Medical term:
tetraplegic
quadriplegia
[kwod″rĭ-ple´jah]paralysis of all four limbs; motor and/or sensory function in the cervical spinal segments is impaired or lost due to damage to that part of the spinal cord, resulting in impaired function in the upper limbs, lower limbs, trunk, and pelvic organs. This term does not include conditions due to brachial plexus lesions or to injuries of peripheral nerves outside the spinal canal. Called also tetraplegia. adj., adj quadriple´gic.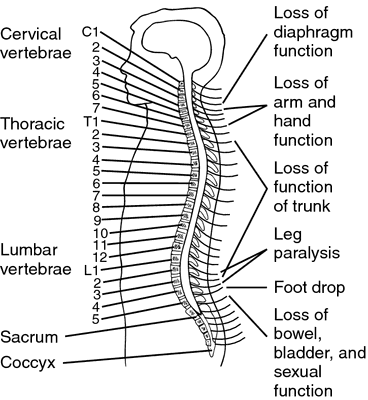
Patient Care. The quadriplegic patient has major sensory and motor deficits and is therefore subject to the many problems associated with immobility and loss of sensation. (See hazards of immobility.) The immediate goal of care is the prevention of complications that can affect all body systems, and maintenance of the integrity of the body systems so that optimum rehabilitation can be achieved. The extent to which the patient may eventually achieve mobility in a wheelchair and some degree of independence is greatly affected by the caliber of care received and the motivation and drive of the individual patient.
Mechanical devices such as braces are helpful in compensating for the loss of muscular function. physical therapy procedures and techniques and occupational therapy are essential aspects of patient care and are vital to the attainment of the goals of rehabilitation. (See also paraplegia.)
Patient education is especially important to the long-range goal of prevention of serious complications. Patients and their families should be aware of the early signs and symptoms of breakdown of the skin (pressure ulcer), fecal impaction, a developing infection, and urinary difficulties. As with any type of long-term care, these patients should be medically evaluated periodically and their care should be under the supervision of a visiting nurse. In spite of the many difficulties that may be encountered by paralyzed patients, it is possible for them to lead useful and personally rewarding lives.
Mechanical devices such as braces are helpful in compensating for the loss of muscular function. physical therapy procedures and techniques and occupational therapy are essential aspects of patient care and are vital to the attainment of the goals of rehabilitation. (See also paraplegia.)
Patient education is especially important to the long-range goal of prevention of serious complications. Patients and their families should be aware of the early signs and symptoms of breakdown of the skin (pressure ulcer), fecal impaction, a developing infection, and urinary difficulties. As with any type of long-term care, these patients should be medically evaluated periodically and their care should be under the supervision of a visiting nurse. In spite of the many difficulties that may be encountered by paralyzed patients, it is possible for them to lead useful and personally rewarding lives.

Quadriplegia.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
qua·dri·ple·gi·a
(kwah'dri-plē'jē-ă),Paralysis of all four limbs.
Synonym(s): tetraplegia
[quadri- + G. plēgē, stroke]
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
tetraplegia
(tĕt′rə-plē′jə, -jē-ə)n.
See quadriplegia.
tet′ra·ple′gic adj. & n.
The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
quad·ri·ple·gi·a
(kwahd'ri-plē'jē-ă)Paralysis of all four limbs.
Synonym(s): tetraplegia.
Synonym(s): tetraplegia.
[L. quadrus, four + G. plēgē, stroke]
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
tetraplegia
Quadriplegia. Paralysis of all four limbs.Collins Dictionary of Medicine © Robert M. Youngson 2004, 2005
Latest Searches:
Voraxaze - Voranil - Voorhoeve - voodoo - VOO - Vontrol - von - vomitus - vomiturition - vomitory - vomitoria - vomito - vomitive - vomiting - vomit - vomica - vomerovaginalis - vomerovaginal - vomerorostralis - vomerorostral -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp