Medical term:
pointed
point
[point]1. a small area or spot; the sharp end of an object.
2. to approach the surface, like the pus of an abscess, at a definite spot or place.
3. a tapered, pointed endodontic instrument used for exploring the depth of the root canal in root canal therapy; called also root canal point.
point A a radiographic, cephalometric landmark, determined on the lateral head film; it is the most retruded part of the curved bony outline from the anterior nasal spine to the crest of the maxillary alveolar process.
absorbent point in root canal therapy, a cone of variable width and taper, usually made of paper or a paper product, used to dry or maintain a liquid disinfectant in the canal. Called also paper point.
point B a radiographic, cephalometric landmark, determined on the lateral head film; it is the most posterior midline point in the concavity between the infradentale and pogonion.
boiling point the temperature at which a liquid will boil; at sea level the boiling point of water is 100°C (212°F).
cardinal p's
1. the points on the different refracting media of the eye that determine the direction of the entering or emerging light rays.
2. four points within the pelvic inlet— the two sacroiliac articulations and the two iliopectineal eminences.
craniometric p's the established points of reference for measurement of the skull.
dew point the temperature at which moisture in the atmosphere is deposited as dew.
far point the most remote point at which an object is clearly seen when the eye is at rest.
point of fixation
1. the point or object on which one's sight is fixed and through which the axis opticus passes.
2. the point on the retina, usually the fovea, on which are focused the rays coming from an object directly regarded.
freezing point the temperature at which a liquid begins to freeze, for water, 0°C (32°F); it is often used interchangeably with melting point, but should be used for substances being cooled while melting point is reserved for substances being heated.
gutta-percha point gutta-percha cone.
ice point the true melting point of ice, being the temperature of equilibrium between ice and air-saturated water under one atmosphere pressure.
isoelectric point (pI) the pH of a solution in which molecules of a specific substance, such as a protein, have equal numbers of positively and negatively charged groups and therefore do not migrate in an electric field.
J point on an electrocardiogram, the junction between the end of the QRS segment and the beginning of the ST segment.
jugal point the point at the angle formed by the masseteric and maxillary edges of the zygomatic bone; called also jugale.
lacrimal point a small aperture on a slight elevation at the medial end of the eyelid margin, through which tears from the lacrimal lake enter the lacrimal canaliculi. See also lacrimal apparatus.
point of maximal impulse the point on the chest where the impulse of the left ventricle is sometimes felt or seen most strongly, normally in the fifth costal interspace inside the mammillary line.
McBurney point a point of special tenderness in appendicitis, about 4 to 5 cm from the right anterior iliac spine on a line between the spine and the navel; it corresponds to the normal position of the appendix. 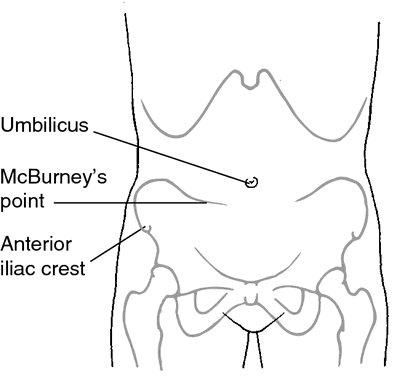

McBurney's point is located midway between the anterior iliac crest and the umbilicus in the right lower quadrant. From Ignatavicius and Workman, 2002.
melting point (mp) the minimum temperature at which a solid begins to liquefy; see also freezing point.
near point the nearest point of clear vision, the absolute near point being that for either eye alone with accommodation relaxed, and the relative near point being that for the two eyes together with employment of accommodation.
nodal p's two points on the axis of an optical system situated so that a ray falling on one will produce a parallel ray emerging through the other.
paper point absorbent point.
pressure point
1. a point of extreme sensitivity to pressure.
2. one of various locations on the body at which digital pressure may be applied for the control of hemorrhage. 

Locations of pressure points. Shaded areas show the regions in which hemorrhage may be controlled by pressure at the points indicated.
root canal point point (def. 3).
silver point in root canal therapy, a tapered and elongated silver plug that is cemented into the canal as a filling. Called also silver cone.
trigger point a spot on the body at which pressure or other stimulus gives rise to specific sensations or symptoms.
triple point the temperature and pressure at which the solid, liquid, and gas phases of a substance are in equilibrium.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
point
(poynt),1. Synonym(s): punctum
2. A sharp end or apex.
3. A slight projection.
4. A stage or condition reached, as the boiling point
5. To become ready to open, said of an abscess or boil, the wall of which is becoming thin and about to rupture.
6. In mathematics, a dimensionless geometric element.
7. A location or position on a graph, plot, or diagram.
8. Decimal point.
[Fr.; L. punctum, fr. pungo, pp. punctus, to pierce]
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
point
(point)n.
1. A sharp or tapered end.
2. A place or locality considered with regard to its position.
3. A stage or condition reached.
v.
1. To direct or aim something.
2. To direct attention with or as if with the finger.
3. To become ready to open, as an abscess or boil.
The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
point
Vox populi A small place. See Alarm point, Blockade point, Breakpoint point, Cell cycle restriction point, Checkpoint point, Critical control point, Dilution end point, Distal point, Dose point, Eye reference point, Fixed point, Flashpoint, Isobetic point, Joint point, Limit point, Loo point, Matrix point, McBurney's point, Murphy's point, Myofascial trigger point, Pressure point, Reorder point, Saddle point, Saddle node point, Satellite point, Shu point, Trigger point.McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine. © 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
point
(poynt)1. Synonym(s): punctum.
2. A sharp end or apex.
3. A slight projection.
4. A stage or condition reached, such as the boiling point.
5. To become ready to open, referring to an abscess or boil, the wall of which is becoming thin and is about to break.
6. In mathematics, a dimensionless geometric element.
7. A location or position on a graph, plot, or diagram.
8. Decimal point.
[Fr.; L. punctum, fr. pungo, pp. punctus, to pierce]
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
point
A small spot, considered only as to its position.
aplanatic point's See aplanatic focus.
blur point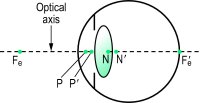

aplanatic point's See aplanatic focus.
blur point
1. The point at which the fixation target appears blurred on the introduction of increasing prisms and/or lens power, as for example in a test for relative convergence. 2. A point on a graph representing the limit of clear, single, binocular vision. See relative convergence; binocular vision single zone of clear.
break point The point at which diplopia occurs when increasing prism or lens power during binocular fixation. See blur point; relative convergence.
cardinal point's Six points on the optical axis of a lens system or thick lens: the two principal foci, the two principal points and the two nodal points. (Sometimes, this definition also includes the axial object and image points.) (Fig. P14) Syn. gaussian points (some authors consider this term synonymous, although it does not include the two nodal points). See cardinal planes.
centration point The point at which the optical centre (of a lens) is to be located in the absence of a prescribed prism, or after any prescribed prism has been neutralized. If the centration point is not specified, it is located at the standard optical centre position (British Standard). See standard optical position centre; decentration.
conjugate point's See conjugate distances.
point of convergence 1. The point of intersection of the lines of sight. 2. The point to which rays of light converge.
corresponding retinal point's See retinal corresponding points.
distance visual point (DVD) An assumed position of the visual point on a lens used for distance vision under given conditions, normally when the eyes are in the primary position.
point of divergence The point from which rays of light diverge
.equivalent point's See nodal points.
far point of accommodation See far point of accommodation.
far point of convergence See convergence, far point of.
point of fixation See point of fixation.
focal point See principal focus.
gaussian p's . The two principal points and the two focal points on the optical axis of a lens system. See cardinal points.
image p . The point at which an object point is formed by an optical system.
point
of incidence The point at which a ray of light intersects a refracting or reflecting surface.
lacrimal point See lacrimal punctum.
near point of accommodation See near point of accommodation.
near point of convergence See near point of convergence.
near visual point (NVP) An assumed position of the visual point on a lens used for near vision under given conditions. See visual point.
neutral point 1. In retinoscopy, it is the point at which the sight hole of the retinoscope is conjugate with the patient's retina. At this point, no reflex motion can be seen by the examiner and the entire pupil is illuminated completely, or is completely dark. This is obtained in a myopic eye when the retinoscope is placed at the far point of accommodation. When testing emmetropes and hyperopes this neutral point is reached when sufficient converging lens power has been added in order to displace the far point (artificially) to the sight hole of the retinoscope. See conjugate distances.
break point The point at which diplopia occurs when increasing prism or lens power during binocular fixation. See blur point; relative convergence.
cardinal point's Six points on the optical axis of a lens system or thick lens: the two principal foci, the two principal points and the two nodal points. (Sometimes, this definition also includes the axial object and image points.) (Fig. P14) Syn. gaussian points (some authors consider this term synonymous, although it does not include the two nodal points). See cardinal planes.
centration point The point at which the optical centre (of a lens) is to be located in the absence of a prescribed prism, or after any prescribed prism has been neutralized. If the centration point is not specified, it is located at the standard optical centre position (British Standard). See standard optical position centre; decentration.
conjugate point's See conjugate distances.
point of convergence 1. The point of intersection of the lines of sight. 2. The point to which rays of light converge.
corresponding retinal point's See retinal corresponding points.
distance visual point (DVD) An assumed position of the visual point on a lens used for distance vision under given conditions, normally when the eyes are in the primary position.
point of divergence The point from which rays of light diverge
.equivalent point's See nodal points.
far point of accommodation See far point of accommodation.
far point of convergence See convergence, far point of.
point of fixation See point of fixation.
focal point See principal focus.
gaussian p's . The two principal points and the two focal points on the optical axis of a lens system. See cardinal points.
image p . The point at which an object point is formed by an optical system.
point
of incidence The point at which a ray of light intersects a refracting or reflecting surface.
lacrimal point See lacrimal punctum.
near point of accommodation See near point of accommodation.
near point of convergence See near point of convergence.
near visual point (NVP) An assumed position of the visual point on a lens used for near vision under given conditions. See visual point.
neutral point 1. In retinoscopy, it is the point at which the sight hole of the retinoscope is conjugate with the patient's retina. At this point, no reflex motion can be seen by the examiner and the entire pupil is illuminated completely, or is completely dark. This is obtained in a myopic eye when the retinoscope is placed at the far point of accommodation. When testing emmetropes and hyperopes this neutral point is reached when sufficient converging lens power has been added in order to displace the far point (artificially) to the sight hole of the retinoscope. See conjugate distances.
2. In dichromats, it is a region of the spectrum that appears colourless. See deuteranopia; protanopia; tritanopia.
nodal point's In a centred optical system they are a pair of conjugate points on the axis which have the property that any incident ray which passes through the first nodal point leaves the system as though from the second nodal point and parallel to the incident ray. Thus the refracted ray is unchanged in direction, although displaced. The distance between the two nodal points is equal to the distance between the two principal points. When the refractive indices on each side of the system are equal, as in the case of a thick lens in air, the principal and nodal points coincide. They are then called equivalent points. In a single refracting surface, the nodal points coincide with the centre of curvature, while the principal points coincide with the vertex of the surface (Figs. P12 and P14). See optical centre; principal plane; vertex.
null p . See nystagmus.
point object See point object.
principal point's The points of intersection of the principal planes with the optical axis. The principal points are the usual reference points from which the focal lengths and the object and image distances are measured (Figs. P12 and P14). See equivalent power.
recovery point The point at which fusion is regained on decreasing the prism or lens power which originally induced diplopia in investigation of relative accommodation and convergence. See relative convergence.
point of regard Usually a synonym of point of fixation. However, in some circumstances it may be a peripheral point in space upon which visual attention is directed, while the eye is looking foveally at a point of fixation. See point of fixation.
point source See point source.
visual point The point of intersection of the visual axis with the back surface of a spectacle lens (British Standard). See distance visual point; near visual point.
point zero A point on the retina of a strabismic eye which has acquired the same visual direction, under binocular conditions, as the fovea of the fixating eye.
nodal point's In a centred optical system they are a pair of conjugate points on the axis which have the property that any incident ray which passes through the first nodal point leaves the system as though from the second nodal point and parallel to the incident ray. Thus the refracted ray is unchanged in direction, although displaced. The distance between the two nodal points is equal to the distance between the two principal points. When the refractive indices on each side of the system are equal, as in the case of a thick lens in air, the principal and nodal points coincide. They are then called equivalent points. In a single refracting surface, the nodal points coincide with the centre of curvature, while the principal points coincide with the vertex of the surface (Figs. P12 and P14). See optical centre; principal plane; vertex.
null p . See nystagmus.
point object See point object.
principal point's The points of intersection of the principal planes with the optical axis. The principal points are the usual reference points from which the focal lengths and the object and image distances are measured (Figs. P12 and P14). See equivalent power.
recovery point The point at which fusion is regained on decreasing the prism or lens power which originally induced diplopia in investigation of relative accommodation and convergence. See relative convergence.
point of regard Usually a synonym of point of fixation. However, in some circumstances it may be a peripheral point in space upon which visual attention is directed, while the eye is looking foveally at a point of fixation. See point of fixation.
point source See point source.
visual point The point of intersection of the visual axis with the back surface of a spectacle lens (British Standard). See distance visual point; near visual point.
point zero A point on the retina of a strabismic eye which has acquired the same visual direction, under binocular conditions, as the fovea of the fixating eye.

Fig. P14 Cardinal points of the eye
Millodot: Dictionary of Optometry and Visual Science, 7th edition. © 2009 Butterworth-Heinemann
point
(poynt)1. Synonym(s): punctum.
2. Sharp end or apex.
3. Slight projection.
4. To become ready to open, said of an abscess or boil, the wall of which is thin and about to rupture.
[Fr.; L. punctum, fr. pungo, pp. punctus, to pierce]
Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions © Farlex 2012
Patient discussion about point
Q. what is the difference between tender points and trigger points. I read somewhere in the net that there are two points called tender and trigger points which are one of the symptoms of fibromyalgia. Is that true? If so what is the difference between tender points and trigger points?
A. What you have read about tender and trigger points are true. A tender point hurts to the touch and causes some degree of pain in that area, while a trigger point may not necessarily be painful to the touch but causes a degree of pain to be felt in another area. Fibromyalgia patients typically have a number of tender points and, according to the American College of Rheumatology, the diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia stipulates that an FMS sufferer should have pain upon palpation (i.e. touch) in eleven of the generally accepted eighteen tender points. A tender point is verified in a physical examination in which approximately nine pounds of pressure are applied by touch and the patient acknowledges that pain is felt.
Q. can Autism appears in any point in life?
A. not really no, ether you diagnose it at the age of 3 or it's not there.
Q. My aunty who is suffering from fibromyalgia feels the position of painful tender/trigger points moves. My aunty who is suffering from fibromyalgia feels the position of painful tender points /trigger points moves. The pain moves. For this reason, pain cannot be bound to specific points. Can anybody help?
A. It’s a usual feeling faced by most. Really you will get more help from this community. We recommend you to consider neurophysiology and neuropsychology which can help you to understand the problem and the quality of pathological inference and its central representation.
More discussions about pointThis content is provided by iMedix and is subject to iMedix Terms. The Questions and Answers are not endorsed or recommended and are made available by patients, not doctors.
Latest Searches:
Voraxaze - Voranil - Voorhoeve - voodoo - VOO - Vontrol - von - vomitus - vomiturition - vomitory - vomitoria - vomito - vomitive - vomiting - vomit - vomica - vomerovaginalis - vomerovaginal - vomerorostralis - vomerorostral -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp