Medical term:
pleurocentesis
thoracentesis
[thor″ah-sen-te´sis]surgical puncture and drainage of the thoracic cavity; it may be done as an aid to the diagnosis of inflammatory or neoplastic diseases of the lung or pleura, or it may be used as a therapeutic measure to remove accumulations of fluid from the thoracic cavity. Called also pleurocentesis.
The procedure is done with the patient sitting up, the arms and head resting on the overbed table or over the back of a chair which the patient straddles. If unable to sit up, the patient is turned onto the unaffected side. The skin at the site of insertion of the needle is cleansed with an antiseptic, and a local anesthetic is injected. The site most often used is the seventh intercostal space, just below the angle of the scapula.
After the procedure is completed the wound usually is sealed with collodion and covered with a sterile dressing. Then a chest x-ray should be done to detect any pneumothorax. The site is checked frequently for signs of leakage. The total amount and character of the fluid obtained is noted on the patient's chart. Samples of fluid are sent to the laboratory for evaluation if requested. Immediately following the thoracentesis the patient is positioned on the unaffected side to rest the site of insertion of the trocar and allow it to seal itself. The patient is observed for signs of dizziness, changes in skin color, and respiratory and heart rate changes. Other signs of complications following thoracentesis include excessive coughing, blood-tinged sputum, and tightness of the chest.
Possible aftereffects of the procedure include pneumothorax, subcutaneous emphysema (accumulation of air in the tissues of the skin), and bacterial infection. A mediastinal shift resulting from removal of large amounts of fluid from the thoracic cavity may produce cardiac distress and pulmonary edema.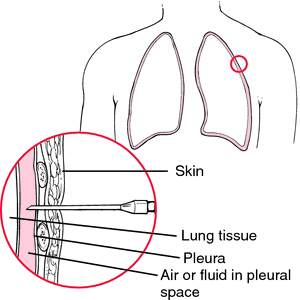
The procedure is done with the patient sitting up, the arms and head resting on the overbed table or over the back of a chair which the patient straddles. If unable to sit up, the patient is turned onto the unaffected side. The skin at the site of insertion of the needle is cleansed with an antiseptic, and a local anesthetic is injected. The site most often used is the seventh intercostal space, just below the angle of the scapula.
After the procedure is completed the wound usually is sealed with collodion and covered with a sterile dressing. Then a chest x-ray should be done to detect any pneumothorax. The site is checked frequently for signs of leakage. The total amount and character of the fluid obtained is noted on the patient's chart. Samples of fluid are sent to the laboratory for evaluation if requested. Immediately following the thoracentesis the patient is positioned on the unaffected side to rest the site of insertion of the trocar and allow it to seal itself. The patient is observed for signs of dizziness, changes in skin color, and respiratory and heart rate changes. Other signs of complications following thoracentesis include excessive coughing, blood-tinged sputum, and tightness of the chest.
Possible aftereffects of the procedure include pneumothorax, subcutaneous emphysema (accumulation of air in the tissues of the skin), and bacterial infection. A mediastinal shift resulting from removal of large amounts of fluid from the thoracic cavity may produce cardiac distress and pulmonary edema.

Technique of thoracentesis. The needle is advanced only as far as the pleural space.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
tho·ra·cen·te·sis
(thō'ră-sen-tē'sis),Paracentesis of the pleural cavity.
Synonym(s): pleuracentesis, pleural tap, pleurocentesis, thoracocentesis
[thoraco- + G. kentēsis, puncture]
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
tho·ra·cen·te·sis
(thōr'ă-sen-tē'sis)Paracentesis of the pleural cavity.
Synonym(s): pleural tap, pleurocentesis, thoracocentesis.
Synonym(s): pleural tap, pleurocentesis, thoracocentesis.
[thoraco- + G. kentēsis, puncture]
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
Latest Searches:
Voraxaze - Voranil - Voorhoeve - voodoo - VOO - Vontrol - von - vomitus - vomiturition - vomitory - vomitoria - vomito - vomitive - vomiting - vomit - vomica - vomerovaginalis - vomerovaginal - vomerorostralis - vomerorostral -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp