Medical term:
phagocytosed
phagocytosis
[fag″o-si-to´sis]the engulfing of microorganisms or other cells and foreign particles by phagocytes. adj., adj phagocytot´ic.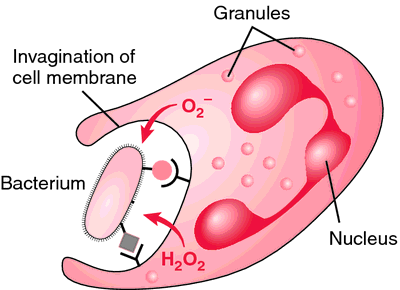

Phagocytosis. From Damjanov, 2000.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
phag·o·cy·to·sis
(fag'ō-sī-tō'sis),The process of ingestion and digestion by cells of solid substances, for example, other cells, bacteria, bits of necrotic tissue, foreign particles.
See also: endocytosis.
See also: endocytosis.
[phagocyte + G. -osis, condition]
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
phagocytosis
(făg′ə-sī-tō′sĭs)n.
The engulfing and ingestion of foreign bodies such as bacteria or other cells by phagocytes or certain protists, such as amoebas.
phag′o·cy·tot′ic (-tŏt′ĭk) adj.
The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
phag·o·cy·to·sis
(fāg'ō-sī-tō'sis)The process of ingestion and digestion by cells of solid substances, e.g., other cells, bacteria, bits of necrotic tissue, foreign particles.
See also: endocytosis
See also: endocytosis
[phagocyte + G. -osis, condition]
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
phagocytosis
(fag?o-si-to'sis) [? + ? + osis, condition]
PHAGOCYTOSIS
A three-stage process by which phagocytes (neutrophils, monocytes, and macrophages) engulf and destroy microorganisms, other foreign antigens, and cell debris. Generally, these substances must be covered with opsonins, such as antibodies or complement, to initiate binding with cell receptors on the phagocytes, the first stage in phagocytosis. In the second stage, the particle is engulfed and enclosed in a vacuole (phagosome). During the third stage, the phagosome merges with lysosomes whose enzymes destroy the engulfed particle. See: illustration; defensin; lysozyme; macrophage; neutrophil; oxygen radical
Most bacteria are killed during phagocytosis by oxygen radicals, which are formed during the respiratory burst when phagosomes and lysosomes merge. When oxygen radical production is excessive, tissue damage occurs. Lysozymes, defensins, and bacteriocidal permeability-increasing (BPI) protein also destroy bacteria and other organisms; their actions do not depend on the generation of oxygen radicals.
induced phagocytosis
Phagocytosis that is stimulated by the presence of opsonins such as antibodies.
spontaneous phagocytosis
Phagocytosis that occurs in the absence of opsonins.
Medical Dictionary, © 2009 Farlex and Partners
phagocytosis
The envelopment and destruction of bacteria or other foreign bodies by PHAGOCYTES.Collins Dictionary of Medicine © Robert M. Youngson 2004, 2005
phagocytosis
the ingestion of materials (subcellular particles, cells) from the outside of a cell into its interior, forming a cytoplasmic vacuole.Collins Dictionary of Biology, 3rd ed. © W. G. Hale, V. A. Saunders, J. P. Margham 2005
Phagocytosis
A process by which a white blood cell envelopes and digests debris and microorganisms to remove them from the blood.
Mentioned in: Legionnaires' Disease, White Blood Cell Count and Differential
Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights reserved.
phagocytosis
The process of ingestion of solid substances (e.g. cells, bacteria, parts of necrosed tissue) by cells and transported to a site within the cell where it is broken down by lysosomal enzymes.
Millodot: Dictionary of Optometry and Visual Science, 7th edition. © 2009 Butterworth-Heinemann
phag·o·cy·to·sis
(fāg'ō-sī-tō'sis)Process of ingestion and digestion by cells of solid substances.
[phagocyte + G. -osis, condition]
Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions © Farlex 2012
Latest Searches:
Voraxaze - Voranil - Voorhoeve - voodoo - VOO - Vontrol - von - vomitus - vomiturition - vomitory - vomitoria - vomito - vomitive - vomiting - vomit - vomica - vomerovaginalis - vomerovaginal - vomerorostralis - vomerorostral -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp