyThis content is provided by iMedix and is subject to iMedix Terms. The Questions and Answers are not endorsed or recommended and are made available by patients, not doctors.

