Medical term:
nifedipine
nifedipine
[ni-fed´ĭ-pēn]nifedipine
Pharmacologic class: Calcium channel blocker
Therapeutic class: Antianginal, anti-hypertensive
Pregnancy risk category C
Action
Inhibits calcium transport into myocardial and vascular smooth muscle cells, suppressing contractions. Dilates main coronary arteries and arterioles and inhibits coronary artery spasm, increasing oxygen delivery to heart and decreasing frequency and severity of angina attacks.
Availability
Capsules: 5 mg, 10 mg, 20 mg
Tablets (extended-release): 10 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg, 60 mg, 90 mg
Indications and dosages
➣ Vasospastic (Prinzmetal's) angina; chronic stable angina
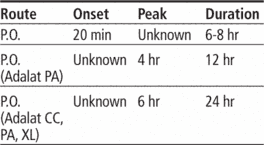
Adults: Initially, 10 mg P.O. (immediate-release) t.i.d. titrated over 7 to 14 days; usual effective range is 10 to 20 mg t.i.d., not to exceed 180 mg/day. Patient may be switched to extended-release at nearest equivalent of immediate-release daily dosage (for instance, 30-mg immediate-release dose may be switched to 90-mg extended-release dose). Total extended-release dosage should not exceed 90 mg/day.
➣ Hypertension
Adults: 30 to 60 mg/day P.O. (extended-release only) titrated over 7 to 14 days to a maximum of 120 mg/day
Off-label uses
• Aortic regurgitation
• Heart failure
• Migraine
• Prevention of labor
Contraindications
• Hypersensitivity to drug
Precautions
Use cautiously in:
• chronic renal insufficiency
• hypotension, aortic stenosis, heart failure, significant left ventricular dysfunction (especially when used with beta-adrenergic blockers), peripheral edema
• elderly patients
• pregnant or breastfeeding patients (safety not established)
• children (safety not established).
Administration
• Give immediate-release form with or without food. If GI upset occurs, give with meals, but never with grapefruit or grapefruit juice.
• Don't crush or break extended-release tablet. Make sure patient swallows it whole. Give on empty stomach, and not with grapefruit or grapefruit juice.
• Know that Procardia XL and Adalat CC are not equivalent because of their pharmacokinetic differences.
• Be aware that only extended-release tablets are used to treat hypertension.
Adverse reactions
CNS: headache, dizziness, fatigue, asthenia, paresthesia, vertigo
CV: peripheral edema, chest pain, hypotension
EENT: epistaxis, rhinitis
GI: nausea, constipation
GU: urinary frequency, erectile dysfunction
Musculoskeletal: leg cramps
Skin: flushing, rash
Interactions
Drug-drug. Beta-adrenergic blockers: increased risk of heart failure, severe hypotension, or angina exacerbation
Cimetidine: increased nifedipine blood level
Coumarin anticoagulants: increased prothrombin time
Digoxin: increased risk of digoxin toxicity
Quinidine: decreased quinidine blood level
Drug-diagnostic tests. Antinuclear antibody, direct Coombs' test false-positive results
Drug-food. Grapefruit, grapefruit juice: increased nifedipine blood level and effects
Drug-herbs. Ephedra (ma huang), yohimbine: antagonism of nifedipine effect
Ginkgo, ginseng: increased nifedipine blood level
St. John's wort: decreased nifedipine blood level
Drug-behaviors. Alcohol use: additive hypotension
Patient monitoring
• Monitor vital signs and cardiovascular status. Stay alert for chest pain and edema.
• Watch for rash.
Patient teaching
• Tell patient he may take immediate-release form with or without meals. If GI upset occurs, tell him to take it with meals, but never with grapefruit or grapefruit juice.
• Caution patient not to crush or break extended-release tablets. Tell him to swallow them whole. Advise him to take on empty stomach, and not with grapefruit or grapefruit juice.
• Inform patient that angina attacks may occur 30 minutes after a dose. Explain that these attacks are usually temporary and don't mean that drug should be withdrawn.
Tell patient to report rash immediately.
• Caution patient to avoid driving and other hazardous activities until he knows how drug affects concentration, balance, and alertness.
• Instruct patient to consult prescriber before taking herbs or over-the-counter drugs (especially cold remedies).
• As appropriate, review all other significant adverse reactions and interactions, especially those related to the drugs, tests, foods, herbs, and behaviors mentioned above.
nifedipine
(nī-fĕd′ə-pēn′)nifedipine
Procardia® Cardiology A dihydropiridine CCB vasodilator used for angina, as a short-acting antihypertensive–↓ BP, resulting in a ↓ left ventricular volume and myocardial mass, ↑ ejection fraction Side effects Tachycardia, headache, peripheral edema, cerebral ischemia, stroke, severe hypotension, AMI, conduction defects, fetal distress, death. See Calcium channel blockers, Hypertension, TIBBS.nifedipine
A CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKER drug used to control the symptoms of ANGINA PECTORIS and to treat high blood pressure (HYPERTENSION). It has a powerful effect in widening (dilating) arteries, including the coronary arteries, and this improves the blood supply to the heart muscle. The drug, however, causes flushing, headache, skin itching and dizziness. It is often used in combination with a BETA-BLOCKER. Nifedipine has been used effectively to prevent high altitude lung oedema, a feature of mountain sickness. The drug is on the WHO official list. Brand names are Adalat, Adipine MR, Angiopine MR, Cardilate MR, Coracten, Fortipine LA, Tensipine MR and Unipine XL.Latest Searches:
Voraxaze - Voranil - Voorhoeve - voodoo - VOO - Vontrol - von - vomitus - vomiturition - vomitory - vomitoria - vomito - vomitive - vomiting - vomit - vomica - vomerovaginalis - vomerovaginal - vomerorostralis - vomerorostral -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp